How Do I Know If I Have a Lumbar Disc Herniation, and Who Is the Best Doctor for Minimally Invasive Disc Herniation Surgery?
Lumbar Disc Herniation
Lumbar disc herniation, also known as a slipped disc, is a painful condition in which the disc between the vertebrae in the lower back moves out of its normal position, potentially compressing nearby nerves. It is typically diagnosed through clinical examination by a doctor and may require imaging tests like MRI to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment depends on the severity of the condition. In mild to moderate cases, recommendations may include rest, physical therapy, pain relievers, and corticosteroid injections. In severe cases, surgery may be an option, but it is often considered a last resort. To prevent disc herniation, it’s essential to maintain the strength of the back muscles through regular exercises, practice proper posture when sitting and lifting, and avoid excessive weight.
How Do I Know If I Have Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Many people experience problems with lumbar disc herniation, a condition that causes pain, limited mobility, and difficulty performing daily activities. If you suspect you have lumbar disc herniation, here are some signs that may help confirm it:
- Recurrent Lower Back Pain: If you suffer from recurring pain in the lower back, especially when attempting normal activities like prolonged sitting or lifting heavy objects, this could be a sign of lumbar disc herniation.
- Numbness or Tingling in the Legs: Lumbar disc herniation can affect the nerves that pass through the spine, leading to numbness or tingling sensations in the legs. If you experience any of these symptoms, it may be due to disc herniation.
- Muscle Spasms and Difficulty in Movement: You may struggle to move or bend your spine and may experience muscle spasms around the affected area. These movement difficulties and muscle spasms can result from nerve compression due to disc herniation.
- Exacerbation of Symptoms with Physical Activity: If your symptoms worsen when you engage in physical activities like walking or running, this could be an additional indication of lumbar disc herniation.
- Leg and Hip Pain: Lumbar disc herniation may be accompanied by pain in the hips and legs, with pain spreading from the lower back to the leg and foot.
If you have similar symptoms and suspect lumbar disc herniation, it’s essential to consult a doctor for a precise evaluation and diagnosis. The doctor may recommend ultrasound or MRI scans or other tests to confirm the diagnosis and establish an appropriate treatment plan.
Can Lumbar Disc Herniation Be Cured?
Lumbar disc herniation is a common condition affecting many people. When a disc slips out of place, it deviates from its natural position and may compress nearby nerves, causing severe pain and various effects on mobility and daily life. This raises the question for many: can lumbar disc herniation be cured?
It’s important to remember that the spine is a vital and multifunctional part of the human body. Typically, spinal problems occur due to various factors such as strenuous work, injuries, joint inflammations, or aging. Although lumbar disc herniation can be a troublesome and painful condition, complete recovery may be possible in many cases.
Treatment options vary based on the individual and the severity of the herniation. In mild cases, doctors may recommend rest, avoidance of activities that strain the back, physical therapy, and medications to manage pain and inflammation. In severe cases, surgery may be considered as a last resort.
It’s worth noting that most cases do not require surgery, and with proper care and suitable treatment, individuals can often return to their normal lives without pain and limitations. Ultimately, a person with disc herniation should know that hope for recovery exists, and they can receive appropriate assistance to achieve it.
How Does a Lumbar Disc Herniation Patient Sleep?
Many people suffer from back problems such as lumbar disc herniation, which can cause severe pain and difficulty in movement. Getting a good night’s sleep is one of the most critical factors contributing to recovery and pain relief for patients with this condition. Here are some tips on how a lumbar disc herniation patient can sleep correctly:
- Appropriate Pillow: Lumbar disc herniation patients should choose a suitable pillow that supports the natural curves of the neck and back. Using a pillow with adjustable layers that can accommodate your individual needs is preferable.
- Sleeping Position: If you have lumbar disc herniation, sleeping on your side is considered the most suitable position. Place a pillow between your thighs for added support and better balance.
- Relaxation Before Bed: Before bedtime, try to relax and calm your muscles. You can practice deep breathing or meditation exercises to reduce tension and muscle stress.
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is an important factor in reducing pressure on the back and achieving better sleep quality. Follow a balanced diet and engage in regular physical exercise.
- Gentle Stretching Before Bed: Gentle stretching exercises before bedtime may be beneficial. You can engage in low-impact exercises like walking or swimming to improve blood circulation and alleviate chronic pain.
