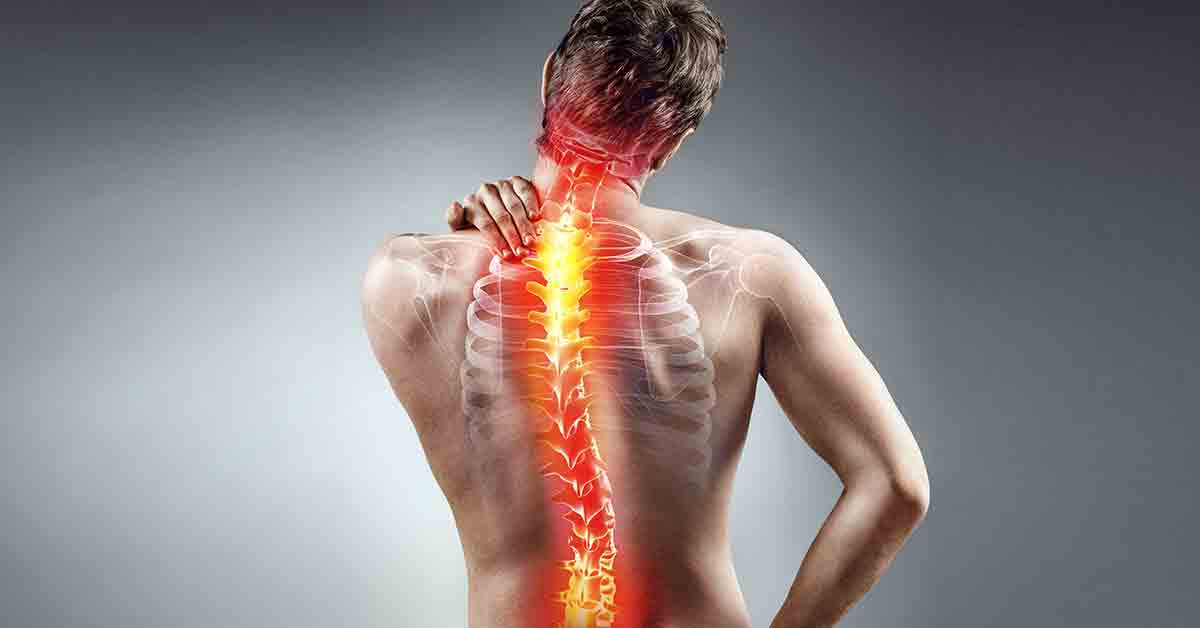
Learn more about spinal discs and whether they are dangerous
Spinal Discs
Everything you need to know about spinal discs and how to deal with them.
Spinal discs are one of the most common health problems that affect many people around the world. Spinal discs are a condition that affects the cervical disc, leading to a number of painful symptoms that can affect individuals’ quality of life. In this article, we will discuss the causes of spinal discs, their symptoms, and treatment methods.
Causes of Spinal Discs
The causes of spinal discs vary, and each person may have different reasons. Here are some common causes of spinal disc problems:
- Aging: Unfortunately, as people age, the flexibility of the discs in the back decreases, making them more prone to damage and slipping.
- Stress and Pressure: Engaging in daily activities that involve heavy lifting or constant bending may lead to excessive pressure on the discs in the back, resulting in disc herniation.
- Acute Injuries: Severe injuries to the back can occur due to falls, car accidents, or excessive sports activities, and these injuries can lead to disc herniation.
- Hormonal Changes: Some cases of spinal discs may occur in women during pregnancy or after childbirth due to hormonal changes that affect the cervical disc.
