What Is a Shoulder Joint Injection? And How Long Does the Treatment Take?
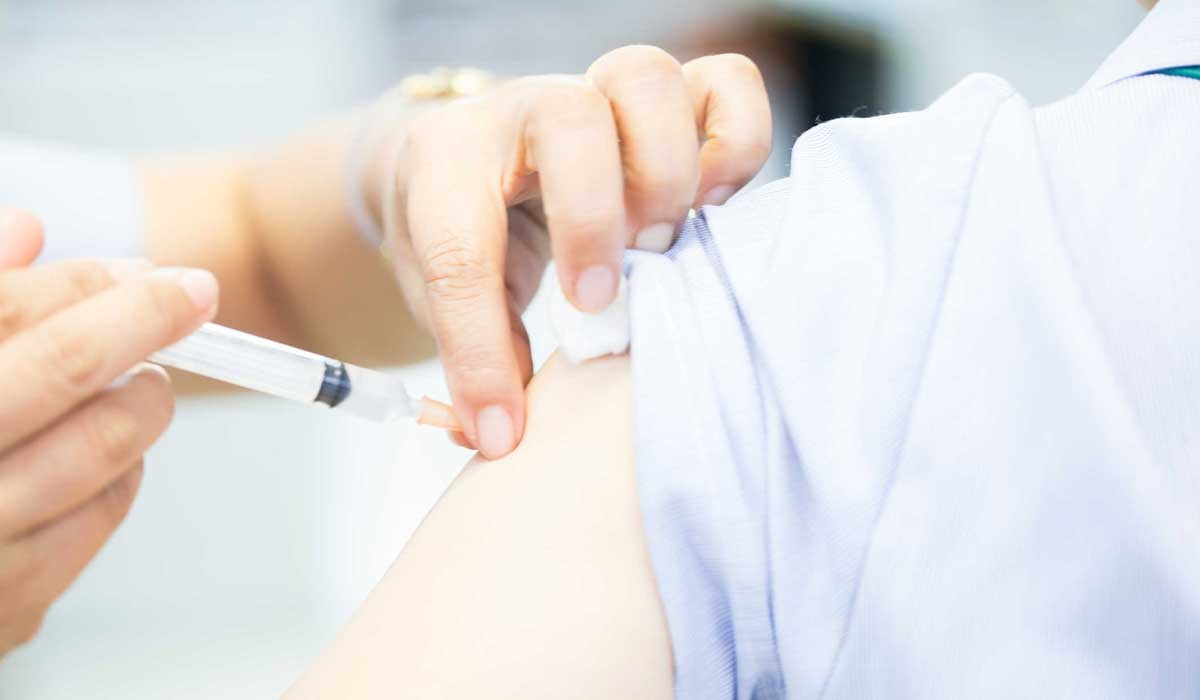
Shoulder Joint Injection
A shoulder joint injection may be one of the options offered by doctors to treat certain health issues in this important joint. This injection can be beneficial in cases such as tendonitis, joint pain, or restoring joint mobility due to various factors like injury or wear and tear. In this article, we will provide an overview of shoulder joint injections, how they are administered, and what to expect from them.
