What is the cottony cartilage? Can it be healed?
What is lumbar disc herniation?
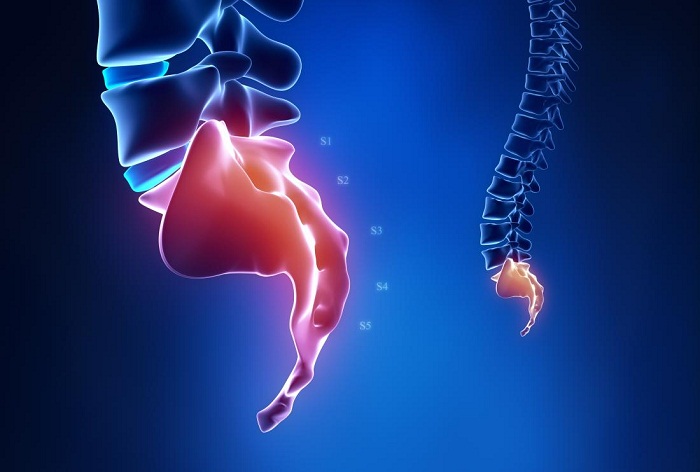
Lumbar disc herniation is a condition where the intervertebral disc in the spine, specifically in the lumbar (lower back) region, slips out of place. It is considered a common spinal disorder and can lead to various painful problems and symptoms.
The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae located in the lower part of the spine. These vertebrae provide support, mobility, and stability to the spine. However, in some cases, the intervertebral disc between two vertebrae may slip, leading to the appearance of lumbar disc herniation.
Common symptoms of lumbar disc herniation include:
- Pain and numbness in the lower back.
- Pain radiating down to the legs.
- Aggravation of pain at night or during certain movements.
- Weakness in the lower muscles (such as weakness in the legs).
Lumbar disc herniation can result from various factors, including:
- Injuries and trauma to the spine.
- Strenuous physical activities and heavy lifting.
- Medical conditions that weaken the disc tissues.
- Aging and the gradual deterioration of the discs over time.
When diagnosing lumbar disc herniation, the appropriate treatment is determined based on the severity of the symptoms and the patient’s condition. Treatment options may include:
- Physical therapy: Involves exercises and techniques to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve flexibility.
- Medications: The doctor may prescribe pain relievers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce symptoms.
- Interventional treatments: The doctor may recommend interventions such as massage, heat or cold therapy, and deep tissue massage.
- Surgical intervention: In cases where symptoms do not respond to other treatments, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove the herniated disc or perform spinal fusion.
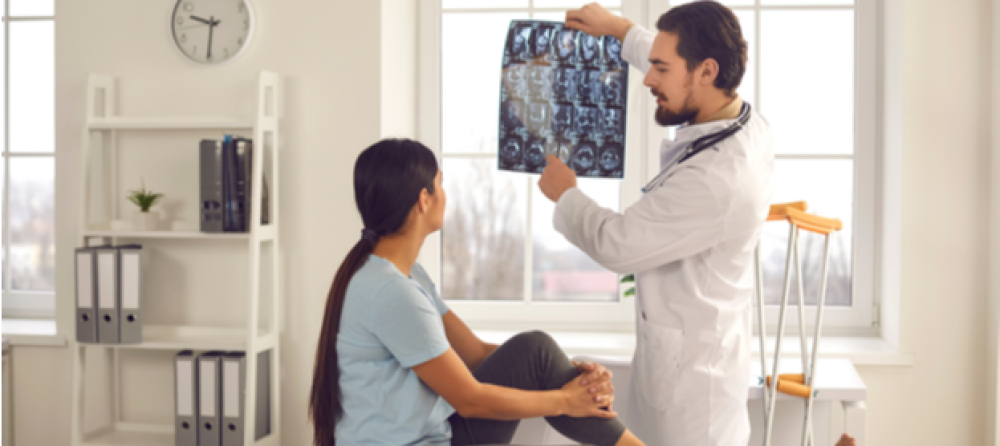
It is essential to consult a specialized doctor for the diagnosis of lumbar disc herniation and the prescription of appropriate treatments. Patients should adhere to the prescribed treatment and follow medical guidance to improve their condition and reduce pain.