Symptoms of Spinal Discs
Spinal discs can cause a variety of symptoms that vary from person to person. Here are the most common symptoms associated with spinal discs:
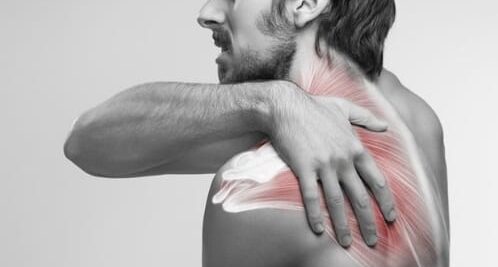
- Neck Pain: Individuals with spinal discs may experience severe neck pain, which can occur on one side of the neck or both sides.
- Limited Mobility: Those affected by spinal discs may experience restrictions in neck movement and have difficulty moving it due to pain.
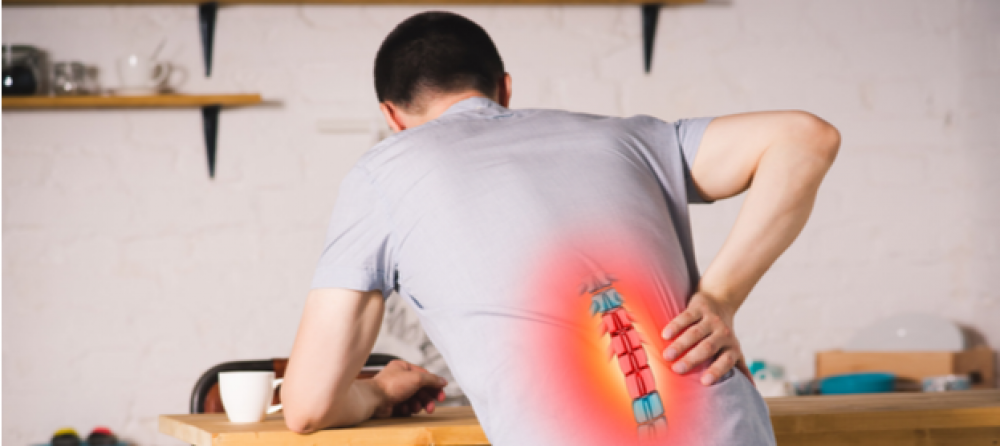
- Lower Back Pain: People with spinal discs may complain of severe lower back pain, which can extend to the base of the spine and legs.
- Radiating Pain: Affected individuals may feel sharp muscle contractions in the back or legs when walking or performing simple activities such as sneezing or stretching.
- Tingling and Numbness: Those with spinal discs may experience tingling and numbness in the lower limbs, which can make it difficult to walk long distances.
Treatment of Spinal Discs
Dealing with spinal discs requires several steps and lifestyle changes. Here are some common ways to treat spinal discs:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is a fundamental part of treating spinal discs. It involves the use of massage techniques and simple exercises that promote flexibility and pain relief.
- Lifestyle Changes: Individuals with spinal discs are advised to change their lifestyle by engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling and avoiding activities that require heavy lifting or constant bending.
- Medications: Doctors may prescribe pain-relieving medications to alleviate the bothersome symptoms associated with spinal discs. However, it is advisable to consult a doctor before taking any type of medication.
