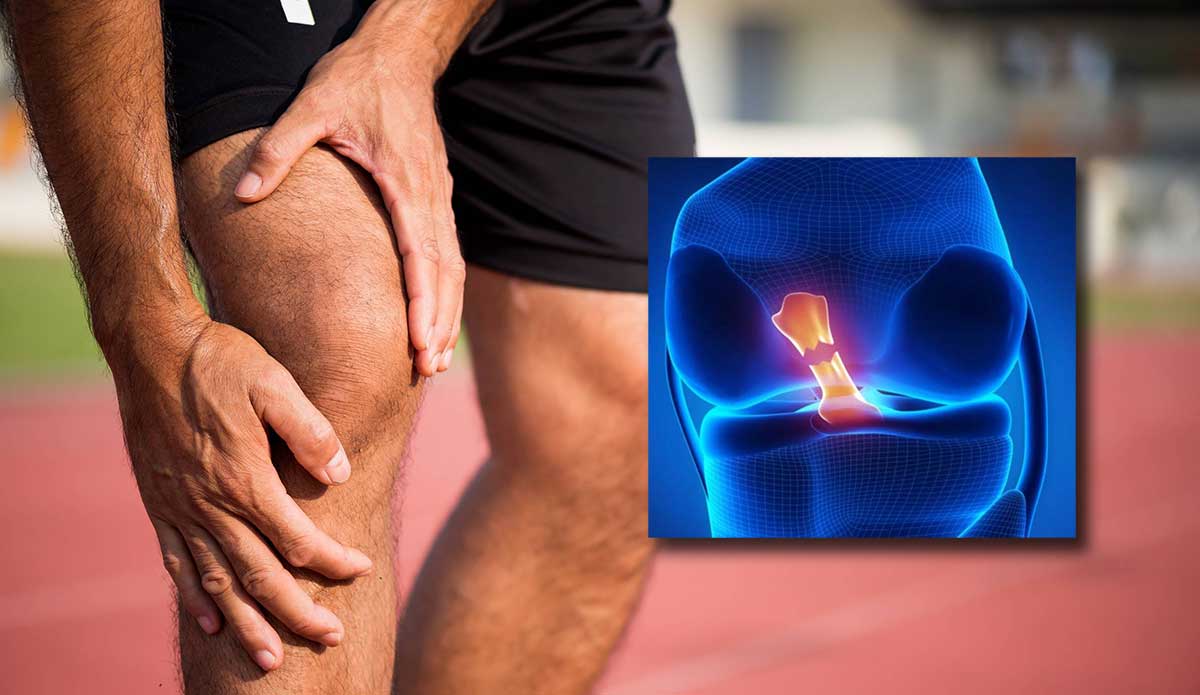
Knee Cartilage Degeneration: Symptoms and Can It Regrow?
Knee Cartilage Degeneration
Knee cartilage degeneration is a condition that affects many people, either due to long-term knee stress or sudden injuries, such as those experienced by athletes. If you are dealing with this problem, you may wonder if there is an effective treatment for knee cartilage degeneration.
In this article, we will shed light on the causes and symptoms of knee cartilage degeneration and outline the various treatment options. Treatment options can range from medications to personal care methods to surgical procedures, depending on the severity of the degeneration and its impact on your daily life.
Symptoms of Knee Cartilage Degeneration
Before delving into how to treat knee cartilage degeneration, it is important to be aware of the symptoms that may indicate this condition. Here are some common symptoms of knee cartilage degeneration:
1. Knee Pain: One of the primary symptoms of knee cartilage degeneration is pain. The pain may be constant or worsen during daily activities.
2. Knee Swelling: Knee cartilage degeneration can be accompanied by swelling in the affected joint, as fluids accumulate, causing localized swelling.
3. Difficulty in Mobility: Many patients with knee cartilage degeneration experience difficulty in walking or bending their knees due to pain and the anticipation of no improvement.
4. Joint Stiffness: You may feel joint stiffness or hear a cracking sound when moving your knee, which is another indicator of cartilage degeneration.
Treatment Options for Knee Cartilage Degeneration
The treatment of knee cartilage degeneration depends on the patient’s condition and its severity. Physicians may start by prescribing medications as an initial step in treating cartilage degeneration. Some medications that may be prescribed include:
1. Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): These medications work to relieve pain associated with cartilage degeneration and reduce inflammation within the joint.
