Arthritis: Its Causes, Treatments, and the Difference from Rheumatism
Arthritis: Its Causes and Treatments
Arthritis is a chronic condition affecting the joints and surrounding tissues. It is a common issue worldwide, impacting millions of people of various ages and nationalities. Arthritis can manifest in different forms and cause painful symptoms and negative effects on the lives of those affected. This article will explore the primary causes of arthritis and its treatment methods.
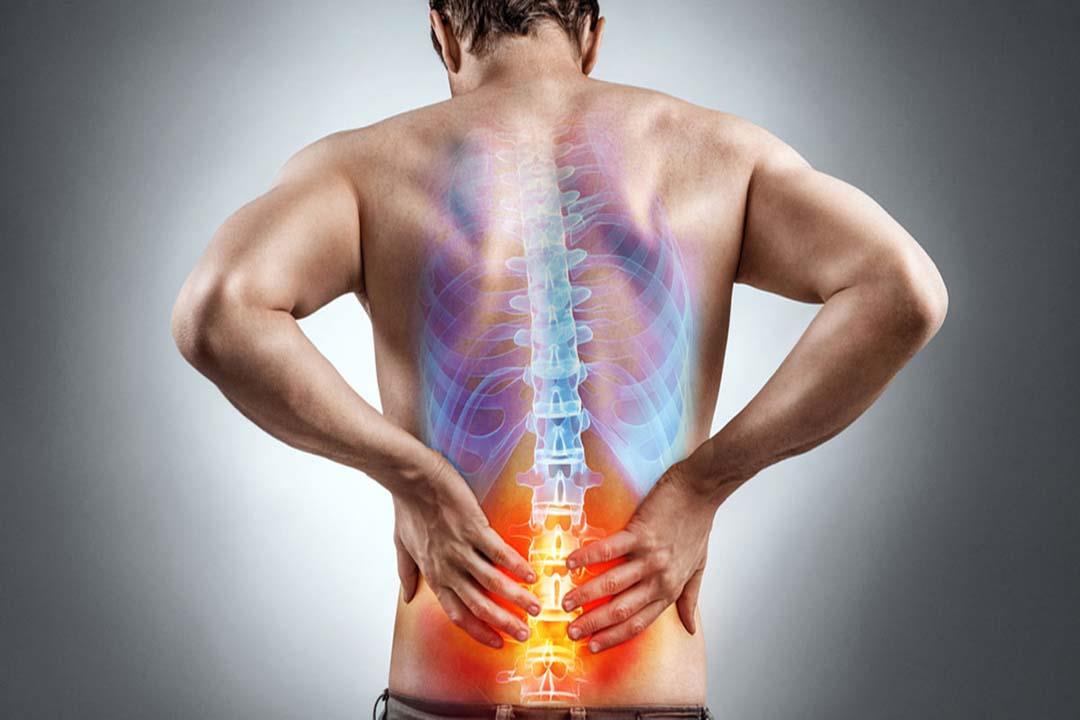
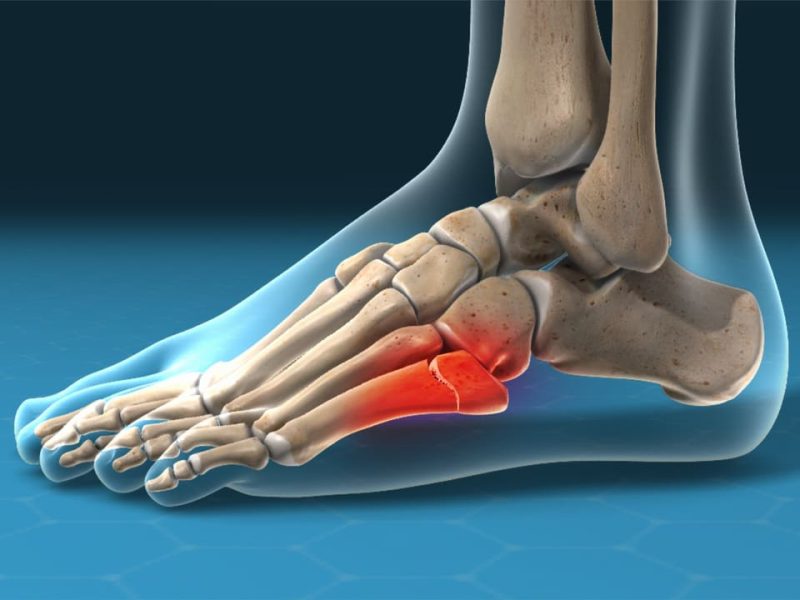
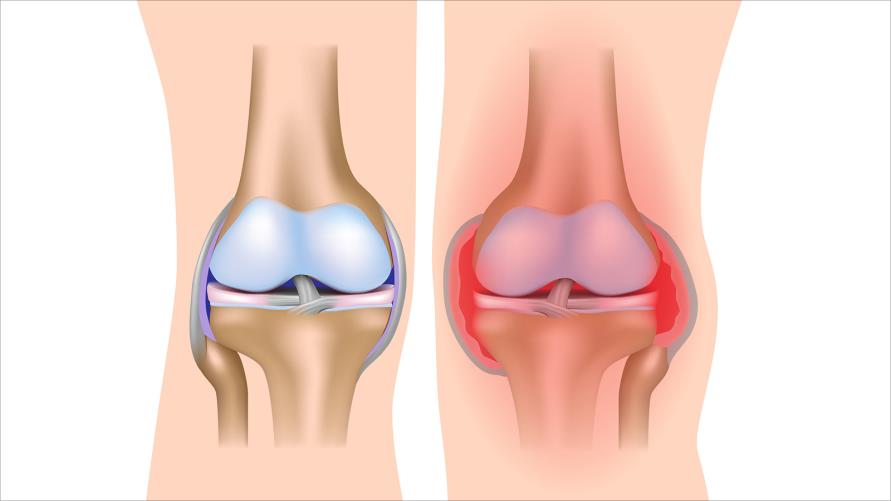
Arthritis is a medical condition characterized by swelling, pain, and redness in the body’s joints. There are many types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, gouty arthritis, sclerotic arthritis, idiopathic arthritis, viral arthritis, among others.
The symptoms of arthritis depend on the type of inflammation but generally include common symptoms like pain, swelling, and stiffness in the affected joints, and difficulty moving. Various joints in the body can be affected, including both large and small joints.
It is essential to consult a doctor if joint inflammation is suspected, as a doctor can provide an accurate assessment and develop an appropriate treatment plan based on the type and severity of the inflammation. Treatment options may include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, lifestyle changes, and in some cases, surgical treatment may be necessary.