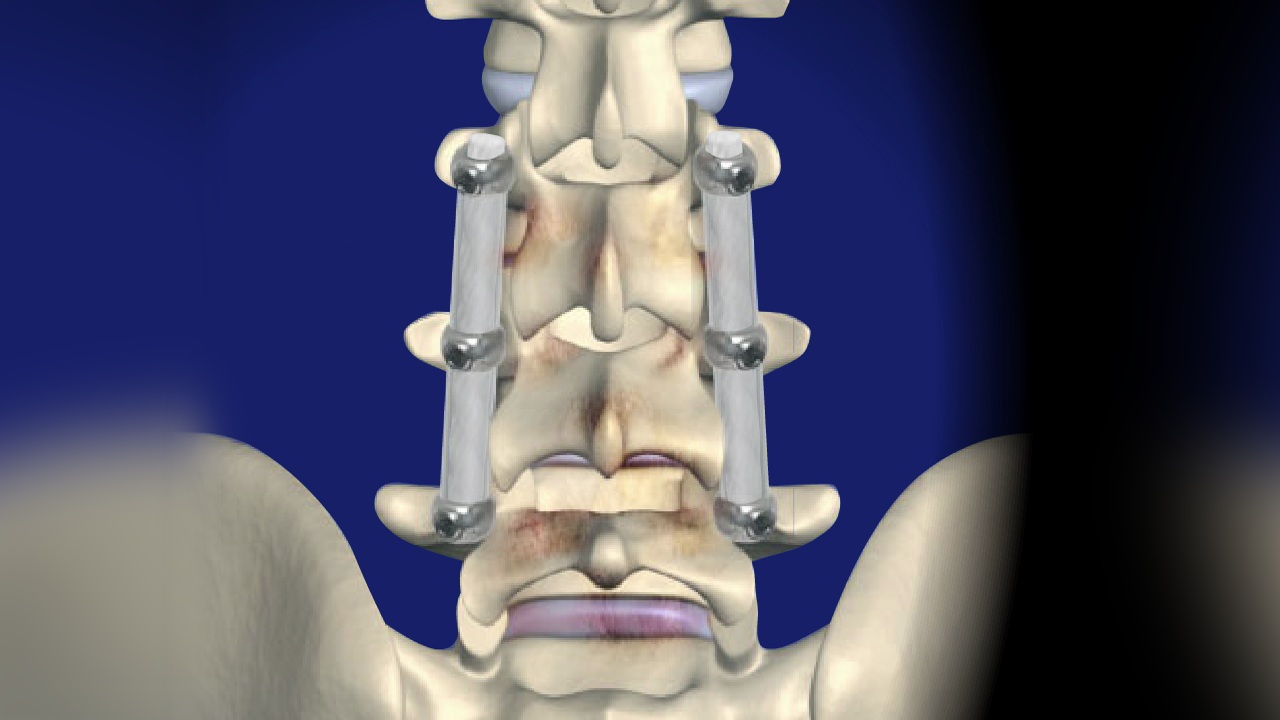
- Surgery: If individuals with spinal discs do not respond to conventional treatments, doctors may recommend surgery to remove the affected disc or stabilize the spine.
Always consult with a doctor before adopting any treatment methods and make sure to follow their instructions carefully.
Prevention of Spinal Discs
It’s worth noting that prevention plays a crucial role in avoiding spinal disc problems. Here are some guidelines that may help you prevent spinal discs:
- Engage in Proper Exercise: Make sure to engage in low-impact exercises that strengthen the back muscles and maintain their flexibility.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: There is a strong connection between excess weight and the occurrence of spinal discs. Avoid excessive weight gain and maintain a healthy lifestyle to reduce the likelihood of this problem.
- Maintain Good Posture: Ensure that you sit properly and support your back while sitting, avoiding a hunched sitting position for extended periods.
- Reduce Back Pressure: Avoid excessive lifting of heavy objects and distribute weights evenly on both sides when lifting.
Always seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms indicating the presence of spinal discs, as they can provide the proper diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatments.
Spinal discs can be a painful and challenging health condition, but it can be managed and overcome with the right methods. Take care of your spinal health and follow preventive measures to maintain a healthy and strong back.
What Are the Symptoms of Spinal Disc Herniation?
Many people suffer from back pain that can be bothersome and affect their daily quality of life. One common cause of this pain is spinal disc herniation. Understanding the symptoms associated with this condition can help you determine if you are experiencing it or not. In this article, we will take a look at the main symptoms of spinal disc herniation.