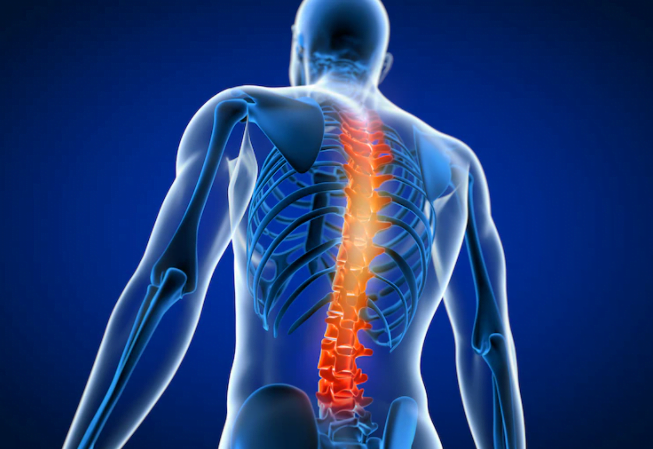
What causes lumbar spine pain?
Lumbar spine pain can be caused by severe compression of the surrounding nerve roots. The lumbar spine consists of bony structures in the lower middle part of the spine and plays a crucial role in supporting and directing movement. Here are some common causes of lumbar spine narrowing:
- Bone Spurs: Lumbar spine narrowing can occur due to the formation of bone spurs. These spurs can exert pressure on nerve roots and cause pain.
- Ligament Thickening: Thickening of the ligaments surrounding the lumbar vertebrae can cause narrowing of the spinal canal and compression of nerve roots, leading to lower back pain.
- Disc Herniation: In cases of disc herniation, the inner part of the disc can slip out, pressing on nerve roots in the lumbar spine and causing pain.
- Joint Deformities: Deformities in the lumbar spine joints can lead to spinal canal narrowing and nerve root compression, resulting in lower back pain.
- Osteoporosis: Gradual collapse of the lumbar vertebrae due to osteoporosis is one of the common causes of lumbar spine pain. The vertebrae become weaker and less able to withstand pressure, increasing the likelihood of narrowing and pain in the lumbar spine.
If you are experiencing lower back pain or limited mobility in the spine, the mentioned factors could be potential causes. However, always remember to consult with a specialized doctor for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What are the symptoms of lumbar disc herniation?
What are the symptoms of lumbar disc herniation (slipped lumbar discs)?
Lumbar disc herniation is a common condition that affects individuals in middle age. This condition impacts the spinal column and can result in severe pain and overall weakness in the body. Here are the main symptoms of lumbar disc herniation:
- Persistent back pain: Those with lumbar disc herniation may experience severe pain in the back area, which can persist for an extended period.
- Leg stiffness or lower back stiffness: Lumbar disc herniation can lead to stiffness in the legs or a feeling of stiffness in the lower back area.
- Pain when pressing on the lower back area: Individuals with lumbar disc herniation may feel pain when pressure is applied to the lower back area.
- Thigh pain: Pain resulting from lumbar disc herniation can radiate to the thigh, causing difficulty in movement and discomfort.
- Difficulty walking or standing for extended periods: Some individuals with lumbar disc herniation may find it challenging to walk for extended periods or stand for a long time due to pain and spinal stiffness.
Although lumbar disc herniation is a common condition, its diagnosis requires a specialized medical examination to confirm the condition and determine the appropriate treatment steps.
If similar symptoms appear, individuals should consult a specialized doctor to assess the situation, identify the proper treatment, and take preventive measures to maintain spinal health.
What is the treatment for lumbar disc herniation?
