About knee cartilage surgery
Knee cartilage surgery has a lot of details regarding recovery time, pre and post-surgery procedures, complications, and other adequate information found in the following article.
Knee cartilage surgery
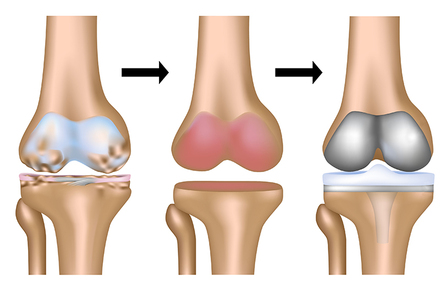
Joints are of great importance in the movement of a person freely and a greater ability to move from one position to another, such as standing and sitting, or moving up or down, etc., and the knee joint is the largest in the joints of the body and is very complex.
The knee joint arises from bones, ligaments, and cartilage as well, which facilitate the movement of the leg and connect it with the thigh bones. Knee injuries are different and multiple, and one of them is cartilage ruptures and damage to it, and there are two types of knee cartilage: the articular and meniscal.
Symptoms of knee cartilage damage
The symptoms of a knee rupture appear directly on the patient as follows:
- The presence of pain in the joint itself, especially when pressed.
- The patient feels swelling and heat in the affected joint.
- Reducing the ability to move normally.
- Cartilage erosion causes roughness and friction in the joint.
Causes of rupture and damage to the knee cartilage
There are more than one factor that may contribute to the knee being eroded or atrophied, including the following:
- Exposure to a strong knee collision, which usually occurs with athletes and high-risk business owners, leads to exposure to damage or tearing of the cartilage.
- Obesity and weight gain above the appropriate rate for the person increase the load and pressure on the knee and thus leads to damage in one way or another to the cartilage.
- Lack of exercise, even in a simple way, such as walking, can cause the joint to be damaged and the cartilage to be negatively affected.
- Some diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, may increase the chance of damage or atrophy of knee cartilage.
Usually, in the case of knee injuries, doctors prefer to start with home treatment and give the necessary medications to the patient at this stage, after which the patient begins physical therapy, which is several exercises and natural therapies that help in recovery.
In the final stages of knee cartilage damage, surgical treatment is the best solution, and it has more than one form, including replacement of damaged cartilage or autografting, and others, including what is performed by arthroscopy, and others that require open surgery, and the type of surgery is determined by the doctor.
Arthroscopic knee cartilage surgery
Endoscopy or the use of binoculars in surgeries is the best and preferred by many doctors in the current period due to the great development that has taken place in it and the number of advantages it provides to the patient, including the speed of recovery from surgery and the possibility of using partial anesthesia and others.
The knee joint is subjected to a great load and can reach many times the weight of the body, especially in the event of activity, and the increase in pressure may lead to a rupture of the sliding cartilage and damage to its constituent tissues, and this causes severe pain and difficulty in movement.
Reasons for preferring arthroscopic knee surgery
There are many cases in which doctors prefer to perform laparoscopic surgery because of its many advantages, including:
- It can reduce tissue damage.
- Performing the surgery with partial anesthesia.
- Rapid wound healing.
- Reduce the incidence of infection.
- It does not require a deep incision, but only several stitches.
Before arthroscopic knee surgery
Doctors explain to you some of the instructions and procedures followed before performing arthroscopic knee surgery to be fully prepared psychologically and physically before it, and these recommendations are as follows.
- Commitment to physical therapy in the pre-operative period according to the rehabilitation program.
- Taking certain types of medications prescribed by the attending physician and not changing them without consulting him.
- Fasting and abstaining from food for 12 hours before the operation.
- Taking a sufficient amount of rest and psychological rehabilitation is of great importance in preparing the patient for surgery.
Arthroscopic knee cartilage surgery steps
There are several notes that you should know about arthroscopic cartilage surgery, which are:
- The doctor begins by injecting the affected knee with anesthesia – in the case of partial anesthesia – and works to numb the entire leg.
- The surgeon uses a tube-like endoscope with a light source and a camera attached, which visualizes the current condition of the knee and allows him to operate with greater precision.
- A saline solution is pumped into the knee so that the vision is clearer when the endoscope is inserted into the knee.
- The doctor makes several holes in the knee and inserts small surgical tools through them to perform the repair and correct the problem in the knee.
- After the surgery, the surgeon takes out the tools, sterilizes the joint, expels the saline fluid present in it, and sews the holes again.
- The operation usually does not exceed 60 minutes, after which the patient returns to his room in the hospital.
Post-knee cartilage surgery
The patient needs to get some rest after knee cartilage surgery, and for the person to take into account that he keeps the doctor’s instructions for him and reduces the load placed on the knee, so he uses crutches for several weeks after the operation.
There is an integrated rehabilitation program that takes place for a patient with cartilage damage after the operation, the physiotherapist follows him up, and he proceeds with the development of the condition and the extent of its improvement based on the exercises and treatment prescribed for him in coordination with the treating doctor, and the person can leave the hospital within a day of the surgery while following the doctors’ instructions.