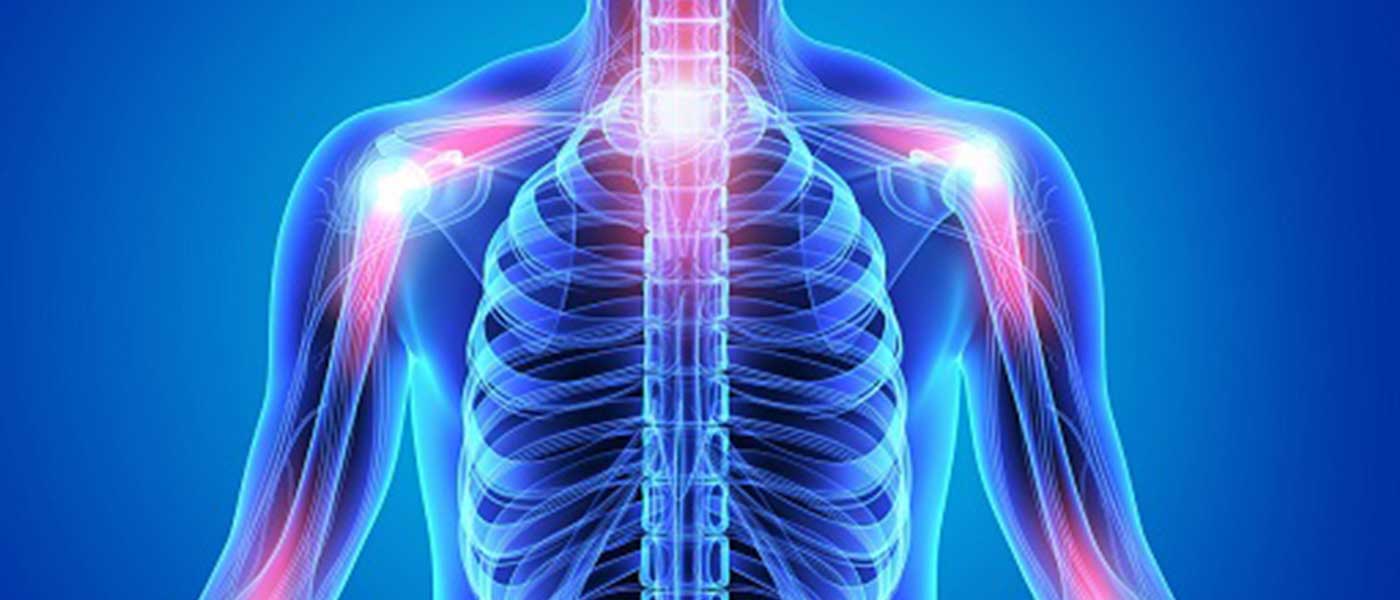
- Back Pain: One of the most common symptoms of spinal disc herniation is experiencing pain in the area of the herniated disc. The pain may start gradually and worsen over time. The affected person usually feels pain in the same location as the herniated disc. In some cases, the pain may radiate to the nearest point of the arms or legs from the herniated disc.
- Tingling and Numbness: Tingling and numbness are also common symptoms of spinal disc herniation. When the disc begins to press on the nerve roots, it becomes difficult to transmit necessary signals to the extremities, causing the affected person to feel tingling and numbness in the hands, feet, or even the head.
- Muscle Weakness: Spinal disc herniation can lead to a disruption in the transmission of nerve signals to the muscles, resulting in overall muscle weakness in the extremities. The affected person may have difficulty moving some muscles or notice slowness in certain reactions.
- Difficulty Standing or Sitting: The pain caused by spinal disc herniation can be so severe that it worsens when trying to sit, stand, or remain in one position for an extended period. Standing and sitting in this condition may increase the pressure on the disc and surrounding nerves.
- Sudden and Sharp Pain: In the early stages of the condition, the patient may experience sudden and sharp pain when performing certain movements. This occurs when the disc applies slight pressure to the surrounding nerves when bending or moving in a certain way.
- Pain on One Side of the Body: Sometimes, the pressure of the disc on specific nerves can cause a feeling of numbness, coldness, or even pain that only affects one side of the body without the other.
- Back Pain when Sneezing or Coughing: Movements like sneezing and coughing, or even pressing on the abdominal area for the affected person, can increase back pain and discomfort.
