What are the Thoracic Vertebrae? Understanding the Causes of Pain in Them!
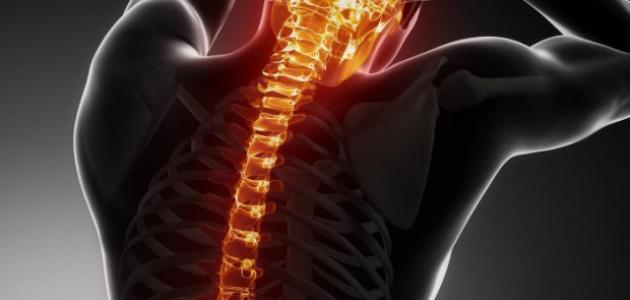
What are the thoracic vertebrae?
The thoracic vertebrae are a part of the human spinal column that is divided into three main sections: the cervical vertebrae, the thoracic vertebrae, and the lumbar vertebrae, which are connected by ribs to the sternum, collectively forming the rib cage. This thoracic cage plays a crucial role in protecting vital organs such as the heart and lungs, and it also aids in respiration.
There are some specific characteristics of the thoracic spine, where the right half of the thoracic skeletal structure and the spinal arches of three thoracic vertebrae appear from the front. It also contains a segment of the costovertebral joints exposed from the third to the ninth vertebrae. The first vertebra and the vertebrae from the ninth to the twelfth have some structural peculiarities.
It’s worth noting that thoracic spine pain is relatively rare, and often the fear of developing thoracic disc herniation is exaggerated. Among the causes that can lead to the appearance of thoracic vertebrae syndrome are problems related to the heart and lungs.
When searching for the causes, the person should first evaluate their physical posture. Is their sitting position at the desk with a hunched back? Do they lift heavy objects and strain their thoracic vertebrae more than they should? Are their back muscles weakened due to lack of movement?
Most likely, the answers to many will be “yes.” In this case, it means that there are some factors that must be taken into consideration to maintain the health of the thoracic vertebrae.
What are the symptoms of thoracic vertebrae pain?
Many people suffer from pain in the thoracic vertebrae area, which is a common problem affecting numerous individuals worldwide. Here are some common symptoms of thoracic vertebrae pain:
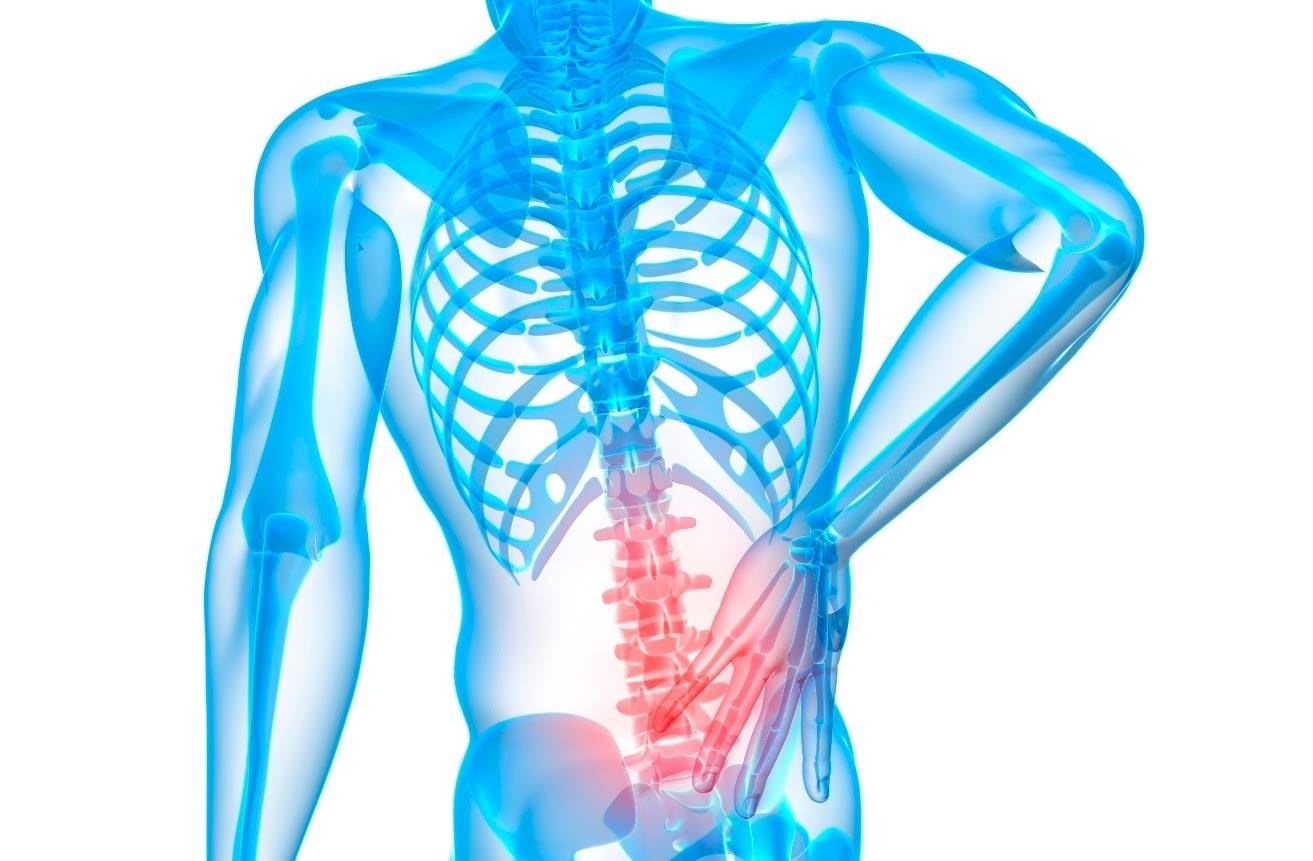
- Back pain: Affected individuals may experience pain in the upper part of the back, which can be mild at times and moderate to severe in other cases. The pain may become sharp when moving, bending, or applying pressure to the affected area. The pain may also radiate to the ribs due to the connection between the thoracic vertebrae and the ribs.
- Feeling of fatigue: Those affected may feel general fatigue and tiredness in the thoracic vertebrae area.
- Muscle spasms: Muscle spasms may occur in the thoracic vertebrae area, which is a common symptom of thoracic vertebrae pain.
- Sensitivity to touch and drowsiness: Those affected may be sensitive to touch in the thoracic vertebrae area and may also experience increased drowsiness.
- Neck, shoulder, and front chest pain: Individuals may feel pain in other areas related to the thoracic vertebrae, such as the neck, shoulders, and the front chest area.
- Muscle weakness and poor posture: In advanced cases, individuals may experience weakness in the muscles surrounding the thoracic vertebrae, leading to poor posture.