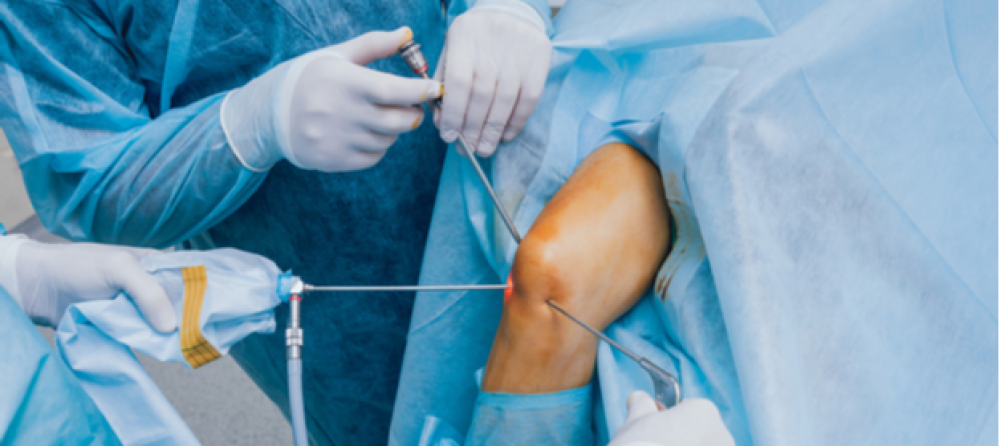
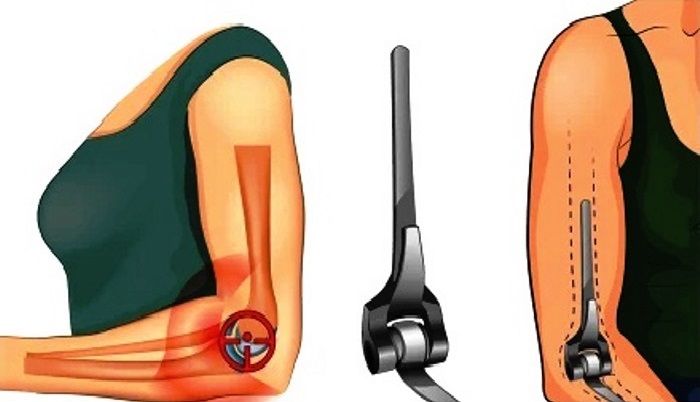
- What Is a Shoulder Joint Injection? A shoulder joint injection is a medical procedure in which an anti-inflammatory medication is injected directly into the joint. This injection is typically performed in an operating room under the supervision of a specialist physician. A guidance system is used to help the doctor accurately direct the needle into the joint.
- When Is a Shoulder Joint Injection Given? The prescription of a shoulder joint injection depends on the patient’s condition and individual symptoms. This injection can be helpful in several conditions, including:
Tendonitis: Shoulder joint injections may be beneficial for conditions like chronic rotator cuff tendonitis. Joint Pain: Localized injections can be used to relieve pain in the shoulder joint. Restoring Joint Mobility: Injections may assist in regaining joint mobility following injury or degeneration.
- How Is a Shoulder Joint Injection Administered? A shoulder joint injection should be administered by a qualified physician under medical supervision. The needle is placed into the joint after applying local anesthesia. X-ray or computed tomography (CT) scan-guided techniques can be used to precisely direct the needle to the correct location in the joint. After the injection, a bandage or ice application may continue to reduce swelling and alleviate pain.
- What Are the Potential Complications of a Shoulder Joint Injection? Although a shoulder joint injection is often considered a safe and effective procedure, some rare complications may occur. These complications may include:
Infection in the joint. Bleeding within the joint. Difficulty breathing or swelling in the neck and face (relatively rare complications).
- Post-Injection Shoulder Joint Guidelines
After receiving the injection, the doctor may provide the patient with some guidelines to achieve the best treatment outcomes. The patient may be advised to apply a compression bandage for a specific period after the injection. Additionally, the patient may be instructed to avoid strenuous activities and exposure to cold.
Shoulder joint injection is a medical procedure that can be effective in treating certain joint problems. This procedure is generally safe and should be performed by a qualified medical professional. Before undergoing any medical procedure, it is important for the patient to consult with a specialist and discuss the potential benefits and risks.
How long does shoulder joint treatment take?
Shoulder joint injuries are common and can cause pain and restricted shoulder movement. When diagnosed with a shoulder joint issue, many people wonder how long the treatment will take for the joint to heal and normal shoulder function to return. In this article, we will provide important information about the duration of treatment for shoulder joint issues.
Initial Treatment Phase: When a shoulder joint injury is diagnosed, the initial treatment involves reducing inflammation and alleviating pain. Treatment may include applying ice to the affected area and taking pain-relieving medications as directed by the doctor. This phase typically lasts for 2-3 weeks, depending on the severity of the injury.
Surgical Phase: In some cases, doctors may recommend arthroscopic surgery for optimal treatment of the damaged shoulder joint. During this surgery, adhesions in the joint are removed, and any existing damage is corrected. It is essential to follow the necessary recovery period after surgery, which is expected to last for about two months.