Knee rehabilitation after cartilage surgery
The process of rehabilitating the injured person or the period after the cartilage operation is very important because it helps the person to recover in quick time and the patient avoids any complications that may occur after the surgery, and there are some tips provided by doctors after the knee cartilage operation.
Procedures after knee cartilage surgery
- Using ice packs that reduce swelling in the knee.
- Take the painkillers prescribed by the doctor to the patient, and some also advise taking aspirin to avoid clots, especially with immobility for a while.
- The injured person should raise the foot to be slightly higher than the heart, and this helps speed up the healing process.
- Rest completely, keep the dressing clean and change it regularly.
- Using a passive movement device that works to enhance blood circulation in the injured part and accelerate the healing process.
- Continue the physical therapy program prepared for the person after surgery, especially in the first four weeks.
- The person can return to his normal activities in the second month after the operation if the procedures are fully adhered to.
Walking after knee cartilage surgery
The timing of walking differs from one person to another depending on the patient’s health condition, and this is of course determined by the attending physician and is due to the body’s response to recovery, but in general, rehabilitation and physical therapy exercises play an effective role in accelerating the person’s ability to move, and usually, the person starts moving in the first month.
Post-knee cartilage surgery exercises
Some exercises are practiced under medical supervision after cartilage surgery, as follows:
Thigh strengthening exercises
- The patient can use a towel or a small pillow to place it under the knee and press it for 5 seconds while repeating the exercise 8 to 10 times.
- The patient can lie on the front of the body, put a small pillow under the ankle, and press it gently, then gradually increase the pressure for 5 seconds and repeat it 10 times.
- The injured person can stand upright against the wall, lift the injured foot up at an angle of 90 degrees, grab it from behind with the hand, and pull it up as much as possible for 5 seconds.
Lifting exercises
- The person can raise the foot up at an angle of 30 degrees and lower it, relying on body weight only, while maintaining the flexion of the other leg for 5 seconds.
- The injured person can raise the foot up when standing without bending the knee for 10 seconds and return it to its original position.
It is important that the exercises and activities that the knee cartilage sufferer performs after the operation are under integrated medical supervision to provide him with the necessary care and to learn correctly how to perform the exercises.
Duration of pain after arthroscopic knee meniscus surgery
Usually, the person can return to his normal activity within two to three months after the operation, and this is due to the patient’s response to drug treatment and physical therapy after surgery, and the pain gradually decreases until the patient reaches full recovery.
When can the patient walk after knee cartilage surgery?
There are some instructions that the attending physician explains to the patient in the period after the cartilage operation, which helps the patient to reach the stage of recovery and return to normal activities as before.
An integrated rehabilitation program is carried out in the first four weeks of the operation, after which the patient begins to take his first steps and move with caution until he is able to walk and move regularly, and after this period a new phase of physical therapy begins, which may last for another four weeks, according to the patient’s condition and extent of improvement.
Duration of rest after knee cartilage surgery
For most people who underwent knee cartilage surgery, complete rest was imposed in the first weeks of surgery with regular physical therapy, and the person begins to move and walk gradually in the third or fourth week.
The recovery period for a knee cartilage patient after the operation takes approximately 3 months, taking into account the lack of prejudice on the joint or making sudden movements and walking according to the treatment plan previously agreed upon with the attending physician.
Knee cartilage damage
Knee cartilage surgery, like other operations, may expose the patient to some complications and risks, but this matter can be avoided by following the doctors’ instructions and also choosing an experienced surgeon in this field.
Complications of knee cartilage surgery
Infection: A patient with torn cartilage after surgery may be exposed to a bacterial infection that causes ulcers and damage to the joint when its symptoms are severe.
Swelling: After cartilage surgery, it is possible that swelling affects the affected joint and causes some pain, but the patient takes medications that help reduce swelling, and cold water compresses also have an effective role in this case.
Cartilage erosion: Knee cartilage erosion can occur despite the operation, and this may be due to arthritis.
Exposure to clots: Performing surgeries in general make a person more susceptible to clots due to sitting for long periods and lack of movement, and smokers are the most vulnerable to blood clots.
Knee cartilage surgery success rate
According to recent research that has been published recently, the success rate of knee cartilage surgery is up to 90%, and the patient’s recovery is quick after that, and he can return to his normal life regularly after several months of adhering to the doctors’ instructions.
Is knee cartilage cutting dangerous?
There are two types of cartilage in the knee, the articular, and the meniscus. Usually, the meniscus at the front of the knee is more susceptible to injury than the meniscus, and many symptoms appear on the patient when the cartilage is cut, including pain and limitation of the person’s movement.
Damage to the knee that causes cuts, if neglected and not properly cared for, may lead to problems in the joint, the person losing the ability to move the knee, and suffering from roughness and pain in the affected part.