2. Analgesics: Analgesics are used to provide temporary pain relief, and their use depends on the patient’s condition and improvement.
3. Physical Therapy: Physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the knee, improve flexibility, and provide support for the joint.
In addition to medication and physical therapy, lifestyle modifications, weight management, and the use of assistive devices like knee braces can also be part of the treatment plan. In severe cases of knee cartilage degeneration, surgical interventions such as arthroscopy or knee replacement surgery may be necessary.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment approach based on your specific condition and needs.
As for the possibility of regrowing knee cartilage, it’s important to note that once cartilage is damaged, it has limited natural regenerative capacity. Current treatments aim to manage symptoms, improve joint function, and slow down the progression of degeneration rather than regrowing cartilage. Researchers are continually exploring regenerative therapies, but they are still in the experimental stages and not widely available for clinical use.
In conclusion, early diagnosis and appropriate management are crucial in addressing knee cartilage degeneration. Seeking medical advice and adhering to a comprehensive treatment plan can help improve your quality of life and reduce pain and discomfort associated with this condition.
In addition to medication, patients can try home treatments to alleviate the symptoms associated with knee cartilage deterioration. The care methods that can be followed include:
- Ice and heat application: Using ice packs or warm wax on the affected joint can help temporarily relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Braces and supports: Braces and supports can be used as a means to protect your knee from further cartilage wear and to reduce pain.
- Engaging in appropriate physical exercises: Consult your doctor about exercises you can perform to strengthen the knee muscles and improve joint support.
If the patient does not respond to medications and self-care methods, surgical intervention may be required to treat knee cartilage deterioration. Surgical operations typically involve removing soft tissue and damaged edges from the knee cartilage and repairing existing damage.
It is important to remember that before making a decision about treatment options, the patient should consult their doctor and consider the recommendations provided based on their health condition.
Is there a cure for knee cartilage deterioration?
Knee cartilage deterioration is a troubling condition suffered by many people, causing pain and reduced joint mobility. Although there is no direct cure for knee cartilage deterioration, there are a number of ways to reduce symptoms and improve the quality of life.
In this article, we will review some methods that can be effective in treating knee cartilage deterioration:
Medical treatment: Doctors typically begin treating knee cartilage deterioration by prescribing some medications that can relieve joint pain and inflammation. These medications include:
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: These medications help relieve pain and joint inflammation and contribute to the gradual healing of cartilage.
- Pain relievers: The doctor may temporarily prescribe pain relievers to alleviate pain.
- Immunosuppressants: In some advanced cases, these medications can be prescribed to reduce joint inflammation.
Physical rehabilitation: The doctor may recommend physical therapy sessions to strengthen the muscles surrounding and supporting the knee. Physical rehabilitation contributes to improving muscle strength and flexibility, which helps reduce pressure on the cartilage and improve joint function.
Weight loss: If the person is overweight, losing some weight can be beneficial to reduce the pressure on the knee. It is advised to engage in physical exercises and adopt a healthy diet to shed excess weight.
Using braces and supports: It may be beneficial to use knee braces or supports, as they help evenly distribute pressure on the joint and relieve it. You can obtain braces and supports from the pharmacy and use them as directed by your doctor.
Home measures: A person suffering from cartilage wear can take some home measures for comfort and to reduce symptoms. Among these measures:
- Avoid overexerting the knee and rest when feeling pain.
- Apply ice to the joint to relieve pain and inflammation.
- Practice physical exercises to improve the strength and flexibility of the muscles surrounding the knee.
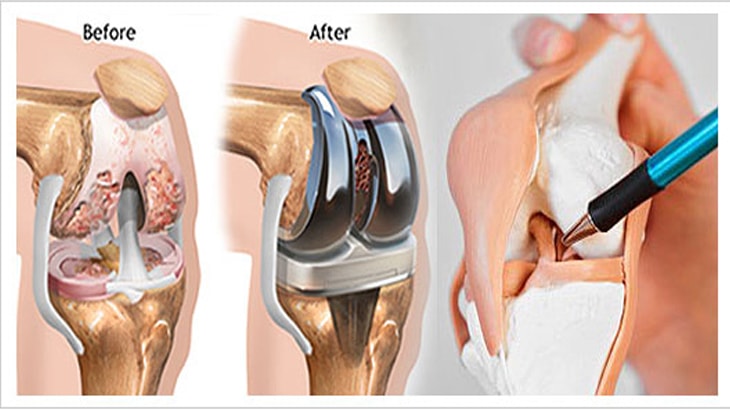
Surgical Treatment: In advanced cases and when symptoms do not improve with non-surgical methods, treating knee cartilage erosion may require surgery. The operations for treating knee cartilage erosion vary depending on the patient’s condition and the severity of the erosion, including:
- Removal of damaged tissue: This procedure involves removing the damaged tissue from the knee cartilage, thus improving joint function.