In conclusion, arthritis is a common health problem that affects the quality of life of those afflicted. The disease should be treated cautiously according to the guidance of treating physicians, and attention should be paid to prevention and following a healthy lifestyle to reduce the risk of this chronic disease.
How to Know if You Have Arthritis?
Arthritis is a painful and disturbing health condition that can significantly affect people’s lives. It can be difficult to diagnose arthritis in its early stages, as the symptoms may be unclear and similar to other diseases. Therefore, it’s important to be aware of the early signs of arthritis and see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and to start appropriate treatment. In this article, we will look at some signs indicating you might have arthritis.
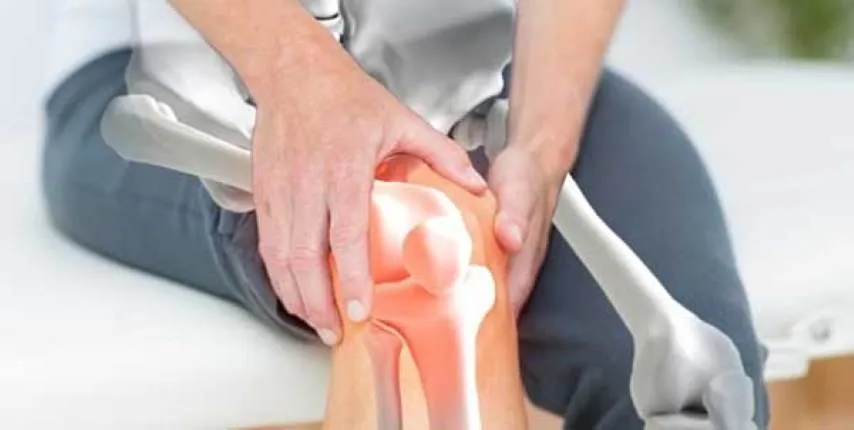
Joint Pain and Swelling: When suffering from arthritis, you may experience sharp or chronic pain in the affected joints. The pain can be so severe that it hinders your daily movement and routine activities. The pain may worsen during movement and swelling may increase in the inflamed joint due to fluid accumulation. Difficulty Moving and Stiffness: Arthritis can cause difficulty moving and stiffness in the affected joints, especially in the morning or after long periods of rest. You may feel stiffness and an inability to move the joints easily. This stiffness may gradually decrease over time with movement and warming up.