These are some of the main symptoms of spinal disc herniation. It is important to seek medical care if you are experiencing any of these symptoms. Your doctor may use pain relievers, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes as initial treatments, but if the symptoms persist or your condition is severe, you may need surgical treatment options. Minimally invasive surgery is one of the techniques used to treat spinal disc herniation, and it is considered less invasive and can help speed up recovery.
Please note that this article is for reference only and should not be used to diagnose medical conditions. It is advisable to seek professional medical advice for the diagnosis and treatment of any medical condition.
Is Spinal Disc Herniation Serious?
Spinal disc herniation, also known as a slipped disc, is a common condition that affects a significant number of people. Many wonder whether this condition is serious or not, what the possible causes are, and how it can be prevented.
In this article, we will explore a range of questions related to spinal disc herniation and provide comprehensive answers.
Causes of Spinal Disc Herniation
Spinal disc herniation is diagnosed when a portion of the vertebral disc protrudes through an opening in the tougher outer part. These protruded portions exert pressure on the nerve roots surrounding the spinal column, causing pain and numbness in the back and limbs.
The following factors are among the possible causes that may lead to spinal disc herniation:
- Aging: As people age, the discs become less elastic and deteriorate. This may increase the likelihood of disc herniation.
- Injuries and Trauma: Disc herniation can occur as a result of injuries and trauma to the spinal column, such as car accidents or sports-related injuries.
- Poor Posture: Improper sitting or standing postures can lead to uneven loading on the spinal column and back, increasing the risk of herniation.
- Genetic Factors: Having a family history of musculoskeletal disorders may increase the likelihood of disc herniation.
Is Spinal Disc Herniation Serious?
Regarding the question of whether spinal disc herniation is serious, it should be emphasized that the condition itself is not inherently serious. However, not treating it properly can lead to some serious complications.
Complications of spinal disc herniation may include:
- Nerve Damage: Failure to treat spinal disc herniation can lead to permanent nerve damage, causing pain and numbness in the extremities. One or more nerves may be affected.
- Cauda Equina Syndrome: This is one potential complication of untreated spinal disc herniation. It occurs when the bundle of spinal nerve roots located in the lower back is compressed. While it does not pose a life-threatening risk, it can increase the likelihood of permanent weakness in the lower extremities or paralysis.
- Saddle Anesthesia: Saddle anesthesia is a common issue that occurs after untreated spinal disc herniation. Patients may experience numbness in areas that extend from the inner thigh to the back of the legs and the rectal area.
How to Avoid the Severity of Spinal Disc Herniation?
The treatment approaches for spinal disc herniation depend on the level and severity of the herniation and the extent of accompanying pain. The following treatment options may be considered:
- Physical Therapy: This involves learning exercises and positions that help strengthen the back muscles and alleviate pain associated with spinal disc herniation.
- Medications: A variety of medications, including pain relievers, anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, and steroid injections, may be used in the treatment of spinal disc herniation.
- Surgery: If symptoms do not improve after an extended period of other treatments, surgery may be considered. This may involve removing the herniated portion of the disc, replacing it with an artificial disc, or fusing the adjacent vertebrae.
In general, consulting a specialist physician for the diagnosis and treatment of spinal disc herniation is essential. People should also avoid situations and behaviors that may increase the risk of herniation, such as lifting heavy weights improperly and maintaining proper posture while sitting and standing.
In summary, individuals concerned about the health of their spinal columns and discs should be aware that spinal disc herniation is not necessarily serious in itself. However, proper prevention and treatment can reduce the risk of potential serious complications.
What Are the Causes of Spinal Disc Herniation?
Many people suffer from back pain, which can be bothersome and affect their quality of life. Spinal disc herniation, commonly known as a slipped disc, is a prevalent condition that occurs when one of the discs between the vertebrae in the spinal column becomes damaged. In this article, we will examine the causes of spinal disc herniation and how to prevent it.