- Cartilage stimulation: This procedure is used to stimulate the growth of new cells in the cartilage and repair existing damage.
Knee cartilage erosion can be an annoying and difficult condition; however, home measures and non-surgical treatments can help reduce symptoms and improve the quality of life. Patients should consult a doctor to determine the appropriate methods for their condition.
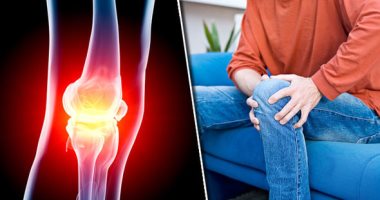
What happens when cartilage erodes?
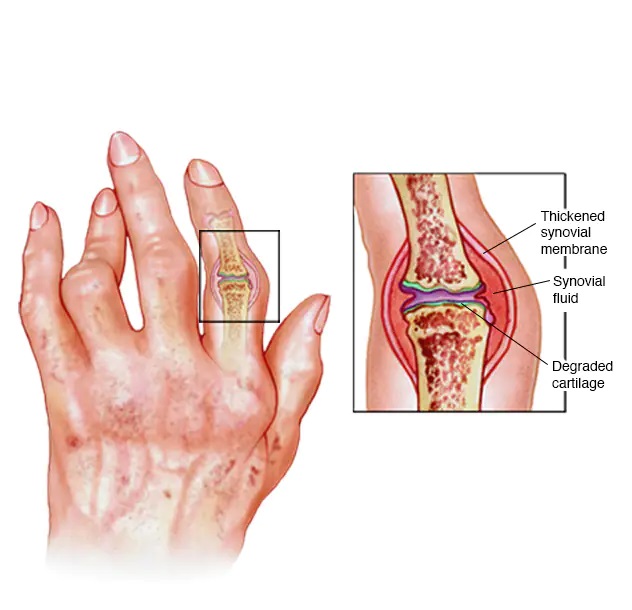
Cartilage is an important part of the skeletal system, covering the ends of interacting bones and acting as a cushion to absorb shocks. However, the erosion of cartilage can cause pain and joint problems. Learn about what happens when cartilage erodes and how to deal with it in this interesting article.
- Rheumatic disorders: Rheumatic disorders are among the most prominent causes of cartilage erosion. As the cartilage erodes, it breaks down and tears gradually, leading to the transformation of the smooth surface that provides movement to the joint into an irregular and rough surface. This erosion can lead to chronic pain and difficulty moving.
- Arthritis: Cartilage erosion can lead to arthritis, where direct bone friction causes the release of chemicals that cause irritation and inflammation in the joints. Arthritis causes sharp pain, swelling, and difficulty in movement.
- Joint stiffness: When cartilage erodes, the direct friction of the bones can lead to the formation of bone growth in the joints, known as stiffness. Stiffness prevents the smooth movement of the joints and can lead to difficulty in movement and restriction of the ability to perform daily activities.
- Muscle weakness: Cartilage erosion can also affect the muscles surrounding the joints. When the cartilage surface is compromised, the muscles may not work properly, weakening muscle strength and increasing the risk of injuries and pain.