- Pain Management: If you experience severe pain before bedtime, you may need to take a small dose of prescribed pain relievers. These medications should be considered as a last resort and not relied upon continuously.
- Sleep Environment: Your bedroom should be comfortable and conducive to rest. Adjusting the room temperature, avoiding bright lights, and minimizing noise may be necessary for a peaceful sleep.
- Back Massage: Gentle back massage before bedtime can be effective in relieving pain and tension. Use circular motions with your fingertips or rely on professional massage techniques if you prefer.
It is essential to consult with a specialized doctor before making any changes to your sleep pattern. They should have a precise understanding of your medical condition and can provide additional advice to improve your sleep and alleviate pain.
Can Lumbar Disc Herniation Worsen?
Lumbar disc herniation is considered a spinal disorder and one of the common complaints among individuals of various ages. Lumbar disc herniation occurs when the disc between the vertebrae slips, resulting in pressure on the surrounding nerves and causing unwanted pain and symptoms.
Can lumbar disc herniation worsen? This is a question that concerns many people who have this condition. The answer is yes; lumbar disc herniation can worsen if not dealt with properly and promptly. When lumbar disc herniation occurs, the slipped disc undergoes damage and wear and tear due to continuous pressure. If the condition is not treated, it can lead to the exacerbation of symptoms and deterioration.
Among the developments that lumbar disc herniation can experience is the tearing of the disc wall, allowing a portion of the affected disc to slip out, leading to what is known as sequestrated disc herniation. Lumbar disc herniation can also result in the wear and tear of adjacent facet joints, increasing symptoms and significantly affecting a person’s mobility and daily activities.
Early diagnosis and effective treatment are crucial to prevent the worsening of lumbar disc herniation. Doctors may recommend conservative treatments such as physical therapy and muscle strengthening exercises to reduce symptoms and improve the condition. If improvement is not observed, surgical intervention may be recommended to remove the damaged disc and relieve pressure on the nerves.
In summary, lumbar disc herniation can worsen if not properly and promptly addressed. Therefore, individuals with this condition should seek appropriate medical care and take necessary steps for early diagnosis and treatment to avoid symptom exacerbation and improve their condition.
Which Vertebrae Are Most Prone to Disc Herniation?
Disc herniations are a common issue in the spine, occurring when a spinal disc moves from its natural position between the vertebrae. Some vertebrae are more susceptible to disc herniation than others, including:
- Cervical Vertebrae: Located in the upper part of the spine, cervical vertebrae are the most vulnerable to disc herniation. This is due to the passage of important sensory and motor nerves through this area, increasing the risk of affecting the spinal disc and causing it to slip.
- Thoracic Vertebrae: These are located in the mid-back area of the spine and are also prone to disc herniation. Thoracic vertebrae play a vital role in supporting and protecting the surrounding nerves and spinal cord, so any disruption in this area can affect the spinal disc and lead to herniation.
Understanding which vertebrae are most susceptible to disc herniation can help take necessary precautions to maintain spinal health. It’s worth noting that other factors such as sports injuries or strenuous work can increase the risk of disc herniation in any vertebra. Therefore, it’s essential to exercise properly and follow a healthy lifestyle to preserve spinal health.
What Are the Exercises for Disc Herniation?
Effective physical exercises are crucial in the treatment of disc herniation. These exercises help strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, improve flexibility, and enhance stability. When performed regularly and correctly, they promote disc healing, reduce pain, and minimize swelling.
Here are some effective exercises for disc herniation that can be done at home or under the supervision of a physical therapist:
- Initial Stretching Exercises: Begin with lying on your back and bending your knees. Then, pull your right knee towards your chest and hold it with your hands for a few seconds. Afterward, slowly release your knee while maintaining tension in the muscle, then repeat the process with your left knee.
- Side Bending Exercises: Stand and hold onto the edge of a stable surface like a desk. Then, bend your body to the right and hold the bend for a few seconds. When finished, return to the neutral position and repeat the process on the other side.
- Back Extension Exercises: Lie face down, with your chest and head lifted while your hands rest on the ground. Extend your legs so that they are straight and your toes touch the floor. Stay in this position for a few seconds, then return to a horizontal position and repeat the process several times.