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy Phase: After surgery, the patient needs to start the rehabilitation and physical therapy phase to regain shoulder movement and strengthen the surrounding muscles. Physical therapy may include motion exercises and muscle-strengthening exercises, along with manual therapy sessions. This phase typically lasts from 4 to 12 months, depending on the complexity of the condition and the joint’s mobility.
Recovery Phase: As the condition improves, and shoulder pain diminishes, the patient enters the recovery phase. During this stage, shoulder movement becomes more extensive, and overall joint function improves. Doctors emphasize that this phase may vary in duration among individuals and depends on the extent of joint disruptions.
With the progression of treatment and rehabilitation, as well as following the recommendations of doctors and specialists, patients can expect a gradual improvement in their condition. However, it’s important to be prepared for variable recovery times and the potential need for ongoing treatment and self-care to prevent re-injury.
It’s worth noting that shoulder joint treatment requires patience and commitment to the recommended treatment plan by healthcare professionals. Patients should consult orthopedic and sports medicine specialists for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Recovery from a shoulder joint issue may take time, but it is certainly worth the effort to regain shoulder health and function.
What is the treatment for shoulder muscle stiffness?
Shoulder muscles are among the most important muscles in the body, playing a crucial role in moving the arm and supporting the shoulder. However, problems and disorders can arise in these muscles, such as shoulder muscle stiffness, which can cause difficulty and pain when lifting and moving the arm.
Shoulder muscle stiffness is a condition characterized by the stiffening and tightening of the shoulder muscles, resulting in reduced flexibility and natural movement. This stiffness can occur due to various reasons, such as injury to the shoulder ligaments or the cartilage surrounding the shoulder joint. If shoulder muscle stiffness is not properly treated, it can lead to worsening of the condition and increased pain and muscle spasms.
There are several ways to treat shoulder muscle stiffness, which we will outline in this article:
Non-Surgical Treatment: Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy is considered an effective method for treating shoulder muscle stiffness. It involves using a scope to remove fibrous tissues and repair damaged ligaments. Afterward, the patient continues with physical therapy until their health improves. Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is one of the fundamental treatments for improving shoulder muscle stiffness. It includes various exercises and techniques that help reduce pain and restore normal shoulder joint movement. Among these exercises, regular shoulder-specific exercises can be practiced to strengthen the shoulder muscles and reduce the risk of injury. Medication: In some cases, the doctor may prescribe pain-relieving medications to alleviate pain and reduce accompanying inflammation associated with shoulder muscle stiffness.
Surgical Treatment: If the patient’s condition does not improve after non-surgical treatment, surgical treatment may be recommended as a last resort. Surgery is considered the final solution for cases of shoulder muscle stiffness, where the shoulder joint is used to repair damaged tissues and ligaments and restore normal shoulder movement. Recovery from surgery may take some time, and the patient may need to return to physical therapy to expedite the recovery process.
It is important to note that treatment depends on the individual patient’s condition and may vary from person to person. Therefore, it is recommended to visit a specialized doctor to diagnose the patient’s condition and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
In conclusion, caution should be exercised, and medical instructions should be followed carefully during the treatment of shoulder muscle stiffness. Regular practice of shoulder muscle-strengthening exercises may help prevent this condition and reduce the risk of injury.
What Are the Risks of Cortisone Injections in the Shoulder?
Cortisone injections in the shoulder are commonly used to treat a variety of conditions related to tendon inflammation and the surrounding bones. However, this treatment can expose your body to some risks, especially when overused. In this article, we will outline some potential risks of cortisone injections in the shoulder.
Muscle Weakness and Tissue Damage: Cortisone injections in the shoulder may affect muscle tissues, leading to long-term weakness and damage. These damages can result in muscle weakness and heart function failure if the prescribed cortisone dosage is exceeded.
Increased Risk of Tendonitis and Frozen Shoulder: Excessive use of cortisone in the shoulder can be a potential factor for tendonitis and frozen shoulder. Tendonitis and frozen shoulder can occur after shoulder surgery or a broken arm.
Calcium Deposits: Calcium may accumulate in the shoulder joint area if tendon inflammation persists for a long time. Patients may experience stiffness, weakness in the shoulder, as well as pain, cracking sounds, or a feeling of grittiness when moving the shoulder.