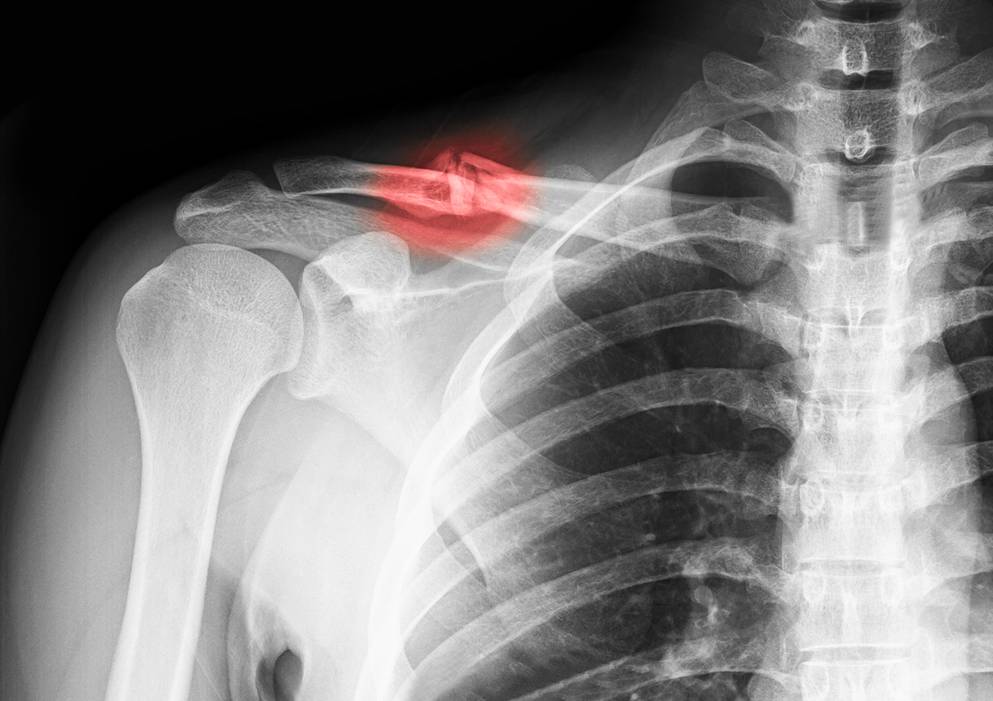
- Knee pain: One example of conditions associated with cartilage erosion is knee pain. The cartilage in the knee can erode due to various factors such as aging or injury. When the knee cartilage erodes, the patient may experience severe pain and find it difficult to move the knee.
Cartilage erosion is a condition where the joint finds it difficult to function smoothly, leading to pain and movement problems. Thus, early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial to minimize the impacts of cartilage erosion. It is advised to visit a doctor to determine the cause of the erosion and outline the necessary treatment, which may include physical therapy, taking painkillers, and weight loss if there is excess weight.
What are the ways to provide cartilage care and maintain joint health? Make sure to:
- Exercise regularly to strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints.
- Maintain a healthy weight, as weight gain increases the pressure on the joints and the risk of cartilage erosion.
- Follow a healthy diet that includes nutrients that promote joint health, such as fatty fish, fruits, and vegetables.
In summary, cartilage erosion is a condition where there is a weakening and wearing away of the cartilage in the joints, leading to pain and difficulty in movement. Preventative care measures such as exercising and maintaining a healthy weight are necessary to preserve joint health and reduce the effects of cartilage erosion. In the case of persistent or severe symptoms, it is recommended to visit a doctor to diagnose the condition and prescribe appropriate treatment.
What are the symptoms of knee cartilage erosion?
Knee cartilage erosion is a common condition that people of various ages may suffer from. Although symptoms can vary from person to person, there are some common symptoms that may indicate the presence of knee cartilage erosion. Let’s identify these symptoms and understand how to deal with them.
- Joint pain: Joint pain is one of the most prominent symptoms that appear with knee cartilage erosion. The affected person may feel pain even at rest, and the pain may increase with daily activities such as walking or climbing. The pain can become constant and persistent over time.
- Swelling and inflammation: Someone with knee cartilage erosion may notice swelling around the joint. The swelling is often due to fluid accumulation in the joint resulting from inflammation or damage to the cartilage.
- Difficulty and restriction of movement: A person suffering from knee cartilage erosion experiences difficulty in moving the joint, which may feel restricted or heavy. This can affect the ability to carry out daily life activities normally.
- Crunching sound: The affected individual may sometimes notice a crunching sound when moving the joint. This sound can be audible when walking or bending, due to the bones rubbing together in the absence of cartilage as a buffer lining.
- Muscle weakness: An individual with knee cartilage erosion may experience less strength in the leg muscles associated with the joint. Therefore, there may be a noticeable weakness in power and stability during walking or standing.