Note that these symptoms are common signs of thoracic vertebrae pain, and symptoms may vary from person to person based on the characteristics of the condition and the severity of the pain. If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is essential to consult your doctor for a proper diagnosis and receive appropriate treatment.
What is the Cause of Thoracic Spine Pain?
There are several reasons that can cause thoracic spine pain. It is essential to identify the specific cause of your pain to receive appropriate treatment. Here are some common causes that may lead to thoracic spine pain:
- Disc Herniation: This occurs when the fibrous disc between vertebrae shifts and puts pressure on the surrounding nerves. It can result from injury or age-related degeneration.
- Ligament and Muscle Tears and Contraction: Tears and contractions in ligaments and muscles can lead to pain in the thoracic spine.
- Spinal Injury: Twisting or instability in the spine due to severe trauma, such as fractures or dislocations, can cause thoracic spine pain.
- Osteoporosis: Weakening and fragility of the vertebrae due to osteoporosis can result in thoracic spine pain.
- Congenital Abnormalities: Structural abnormalities in your spinal column, such as scoliosis or spinal stenosis, can cause thoracic spine pain.
- Nerve Inflammation: Nerve inflammation can cause sharp pain in the thoracic spine.
- Chronic Inflammatory Diseases: Some conditions like rheumatoid arthritis and multiple sclerosis can affect the thoracic spine and cause pain.
- Obesity: Excess weight from obesity can exert extra pressure on the thoracic spine and cause pain.
It’s crucial to consult your doctor to determine the cause of your thoracic spine pain and receive appropriate treatment. These causes are not the only possibilities for thoracic spine pain, but they represent common factors that should be taken into consideration.
Does Disc Herniation Cause Chest Pain?
Disc herniation is a condition in which the discs between vertebrae in the spinal column protrude, including in the thoracic and cervical regions. This condition can cause various symptoms throughout the body, including chest pain.
In the case of thoracic disc herniation, a patient may experience radiating pain across the ribs, extending to the back. The patient may also feel difficulty in breathing correctly due to the impact on chest muscles and their pain. Pain may increase when taking deep breaths, coughing, sneezing, or making any movements involving the chest wall.
Weakness in neck or back muscles is among the risk factors that may increase the likelihood of developing disc herniation. While the exact causes of disc herniation are not always clear, genetic factors and acquired factors are believed to play a role.
In most cases, disc herniation is managed conservatively through rest, weight reduction, the use of pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy exercises. If symptoms do not improve with these measures, surgical intervention may be considered, which may involve the complete or partial removal of the affected herniated disc and fusion of adjacent vertebrae.