Joint Shape Change: In the advanced stages of arthritis, it can lead to a change in the shape of the affected joints. You may notice deformities in the joints, such as bending or abnormal swelling. This can affect your ability to use the joints properly and may cause difficulty in movement.
Other Symptoms: In addition to the above-mentioned symptoms, rheumatoid arthritis may be accompanied by other symptoms such as severe fatigue, fever, and loss of appetite. You may also feel pain and a sense of warmth in the area of the affected joints.
Where Does Arthritis Come From?
Arthritis is a common condition that affects many people around the world. Although the causes of arthritis are not fully known, there are potential factors that may contribute to its emergence and development. Let’s look at some potential factors to avoid and maintain joint health.
Genetic Factors: Arthritis may sometimes be linked to genetic factors. If a family member has this condition, you may have a higher risk of developing it. Knowing your family’s medical history can help determine your likelihood of developing arthritis.
Genes: There are certain genes that increase the likelihood of developing arthritis. For example, inheriting the Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC) syndrome, which affects the immune system and increases the risk of developing rheumatoid and psoriatic joint inflammations.
The Immune System: Some types of arthritis are associated with a malfunction in the immune system, where the immune system attacks healthy joint parts instead of protecting against infection. These immune-related arthritis inflammations are a type known as rheumatoid arthritis.
Smoking: The habit of smoking may increase the likelihood of developing arthritis and accelerate its progression. Smoking affects the immune system and increases its activity in attacking joint tissues.
Environmental Factors: Some studies suggest that environmental factors such as prolonged exposure to secondhand smoke, exposure to chemical fumes, and air pollution can increase the likelihood of developing arthritis.
Psychological Factors: Psychological factors may impact joint health. Mental stress, anxiety, and depression can negatively affect the immune system and increase the risk of developing arthritis.
Injuries: Previous injuries to the joints may increase the likelihood of inflammation in them later. People who have had an injury or surgical procedure in a joint should be cautious and monitor joint health carefully.
It is important for individuals to adhere to a healthy and balanced lifestyle and avoid factors that contribute to an increased risk of developing arthritis. They should also make sure to exercise regularly and follow a healthy diet to maintain joint health and reduce the likelihood of developing inflammation.
These factors might be potential causes of arthritis; however, it is important to consult a doctor for diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Early detection and proper treatment can help in managing arthritis and reducing its symptoms and negative impact on the lives of those affected.
How can I permanently get rid of arthritis?
5 Effective Ways to Permanently Get Rid of Arthritis
Arthritis is a chronic condition that can negatively affect the quality of life of those affected. It can cause severe pain, swelling in the joints, and difficulty moving. If you are suffering from this condition, you might be interested in knowing the most effective ways to permanently get rid of arthritis. In this article, we will review five effective ways that can help in eliminating this problem.
- Follow a Healthy Diet: A healthy diet is an important factor in controlling arthritis inflammation. You should include foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidants, such as fish, fatty fish, leafy vegetables, and nuts in your diet. These foods help reduce inflammation and soothe the pain associated with arthritis. On the other hand, avoid processed foods, carbonated drinks, and artificial sugar, as they are potential causes of increased arthritis inflammation.