Many individuals suffer from lumbar disc herniation, which causes severe lower back pain. To address this issue, there are several effective approaches that can be followed. In this article, we will present 5 methods for treating lumbar disc herniation:
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy is considered one of the effective methods for strengthening the muscles surrounding the spine and improving its flexibility. This treatment includes a set of exercises designed to strengthen the muscles and enhance back stability. Patients may visit a therapist to learn these exercises and correctly apply them at home.
- Medication therapy: In cases of severe pain and swelling, doctors may prescribe pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs. These medications can help reduce pain and swelling associated with lumbar disc herniation, although they do not provide a permanent solution and primarily alleviate symptoms.
- Injection therapy: Doctors may administer anti-inflammatory steroid injections directly into the area affected by lumbar disc herniation to achieve more significant pain relief. These injections may be effective in reducing swelling and inflammation in the affected region.
Surgical Intervention: In cases of severe and persistent lumbar disc herniation, surgery may be the optimal option for recovery. The surgery involves the removal of the affected part of the herniated disc and repairing the damaged area. Surgery can lead to significant improvement in the symptoms of lumbar disc herniation and enhance the patient’s daily mobility and function.
Complementary Therapy: There are various complementary treatments that can be used to alleviate symptoms associated with lumbar disc herniation. Examples include massage therapy, herbal remedies, and chiropractic care. Patients may choose to try some of these therapies as a complement to traditional treatment.
In summary, there are many approaches that can be followed to treat lumbar disc herniation. Patients may need to consult with a doctor to determine the most suitable method and implement it correctly. The key is to strengthen the muscles and improve the flexibility of the back to prevent future problems.
Can Lumbar Disc Herniation be cured?
Lumbar disc herniation can cause a lot of pain and health issues for individuals. While it is a common problem, treatments and preventive measures can help improve the condition and alleviate symptoms.
In this article, we will discuss some tips and strategies that may help in recovering from lumbar disc herniation:
- Rest and Massage: Patients should give the body sufficient rest and a chance to heal. Massage and manual therapy techniques can help relieve pain and improve blood flow to the affected area.
- Gentle Exercises: Some gentle exercises can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the herniated disc and improve spinal stability. It is advisable to consult a doctor or physical therapist to determine suitable exercises.
- Physical Therapy: A doctor may recommend physical therapy to alleviate pain and improve mobility. This may include hydrotherapy or the use of heat and cold measures.
- Proper Clothing: Wearing appropriate clothing and using suitable support devices, such as support belts, in some cases, can help alleviate pain and stabilize the spine.
- Injections and Medications: In some severe cases, the doctor may suggest taking pain relievers or cortisone injections to reduce inflammation.
Regardless of the condition, patients should consult with a specialized doctor to evaluate their situation and determine the most appropriate treatment. Recovery from lumbar disc herniation depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition and its implications, as well as the patient’s commitment to treatment and preventive measures.
Pain caused by lumbar disc herniation should not be ignored, as it can negatively affect the quality of life and the ability to perform daily activities. Proper treatment and care are essential to alleviate symptoms and improve overall health.
Is Lumbar Disc Herniation Serious?
Lumbar disc herniation is a common condition that affects individuals with bulging discs in the spinal column. Although it can cause uncomfortable and debilitating symptoms, it is typically not associated with serious complications. However, this does not mean that the condition should be ignored or left untreated.
To understand the seriousness of lumbar disc herniation, let’s take a closer look at some facts related to this condition:
Back Pain: Chronic back pain is one of the most common symptoms among individuals with lumbar disc herniation. These pains can reduce the ability to perform daily activities and impact the individual’s overall quality of life.
Nerve Damage: Lumbar disc herniation can lead to permanent damage to some nerves in the affected spinal column area. Pressure on the nerves can result in muscle weakness and loss of movement in a specific part of the body.
Muscle Atrophy: Some individuals with lumbar disc herniation experience muscle weakness and difficulty in movement and performing daily activities. Muscle weakness hinders a person’s ability to walk, sit, and carry heavy objects.