- Hot Stones Exercises: Place a mat or carpet on the floor, stand comfortably on one of your feet on the mat. Then, move your foot forward and backward at a moderate pace. After that, move your foot to the right and left in the same manner. Repeat the process with the other foot.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Lie on your back and place your hands on your abdomen. Take a deep breath through your nose and exhale slowly and deliberately through your mouth. Repeat this for 5-10 minutes daily.
Before starting any exercise, consult your doctor to ensure that these exercises are suitable for your specific condition and do not conflict with any other health issues. Additionally, warm up before exercising and cool down afterward to prevent injury.
How Long Does it Take to Treat Disc Herniation?
The duration of treatment for disc herniation varies depending on the specific characteristics of the case, the progression of the condition, and the type of treatment applied. However, the treatment process for this type of injury is typically long-term and requires patience and commitment from the patient.
The duration of treatment is determined by several factors, including:
- Severity of the Disc Herniation: The size and location of the herniation within the disc can impact the duration of treatment. Mild disc herniations are usually treated with non-invasive methods and require less time than more severe cases that may necessitate surgical intervention.
- Early Diagnosis: Early diagnosis of disc herniation is crucial for starting the appropriate treatment promptly. Delayed diagnosis can lead to worsening of the condition and an increase in the duration of treatment.
- Treatment Approaches Used: There are various methods for treating disc herniation, including non-surgical and surgical treatments. The choice of approach depends on the patient’s condition and the recommendations of the treating medical team. Non-surgical treatment typically involves less intervention and requires less time for recovery, while surgical treatment may take longer for healing.
- Patient’s Strength and Activity: The overall strength and activity level of the patient play a significant role in the recovery process. Patients who adhere to rest and therapeutic exercises prescribed by their doctor can contribute to speeding up the healing process and reducing the duration of treatment.
It’s important for patients to be aware that the treatment of disc herniation may require a long time for full recovery. They should follow medical advice and consult their treating physician regarding any new developments or increasing pain. Regular therapy sessions, preventive exercises, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can be essential components of the required treatment to preserve spinal health and avoid future injury.
What Are the Grades of Disc Herniation?
Disc herniation is a condition that affects the spine and is one of the most common health problems worldwide. It causes severe pain and impacts the quality of life for those affected. Disc herniation is categorized into different grades based on its severity and its effects on nerves and surrounding tissues. Here are some common grades of disc herniation:
Grade 1: Grade 1 is the mildest form of disc herniation, where the direct impact on the spinal discs is minimal. In this case, pain typically occurs regularly and does not cause any deformities in the spine. Grade 1 can usually be easily treated with physical therapy and appropriate exercises.
Grade 2: Grade 2 is characterized by escalating back pain with worsening symptoms. Disc herniation leads to inflammation and swelling of the tissues surrounding the affected vertebrae. There is a possibility of deformity in the shape of the disc, and treatment may require anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy to alleviate pain and reduce nerve irritation.
Grade 3: In this grade, disc herniation is more severe and causes sharp and bothersome pain. It may affect the movement of the spine and lead to narrowing of the spinal canal, putting pressure on the nerves. Grade 3 treatment typically requires a combination of physical therapy, pain-relieving medications, and in some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary.
Grade 4: Grade 4 is the most severe form of disc herniation, where the disc has significantly shifted from its natural position. It can have a significant impact on nerve function and spinal discs. It may also compress the spinal cord. Surgical treatment is often required in many cases to achieve relief from severe symptoms.
Disc herniation is a health problem that must be promptly and correctly addressed. Individuals with disc herniation should consult a spine specialist to determine the specific grade of the injury and receive appropriate treatment.
Does Disc Herniation Affect the Nerves?
Disc herniation is a common condition in the spine, referring to a situation where the disc between two vertebrae deviates from its natural position. This herniation can exert pressure on the nerves surrounding the spine, affecting their normal function. When disc herniation occurs, it can lead to compression of the nerve roots passing through the affected vertebral area. This continuous nerve compression can result in severe pain and interference with nerve function.
Symptoms of disc herniation related to nerves can vary and differ from person to person. Patients may experience severe pain in the affected spinal area and the region where the nerves are affected. Additionally, disc herniation can cause numbness or tingling in the upper or lower extremities, muscle weakness, and difficulty controlling movement.
Clinical examination and the patient’s medical history are the first two steps in diagnosing disc herniation and assessing its impact on nerves. In some cases, diagnosis may require additional tests such as X-rays, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or natural spinal processes.