- Engage in Suitable Physical Exercises: Physical exercise is an important method for alleviating arthritis pain and increasing the flexibility and strength of muscles surrounding the joints. You can engage in light weight exercises, aquatic exercises, or even regular walking. Before starting any physical activity, consult your doctor or a physiotherapist to find out which activities are suitable for your condition and to avoid any additional injuries.
- Take Care of Your Weight: Excess weight is a major factor that increases pressure on the joints, causing irritation and pain. Therefore, it is advised to achieve and maintain an ideal weight through a healthy diet and regular exercise. Consult a nutrition specialist to get a dietary plan suitable for reducing excess weight and improving joint health.
- Try Complementary Therapies: There are a number of complementary therapies that can be beneficial in treating arthritis. For example, cryotherapy and laser therapy are common methods used in arthritis treatment. Cryotherapy can help reduce swelling and pain in the joints by lowering the temperature of the inflamed joint. Laser therapy, on the other hand, has shown effectiveness in improving joint movement and reducing pain in some studies.
- Consult a Doctor: If you are suffering from acute and chronic arthritis, you should consult a doctor to get a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The doctor may recommend non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, topical applications, and even physical therapy to relieve symptoms. Surgical intervention is a final option in cases of severe and chronic arthritis.
Using these five methods, you can effectively control arthritis and alleviate its symptoms. However, you must remember that arthritis is a chronic condition that may require long-term management. Therefore, it is important to maintain a healthy lifestyle and receive regular medical care to keep your joints healthy and reduce bothersome symptoms.

What is the appropriate treatment for arthritis?
Arthritis is a condition in which the patient suffers from swelling and pain in the joints due to damage or inflammation. There are several types of arthritis, including rheumatoid arthritis, gouty arthritis, and other common joint inflammations. In this article, we will review more about the appropriate treatment for arthritis.
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs):
- Used to relieve pain and swelling caused by arthritis.
- They work by inhibiting an enzyme called cyclooxygenase, which contributes to the production of high levels of inflammatory chemicals in the human body.
- Some well-known nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs include aspirin, ibuprofen, and naproxen. Antibiotics:
- If arthritis is caused by a bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed to treat the infection and relieve swelling and pain. Disease-Modifying Anti-Rheumatic Drugs (DMARDs):
- Used to treat rheumatoid arthritis and other chronic forms of arthritis.
- They work by reducing the immune system’s response to inflammation and affecting the progression of the disease.
- Some examples of DMARDs include methotrexate and sulfasalazine. Biologics:
- This type of medication is used to treat severe forms of rheumatoid arthritis that have not responded to other treatments.
- Biologics target specific components in the immune system that cause inflammation. Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation:
- Used to strengthen and improve the movement of affected joints and reduce pain.
- Includes rehabilitative exercises, massage, heat and cold therapy, and hydrotherapy. Joint Surgery:
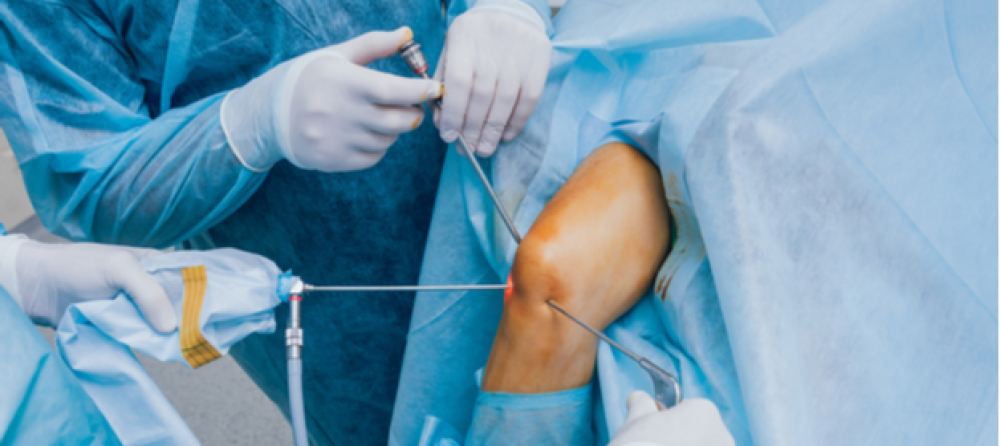
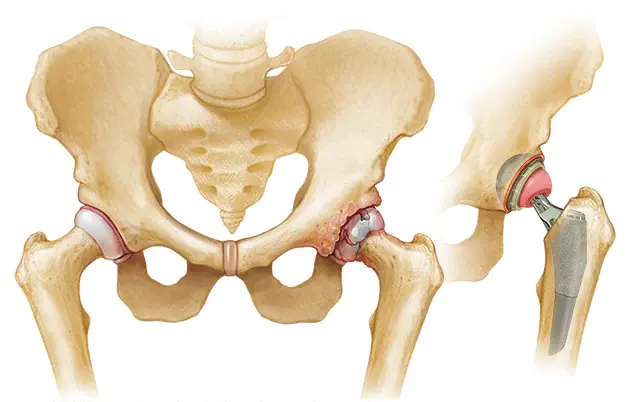
- Used when arthritis is very severe and other treatment methods have not been successful.