- Difficulty with stairs: The affected person faces difficulty in climbing up or down stairs. This is due to the difficulty in moving the joint and the weakness in the leg muscles.
- Electric shocks: An individual with knee cartilage erosion may feel sensations similar to an electric shock when moving the joint. These sensations include feeling an electric current or sharp pain.
If you notice any of these symptoms or suspect the presence of knee cartilage erosion, you should consult a doctor to diagnose the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment usually includes conservative therapies such as reducing painful activities, applying ice, taking pain relievers, and strengthening the leg muscles by practicing exercises recommended by the doctor. Some cases may require surgical intervention to repair knee damage.
When these symptoms appear, it is important not to ignore or trivialize them. Although erosion of knee cartilage is not a pleasant condition, early diagnosis and establishing an appropriate treatment plan can help reduce pain and improve quality of life. Therefore, do not hesitate to consult a doctor if you feel any of these symptoms.
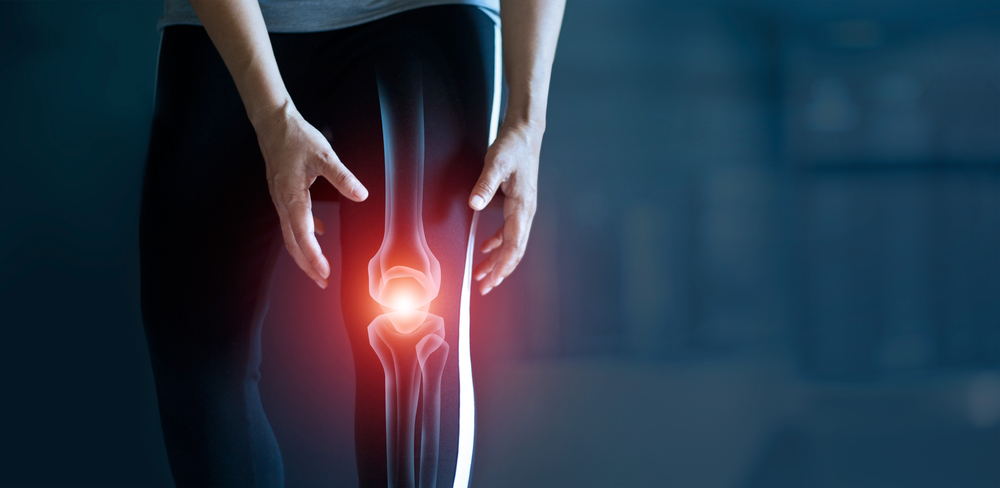
Is it possible for knee cartilage to regrow?
Cartilage is the part that covers the knee joints and acts as a cushion to reduce friction between bones. The cartilage can wear out and get damaged in some cases, such as sports injuries or due to aging. A question that preoccupies many people is: Is it possible for the knee cartilage to grow and regenerate by itself?
If this wear is natural and there is no significant damage to the cartilage, there are some cases where natural regeneration of the cartilage can occur. For example, growth and regeneration of the cartilage may occur in cases of small tears or minor cuts in the cartilage. The cartilage may heal itself by repairing and renewing the collagen fibers that compose it. However, this largely depends on the person’s age and their natural regenerative capacity.