Leg Paralysis: In rare cases, lumbar disc herniation can lead to paralysis in the legs. This occurs when the herniated disc compresses the nerve roots that supply the legs, affecting the ability to walk and move.
When a person experiences severe symptoms due to lumbar disc herniation, surgical treatment may be required to alleviate the symptoms and restore normal spinal function. The type of surgery needed depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of the herniation.
In conclusion, lumbar disc herniation is a medical condition that requires proper care and monitoring. Individuals experiencing symptoms of lumbar disc herniation should visit a specialized doctor for evaluation, diagnosis, and appropriate treatment.
Can Lumbar Disc Herniation Cause Paralysis?
Lumbar disc herniation is considered a significant health concern that requires crucial steps to address it if it occurs. In this article, we will explore what lumbar disc herniation is and to what extent its symptoms and complications can worsen.
What is Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Lumbar disc herniation occurs when the disc between the lumbar vertebrae in the spinal column slips out of place. The herniation can happen in the lower back or the neck. Lumbar disc herniation compresses the nerves surrounding the spinal column, leading to the appearance of symptoms.
Can Lumbar Disc Herniation Cause Paralysis? Yes, in rare cases, and when proper treatment is not received, lumbar disc herniation can lead to the interruption of nerve signals to the muscles responsible for controlling urination. As a result, these nerves do not regain their function, which can lead to paralysis in these muscles.
Complications of Lumbar Disc Herniation: In addition to paralysis, lumbar disc herniation can lead to other complications, such as:
- Chronic Back Pain: Many individuals experience continuous pain in the back due to the constant pressure on the nerves.
- Spinal Cord Dysfunction: In rare cases, lumbar disc herniation can lead to dysfunction in the spinal cord, manifesting as partial paralysis extending from the neck to the back.
Available Treatments for Lumbar Disc Herniation:
When symptoms of lumbar disc herniation appear, it is important to consult a doctor for diagnosis and to establish an appropriate treatment plan. Available treatments may include:
- Rest and Limitation of Physical Activity: Complete bed rest can help alleviate symptoms and reduce pressure on the spine.
- Pain Relievers and Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory medications can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Physical Therapy: The doctor may recommend physical therapy sessions to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve mobility.
In summary, lumbar disc herniation can lead to paralysis in rare cases, so patients with this condition should consult a doctor and receive the necessary treatment to minimize complications and improve their overall condition.
When Can a Patient Sit After Lumbar Disc Herniation Surgery?
After undergoing lumbar disc herniation surgery, sitting in the correct position is an important step in the recovery process. To ensure a healthy recovery, patients should take certain measures and follow recommendations for proper sitting after the surgery.
In this article, we will provide you with a list of important guidelines that patients should follow after lumbar disc herniation surgery:
Medical Consultation: Patients should regularly consult with the treating doctor and adhere to the instructions and advice provided regarding proper sitting after the surgery and the appropriate dosage of prescribed medications.
Sitting in the Correct Position: Patients should sit in a proper and comfortable position to avoid unhealthy sitting postures. It is advisable to sit in an upright and supportive position for the back, avoiding excessive bending and leaning of the body.
Regular Medical Check-Ups: Patients should undergo regular medical check-ups with the treating doctor to ensure a safe recovery and to check for any complications after the surgery.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy Sessions: Patients should start the rehabilitation process after the surgery by gradually increasing walking periods. It is recommended to do this as part of physical therapy sessions. These sessions help in regaining the strength and flexibility of the affected muscles and joints.
Gradual Return to Daily Life: Patients should allow themselves a period of adaptation and gradually return to their daily activities after lumbar disc herniation surgery. Starting with daily movement activities should be done gradually, and proper sitting and sleeping positions should be maintained to avoid post-operative pain.
It’s important to remember that each case may vary, and medical recommendations and guidelines should be consulted with the specialist doctor. Patients should adhere to the medical instructions and treatment plan to ensure a healthy and proper recovery after lumbar disc herniation surgery.