- Aging: One of the most common factors that increase the likelihood of developing spinal disc herniation is aging. The spinal discs typically degenerate over time, making them more susceptible to wear and tear.
- Weak Back Muscles: Weak back muscles can lead to increased pressure on the spinal discs, raising the risk of spinal disc herniation. Muscle weakness can result from a lack of physical activity or genetic issues.
- High-Impact Sports: Some sports that place significant strain on the back, such as weightlifting or powerlifting, as well as activities like football, running, and tennis, can increase the likelihood of spinal disc herniation. Proper technique and avoiding unnecessary strain on the back should be considered when engaging in these sports.
- Improper Lifting of Heavy Objects: Improperly lifting and carrying heavy objects can increase the risk of spinal disc herniation. When lifting objects, it is essential to use correct techniques and evenly distribute the weight across the muscles.
- Obesity: Obesity is another factor that can raise the risk of developing spinal disc herniation. Excess weight places additional stress on the vertebrae and spinal discs, making them more susceptible to damage and degeneration.
- Pregnancy and Childbirth: During pregnancy, the body experiences a significant increase in weight, leading to extra pressure on the back. Additionally, hormonal changes during pregnancy can affect the stability of the spinal discs. The risk of spinal disc herniation may also increase during the birthing process due to the intense strain on the back.
- Previous Back Injuries: If you have previously suffered a back injury, it may increase the likelihood of spinal disc herniation in later years. Previous injuries can result in damage or breakdown of one of the spinal discs, making them more susceptible to degeneration.
- Stress and Psychological Pressure: Continuous stress and psychological pressure can increase the risk of spinal disc herniation. Persistent stress leads to muscle tension and elevated blood pressure, affecting the health of the back and increasing the risk of wear and tear.
- Smoking: Smoking is another factor that can raise the likelihood of spinal disc herniation. Smoking negatively impacts blood flow to the spinal discs, reducing their ability to regenerate and resist degeneration.
- Physical Stress: Continual physical stresses and strains resulting from improper body positioning during daily activities, such as sitting for extended periods in uncomfortable positions, lifting objects incorrectly, and general muscle strain, can lead to the deterioration of spinal discs and an increased risk of spinal disc herniation.
In conclusion, individuals concerned about spinal health and disc-related issues should be aware that spinal disc herniation is not always inevitable. However, taking preventive measures and maintaining proper spinal care can help reduce the risk of this condition.
Preventing Spinal Disc Herniation
Considering the mentioned causes of spinal disc herniation, there are several measures that can be taken to prevent this troublesome issue. Here are some tips:
- Muscle Strengthening Exercises: It is essential to engage in muscle-strengthening exercises, especially for the back and abdominal muscles. Strong muscles surrounding the spinal column can reduce the weight-bearing pressure on the spinal discs and help prevent spinal disc herniation.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Striving to maintain a healthy weight is crucial for preventing spinal disc herniation. Obesity places extra stress on the back, making it more susceptible to damage.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Improperly lifting heavy objects should be avoided. Using the correct lifting technique and avoiding unnecessary strain on the back is essential.
- Engage in Low-Impact Activities: Engaging in low-impact physical activities like swimming and walking is preferable for the back. These activities help maintain muscle strength and strengthen the back without subjecting it to excessive stress.
- Maintain Proper Body Posture: Pay attention to your body posture during daily activities. Your back should be straight and aligned when sitting, standing, and lifting objects, while avoiding unnatural body twists.
- Reduce Stress and Psychological Pressure: Practicing stress and tension-reduction techniques such as meditation and deep relaxation is recommended. Continuous stress can increase the risk of spinal disc herniation.
- Quit Smoking: If you have a smoking habit, quitting is an important step in preventing spinal disc herniation. Smoking negatively affects blood flow to the spinal discs, reducing their ability to regenerate.
-
Consider Physical Therapy Techniques: Physical therapy sessions can promote muscle strength and improve spinal stability, thereby reducing the risk of spinal disc herniation.