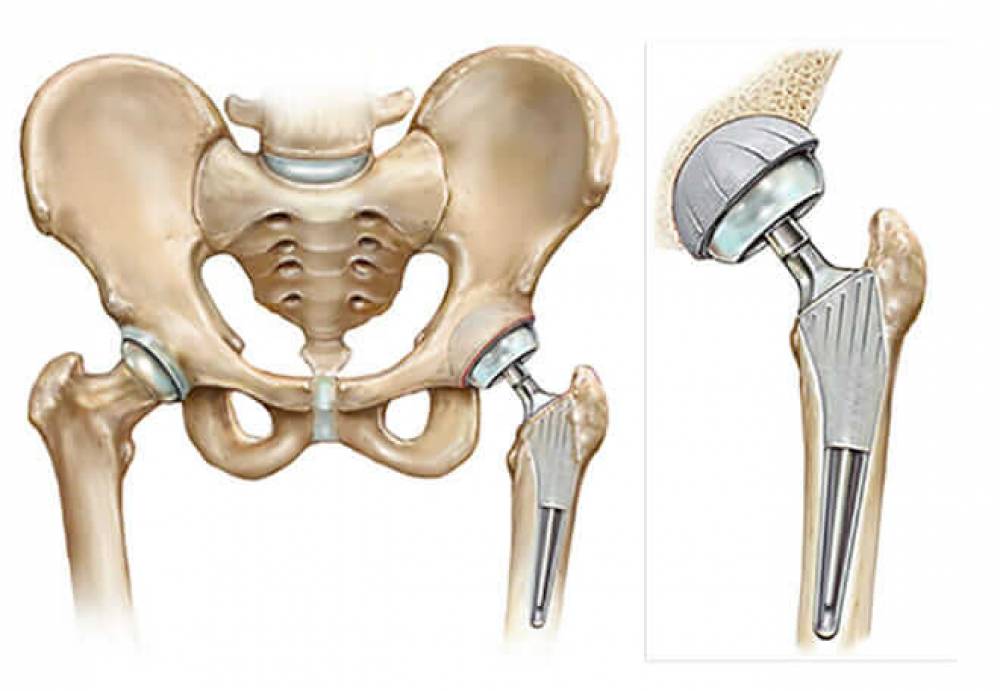
If the cartilage is significantly damaged or there are large tears in it, it may be difficult or even impossible to regenerate naturally. In such cases, surgical treatment may be the best option. The damaged cartilage is replaced with artificial cartilage or from other sources such as donations in knee surgery. The decision to undergo surgery depends on the individual’s condition and the extent to which the wear affects their daily life.
Nevertheless, some regenerative and preventive measures can be followed to maintain the health of knee cartilage and delay chronic wear. These measures may include:
- Exercising: Vigorous exercises for the muscles surrounding the knee, such as strengthening the thigh and buttocks muscles, may enhance stability and strengthen the cartilage.
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Weight gain can increase pressure on the joint and cause excessive wear of the cartilage. It is important to maintain a healthy weight to reduce stress on the joint.
- Taking dietary supplements: Some dietary supplements are considered good for the health of knee cartilage, such as glucosamine and chondroitin supplements. Taking these supplements may help promote cartilage regeneration and alleviate symptoms of roughness.
- Regenerative techniques: There are some regenerative techniques that can be used to treat and regenerate knee cartilage. These techniques include the use of stem cell therapy or beneficial acids for cartilage regeneration.
Generally, it can be said that in cases of minor natural wear and tear, there is some hope for the natural regeneration of cartilage. However, in cases of severe wear or major injuries, surgical treatment may be the best option. It is important to consult a doctor to assess the condition of the knee and make an appropriate decision about the treatment.
How to strengthen knee cartilage?
The health of knee cartilage is important for maintaining the strength and flexibility of the joint. The meniscus cartilage helps guide and distribute stresses within the knee and helps prevent direct exposure of the bones. If necessary, some steps can be taken to strengthen and protect the meniscus and maintain the health of your knees.
Here are 10 tips for strengthening knee cartilage:
- Engage in robust exercises: Strong and diverse, like exercises that strengthen the muscles around the knee such as weightlifting and squats. These exercises help in strengthening the muscles and increasing joint stability.
- Aerobic exercises: Activities like intense jumping or box jumps, and cycling, etc., can improve blood flow to the knee and promote cartilage function.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Keeping a healthy weight reduces the pressure and strain on the knee, which decreases the risk of injury or deterioration of the meniscus condition.
- Follow a balanced diet: Should include magnetizing foods like fatty fish, olive oil, and seeds and nuts, which contain omega-3 fatty acids that help improve joint health.
- Reduce inflammation: Dietary supplements can be used or foods rich in anti-inflammatory properties such as ginger, turmeric, and fish oil, which help alleviate inflammations and improve cartilage health.
- Protect the knee during sports: Appropriate protective gear such as knee guards and suitable footwear should be worn during sports activities that put pressure on the knee.
- Warm-up and cool down: Athletes should warm up the muscles well before starting sports exercises, and ice can be used after exercises to relieve pain and swelling.
- Avoid excessive pressure: Standing for long periods and excessive bending should be avoided, as these movements can lead to the deterioration of the cartilage condition.
- Stress management: Meditation and relaxation techniques can help reduce stress levels and the tension that can affect the health of the cartilage.