It’s important to note that chest pain can have various causes, and consulting a doctor is essential to accurately diagnose the condition and rule out any life-threatening causes, such as a heart attack. Thoracic disc herniation may not always be the clear cause of chest pain, so a medical evaluation is necessary to determine the correct diagnosis.
How Are Thoracic Vertebrae Examined?
Thoracic vertebrae are examined through computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Computed tomography is a common and useful technique for examining thoracic vertebrae. X-rays are used to produce cross-sectional images of the spine to identify any changes or abnormalities in bones or surrounding tissues.
As for magnetic resonance imaging, this examination uses a strong magnetic field and radio waves to produce three-dimensional images of the thoracic vertebrae and surrounding tissues. Magnetic resonance imaging is an accurate and painless diagnostic technique that can clearly depict tumors and structural abnormalities in the thoracic spine.
After the doctor takes images of the thoracic spine, they will analyze and review the images to diagnose any changes or issues in the thoracic vertebrae. The doctor may find it necessary to perform additional tests such as a neurological examination or computed tomography angiography to gather more details and evaluate the condition of the thoracic vertebrae more accurately.
It’s important to provide the doctor with complete and accurate information about your medical history and accompanying symptoms to assist in a precise diagnosis and the development of an appropriate treatment plan. The doctor will take into account the patient’s age, overall health, the type of tumor, and its stage when planning comprehensive treatment, which is essential for a successful recovery from thoracic spine problems.
How to Distinguish Between Muscle Pain and Spinal Pain?
Often, it can be challenging to differentiate between pain resulting from muscle strain and pain caused by vertebral disc herniation. To distinguish between muscular pain and spinal pain, several factors should be considered.
Firstly, it’s essential to consider the source of the pain. In the case of muscle strain, the pain is usually felt in the muscles themselves, but it may also radiate to adjacent areas. In contrast, in the case of vertebral disc herniation, the pain can be in the back itself or be felt in the nerves that extend from the affected vertebrae.
Secondly, pay attention to the symptoms of the pain. In the case of muscle strain, a person may experience sharp pain, muscle spasms, and difficulty in moving the affected joint. On the other hand, in the case of vertebral disc herniation, the pain may be accompanied by tingling or numbness in the limbs, muscle weakness, and difficulty in movement.
Thirdly, a physical examination by a healthcare provider can help distinguish between muscular pain and spinal pain. Doctors can take a patient’s medical history and assess muscle strength and joint mobility to check for normal function.
Finally, medical imaging such as computed tomography (CT) scans or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may be used to accurately diagnose the condition. Through these diagnostic tests, structural and anatomical changes in the vertebrae and surrounding tissues can be seen to determine the cause of the pain.
Therefore, if you suspect you may have vertebral disc herniation or are experiencing back or muscle pain, it is advisable to consult a healthcare provider for an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan that targets the underlying cause.
How Do I Know If I Have Vertebral Disc Herniation?
If you suspect you may have vertebral disc herniation, there are several signs and symptoms that may indicate it. It’s important to pay attention to these signs and seek a medical evaluation if you experience any of them.
One of the symptoms of vertebral disc herniation is a constant pain in the lower back region. This pain may be accompanied by stiffness in the legs or a stiff back. Additionally, you may feel sharp pain when pressure is applied to the lower back area or experience pain in the thigh.
You may have difficulty walking or standing for extended periods due to discomfort caused by the slipped vertebrae. You may also feel pain when bending over or making specific movements. Furthermore, you might experience a tingling or numb sensation in your feet. This can result from pressure on the nearby nerves. In some cases, you may have neck pain and difficulty moving your head. If you experience any of these symptoms, you could be dealing with vertebral disc herniation.
To ensure an accurate diagnosis and initiate the appropriate treatment, it’s advisable to schedule an appointment with a specialized healthcare provider. The doctor should conduct necessary examinations and may use radiographic imaging to assess the condition of the vertebrae. In general, self-diagnosis or relying solely on online information is not recommended. The situation may require a more detailed evaluation, and the doctor can guide you on whether there is a need for treatment or further care.
Preventing vertebral disc herniation is a good practice by maintaining a healthy weight, engaging in appropriate exercise to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, and avoiding movements that strain the back or improper lifting of heavy weights.
With proper care of the spine and appropriate consultation with a healthcare provider, the risk of vertebral disc herniation can be reduced, contributing to overall back health.
Does Spinal Pain Affect the Heart?
The pain associated with spinal problems differs from the pain caused by a heart attack. However, some spinal pains may lead to symptoms resembling those of a heart attack, which can cause concern for the individual. Below, we outline some possible symptoms and provide an explanation of their impact on the heart.