It is essential to treat nerve-impacting disc herniation appropriately and in a timely manner. Treatment may include addressing muscle and nerve pain, assisting in strengthening muscles and improving flexibility, and applying therapeutic exercise techniques to alleviate tension and promote relaxation.
In general, disc herniation affects nerves by directly or indirectly compressing them or their proximity to the spinal discs. Understanding the symptoms and obtaining a proper clinical diagnosis are fundamental to determining the necessary treatment to alleviate disc herniation pain and improve the function of the affected nerves.
Does Lumbar Disc Herniation Affect the Knee?
The lumbar spine and the knee are crucial parts of the body, with the lumbar spine supporting the vertebral column and facilitating body movement, while the knee bears weight and enables lower body movement. However, some may wonder whether lumbar disc herniation affects the knee’s health.
Lumbar disc herniation in the lower back occurs when the disc between the lumbar vertebrae deviates from its normal position. This can happen due to severe pressure on the lumbar disc or as a result of general deterioration in the lower back. When lumbar disc herniation occurs, it can lead to nerve irritation, causing lower back pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs and feet.
Although lumbar disc herniation can cause negative effects on the lower back and legs, it typically does not directly affect the knee. The knee acts as a shock absorber between the thighs and lower legs and is designed to bear weight and absorb shocks. Therefore, the pain and numbness resulting from lumbar disc herniation may not significantly impact the knee’s health.
However, it is crucial to diagnose and treat lumbar disc herniation correctly to avoid the development of problems and worsening of symptoms. Individuals with lumbar disc herniation may need some physical therapy and medical treatments to strengthen the lower back and alleviate pain.
In general, there is a connection between the lower back and the knee concerning the overall movement and balance of the body. Therefore, severe lower back pain can indirectly affect a person’s ability to move correctly and perform daily activities smoothly, which may indirectly impact knee health. It is essential to address lumbar disc herniation comprehensively and consult a specialized physician to create an appropriate treatment plan to maintain the health of both the lower back and knee.
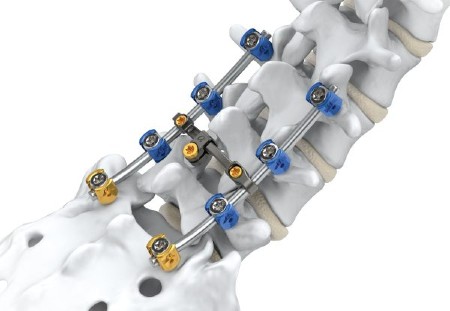
The Best Doctor for Minimally Invasive Herniated Disc Surgery
Minimally invasive herniated disc surgery is a highly significant surgical procedure for treating spinal problems. In this field, Dr. Amr Amal is considered one of the best specialized doctors. He combines extensive experience with exceptional skills in performing this sensitive procedure. Here is a list of reasons that make Dr. Amr Amal the top choice for minimally invasive herniated disc surgery:
Outstanding Experience: With years of practice in spinal surgery, Dr. Amr Amal ranks among the most experienced surgeons in performing minimally invasive herniated disc surgeries. His extensive experience allows him to handle various complex cases with ease and vigilance.
Advanced Surgical Techniques: Dr. Amr Amal follows an advanced and modern approach to performing minimally invasive herniated disc surgeries. He utilizes the latest techniques and the best available tools to achieve outstanding results. He relies on endoscopy to precisely access and visualize the affected disc.
Patient-Centric Care: Dr. Amr Amal is renowned for his courteous patient care and personal attention to patients. He fully understands the impact of pain and psychological stress on patients and strives to alleviate them. He provides psychological support before and after surgery and offers clear guidance to patients on necessary preparations and post-surgery expectations.
Communication and Transparency: Dr. Amr Amal focuses on providing comprehensive and transparent answers to patients’ questions regarding the procedure and potential effects of minimally invasive herniated disc surgery. He communicates sincerely with patients and explains in detail the steps to be taken during surgery and what to expect afterward.
Success and Rapid Recovery: Dr. Amr Amal is committed to ensuring the highest success rates for minimally invasive herniated disc surgery and the shortest recovery periods. He employs techniques to avoid major incisions and works towards achieving rapid recovery and a quick return to normal life.
In summary, Dr. Amr Amal is considered one of the best doctors for minimally invasive herniated disc surgery. He stands out with his extensive experience, advanced execution, and personalized patient care, ensuring excellent results and swift recovery.