- Consult a doctor: In case of any unusual symptoms or poor health condition of the knee, a doctor should be consulted for an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan.
By following these tips, you can strengthen knee cartilage and maintain its health. It must be remembered that each case is different and may require individual attention. Economists of health materials and commercial knee accessories market to citizens by inspiring them to increase satisfaction with their health, based on education with these tools, methods, and advice. Medical tips from a qualified doctor ensure the health of your knees.
What is the food for cartilage?
Cartilage plays a critical role in the health and integrity of joints, as it absorbs shocks and promotes smooth movement of the bones. To maintain the health of the cartilage, proper nutrition and appropriate food must be provided.
The regeneration of cartilage depends greatly on the consumed food. Therefore, it is essential to include healthy foods that help with the flexibility and renewal of cartilage in your daily diet. These foods improve the shape and function of the cartilage, and contribute to reducing joint inflammation and relieving pain.
Here are some foods that are believed to promote cartilage health:
Fatty fish: Fatty fish like salmon and tuna contain omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential elements for cartilage renewal. These acids help reduce joint inflammation and promote overall cartilage health.
- Fruits and vegetables rich in antioxidants: Many fruits and vegetables contain antioxidants that protect cartilage cells from damage caused by free radicals. These include foods such as berries, broccoli, cherries, strawberries, and oranges.
- Seafood: Seafood such as sea urchins, shrimp, and fish are believed to contain important compounds such as chondroitin sulfate, which promotes cartilage regeneration and strengthens its health.
- Collagen sources: Collagen – the main protein in cartilage – can be obtained from sources such as cooked bones, gelatin, and chicken broth. These sources are beneficial for the health of the cartilage and promote its regeneration.
- Foods rich in Vitamin C: Vitamin C is believed to strengthen the collagen fibers in cartilage and enhance its health. Look for citrus fruits, red peppers, strawberries, and mango as a rich source of this vitamin.
The diet for maintaining cartilage health should be balanced and varied, including a wide range of foods beneficial for cartilage. It is also advisable to avoid exposure to saturated fats and refined sugars, as these components can contribute to worsening joint inflammation.
In addition, people with cartilage problems should consult their doctor or nutrition specialist for personal advice and a suitable dietary plan.
Proper and balanced nutrition is one of the fundamental factors in maintaining cartilage health. Enjoy eating these beneficial foods and make them a part of your diet to enhance the health of your joints and the renewal of cartilage.
How to Maintain Knee Cartilage Health?
Knee osteoarthritis is an inevitable condition that commonly occurs with aging and repetitive joint use. The knee joint endures significant daily loads, making it susceptible to wear and tear. Although it’s impossible to completely prevent knee osteoarthritis, its progression can be delayed, and the health of the cartilage can be maintained by following some medical guidelines.
Here are some tips that may help you in preserving the health of your knee cartilage:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Excess weight is a primary reason for the deterioration of knee cartilage, as the more the body weighs, the greater the stress on the joint. Therefore, it’s crucial to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise.
- Engage in appropriate physical exercises: Physical activity may be challenging for some due to knee osteoarthritis, but muscle-strengthening exercises around the joint can be very beneficial in reinforcing the knee’s muscular support and improving its function. Preferably, choose low-impact exercises like cycling or swimming.
- Avoid harmful impacts: Activities that put excessive stress on the knee, such as jumping and running on hard surfaces or landing heavily on your feet, should be avoided. If your job requires standing for long periods, you should take periodic breaks to alleviate the pressure on your knees.
- Utilize physical therapy options: Physical therapy sessions help to strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee and improve flexibility and stability. Physical therapy can be effective in relieving pain and improving movement if there are any knee issues.
- Wear braces and medical devices: Certain specially designed compressive braces for the knee can provide support and reduce stress on the joint. Stabilization devices can also be used to aid in achieving better knee stability during movement.
- Quit smoking: Smoking is a factor that causes inflammation and overall deterioration of cartilage health. Therefore, it is important to stay away from smoking to maintain the health and integrity of the joint.
Overall, it can be said that knee osteoarthritis is an unavoidable condition that cannot be entirely prevented. However, by adopting a healthy lifestyle and appropriate medical care, its occurrence can be delayed, and the health of the cartilage can be preserved.