Possible Symptoms Extent of Impact on the Heart Chest Pain: Chest pain may indicate a problem in the heart or in the spine. Chest pain should be taken seriously and may require medical evaluation to determine the underlying cause. Neck and Jaw Pain: Neck and jaw pain can result from muscle tension or cervical spine issues. However, if the pain is accompanied by other symptoms like shortness of breath or chest pain, there may be a need to visit a doctor to rule out a heart attack. Shortness of Breath: Shortness of breath may be caused by a heart problem; however, it can also result from lung issues or respiratory problems. A medical examination is necessary to determine the exact cause. Thumb and Forefinger Pain: This could be a result of a disorder in the cervical spine. However, it is often unrelated to arterial blockage or a heart attack.
Don’t let this information cause excessive worry. However, if you are experiencing pain and are concerned about your health, it’s best to consult a doctor. The doctor will be able to evaluate your condition and recommend the necessary tests to ensure there are no heart problems.
Remember that any chest pain should be taken seriously, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as shortness of breath or pain in the arms or jaw. In such cases, it is important to seek immediate medical attention or call for emergency medical assistance.
How Do I Know If I Have Spinal Compression?
Feeling a burning pain in the legs and buttocks: One symptom of spinal nerve compression is a sharp, burning pain in the legs and buttocks. It often occurs when the vertebrae of the lumbar spine are affected, and the pain radiates down the legs, intensifying with certain body positions, sneezing, or coughing. Spinal compression may also occur in the fourth and fifth lumbar vertebrae.
Experiencing pain and stiffness in the lower back and neck: Feeling pain and stiffness in the lower back, neck, or along the entire spine is a symptom of spinal nerve compression. The pain can radiate to the lower extremities, leading to difficulty in movement or walking and, in some cases, an increased risk of falls.
Heightened sensitivity to heat and cold: Individuals with spinal nerve compression may notice excessive sensitivity to temperature changes, which results from chronic inflammation due to nerve compression.
Functional impairment of the bladder or bowels: Spinal nerve compression can lead to the loss of bladder or bowel function. Individuals may experience difficulty urinating or defecating and may need to consult a doctor for evaluation and appropriate treatment.
Feeling extreme fatigue and tiredness: Feeling extreme fatigue and tiredness is a common symptom of spinal nerve compression. This can result from chronic inflammation caused by nerve compression.
If you experience any changes in your body or any of the above-mentioned symptoms, it’s best to seek medical advice. Consult a physician to diagnose and address spinal nerve compression and how to manage accompanying symptoms. Staying in touch with medical experts will help you receive proper guidance and recommended actions to improve your condition.
Does Back Pain Affect the Chest Cage?
Does back pain affect the chest cage? 5 important questions to answer that:
Can the compression of the nerve in the upper part of the spine cause the spread of pain to the chest cage and back? Yes, nerve compression can cause pain to spread to other parts of the body, including the chest cage and back. The pain may be accompanied by muscle spasms and stiffness in the affected area of the spine, which can affect your ability to move.
Can cancer cause pain in the middle of the back and chest? Yes, cancer can cause pain in the chest that worsens when you breathe deeply, cough, or laugh. The pain typically radiates to other areas in the middle of the back. Other symptoms you may experience include coughing up blood. If you have these symptoms, there may be suspicion of lung cancer.
Can a person feel pain similar to a heart attack in the back, neck, jaw, and then spread to the chest cage? Yes, a heart attack and angina can be warning signs that you are at risk of having a heart attack. The pain can feel like a heart attack and may radiate from the back, neck, and jaw to the chest cage.
Can gastrointestinal acidity affect the chest cage? Yes, gastrointestinal acidity can cause pain and heartburn behind the chest cage. The pain may spread to the back or abdomen. The pain may increase after eating or in the evening. You may also notice an acidic taste in your mouth or increased pain while lying down or bending.
When should you see a doctor? If you are experiencing back pain that intensifies or spreads to the chest cage, it may be necessary to see a doctor. There may be other possible causes of pain, including spinal problems, heart disease, or digestive system issues. You should always consult a doctor to diagnose the condition and provide appropriate treatment.
Remember to always seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of back pain and its impact on the chest cage.
Best Doctor for Treating Spinal Issues
Dr. Amr Amal is a specialist in treating spinal issues. He is considered one of the renowned doctors in this field. He can provide you with more information about your personal condition and suitable treatment options based on his assessment of your case. To speak with him and get a medical consultation, you should search for his clinic or hospital and contact them to schedule an appointment. Always remember to refer to the date and location of your search for the most up-to-date information when searching for medical information.