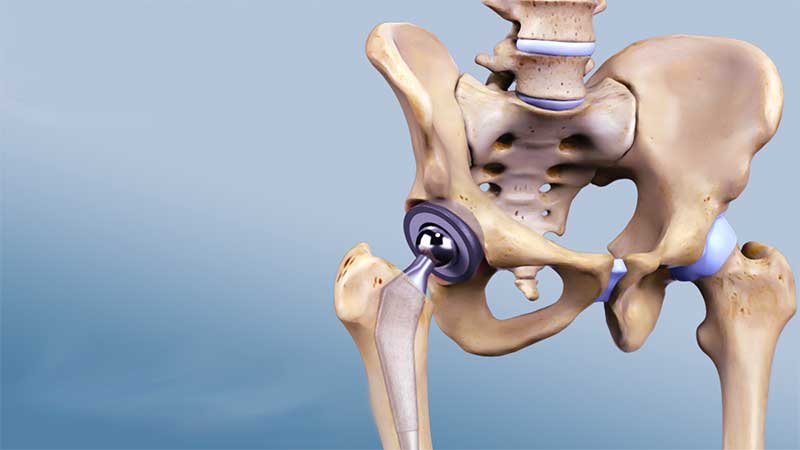
- Joint surgery may involve replacing the damaged joint with an artificial one (joint replacement).
Always remember that these treatments are just general options and the appropriate treatment for arthritis may vary from person to person. Patients should consult with a specialist to determine the most suitable treatment for their individual case. It is also necessary to follow the doctor’s instructions properly and adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes good nutrition and appropriate physical activity for the prevention and management of arthritis.
Is Arthritis the Same as Rheumatism?
Arthritis and rheumatism are two immune system-related disorders that affect the joints and can cause pain, swelling, and limited body movement. Although these two disorders share some common symptoms, they are separate disorders with different inflammatory nature and effects.
Arthritis is a general term meaning inflammation in the joints, whether resulting from rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, spondyloarthropathies, or others. Ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis are the most common and impactful types.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic inflammatory disorder affecting the joints and other parts of the body. It causes inflammation in the joint linings, leading to swelling, pain, and restricted movement. Rheumatoid arthritis can lead to joint destruction over time, potentially causing problems that affect a person’s ability to perform daily activities. Osteoarthritis: Osteoarthritis occurs when the body suffers a bacterial infection, leading to inflammation in the joints. Symptoms of osteoarthritis can include swelling, pain, itching, and numbness in the affected joints.
While both disorders cause swelling and pain in the joints, there are key differences between them. Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic disorder typically affecting small joints in the hands and feet and may impact other body organs like the heart and lungs. Moreover, rheumatoid arthritis occurs when the body’s autoimmune system attacks and progressively destroys the joints.
On the other hand, osteoarthritis results from a bacterial infection in the body. It leads to inflammation in only the affected joints and does not impact other body organs.
In conclusion, both disorders should be diagnosed by a specialist based on symptoms and medical analyses. Both can be treated with medications, physical therapy, and in severe cases, doctors may resort to surgical interventions.