Other Side Effects: Some other side effects may occur after cortisone injections in the shoulder, such as increased pain, redness, and swelling in the injected shoulder. Some individuals may also experience elevated blood pressure or cholesterol levels after cortisone injections.
Exercise Caution:
There are potential risks associated with cortisone injections in the shoulder, so it is advisable to consult a doctor and evaluate the benefits of treatment versus the potential risks. The prescribed dosage should not be exceeded, and the doctor’s instructions should be followed strictly. Doctors may recommend alternative treatment options if they deem cortisone injections inappropriate for your specific condition.
Staying informed about the latest developments in research and care methods is essential. Patients are encouraged to consult qualified and specialized doctors before making any treatment decisions.
How Are Cortisone Injections in the Shoulder Administered?
Cortisone injections in the shoulder can be a beneficial medical procedure for many people suffering from pain and inflammation in this sensitive joint. It is important to know how doctors administer these therapeutic injections in the shoulder to provide relief and alleviate symptoms.
Preparing for the Procedure: Before cortisone injections in the shoulder are administered, doctors undertake necessary preparations. They identify the precise location of the joint that requires treatment and use imaging, such as X-rays, to help them determine the best point for needle insertion.
Local Anesthesia: Doctors often use local anesthesia on the skin and the tissues surrounding the targeted joint to alleviate pain. This is done by injecting a numbing solution above or adjacent to the target site.
Guided Visualization: Using X-rays or CT scans, the doctor guides a thin, long needle to the targeted joint. This helps them precisely control the needle’s placement and smoothly deliver the cortisone injection.
Cortisone Injection: Once the correct needle position is achieved, the doctor administers the cortisone into the joint by gently pushing the treated solution inside.
Needle Removal: After completing the injection, the doctor removes the needle. They may apply a bandage or adhesive to cover the injection site, and the nature of the covering depends on the treating physician’s instructions.
Post-Procedure Care: After cortisone injections in the shoulder, the patient may experience some temporary pain or discomfort in the joint. The doctor may recommend taking pain relievers to alleviate the symptoms. Additionally, the patient may need to limit the use of the treated joint for a short period to allow the cortisone to take effect.
Follow-Up Treatment: Following cortisone injections in the shoulder, the doctor will schedule appropriate follow-up appointments. This is aimed at monitoring the treatment’s effectiveness and evaluating symptom improvement and comfort. The procedure may be repeated if necessary based on the body’s response to the initial injections. Cortisone injections in the shoulder are a medical procedure that requires significant expertise and skill from the treating physician. By utilizing radiographically guided techniques and determining the correct needle placement, significant improvement in shoulder pain and inflammation-related symptoms can be achieved. Patients should receive cortisone injections as part of a comprehensive treatment plan prescribed by a specialized doctor.
How Long Does Cortisone Injection Last in the Body?
Among the many health problems that may warrant cortisone injections, the use of this type of injection is widespread for treating conditions ranging from arthritis to tendonitis. A cortisone injection can alleviate pain, reduce inflammation in the body, and promote healing. However, many people wonder how long the effects of a cortisone injection last in the body.
When Does the Effect of Cortisone Injection Start?
In general, the effects of cortisone take about five days to become noticeable. While it may take a few days or longer for the effects of cortisone to start taking place, many patients report immediate improvement after the injection. This could be due to the immediate pain relief provided by the injection. When Does the Effect of Cortisone Injection End? After the injection, the effects of cortisone typically last anywhere from a few minutes or hours to a maximum of seven days. However, it’s important to note that the duration of cortisone’s effects on an individual can vary depending on the condition, dosage, and injection site. In some cases, the effects may last for weeks or even months. Factors Affecting the Duration of Cortisone Injection:
- Type of Health Issue: Some conditions, such as chronic arthritis or tendonitis, may require multiple doses of cortisone to achieve the desired improvement. In these cases, the effects of cortisone may last longer.
- Number of Injections: The number of injections received can also affect the duration of cortisone’s effects. Sometimes, patients may need to receive multiple injections over a specific period to effectively alleviate symptoms. In such cases, the duration of cortisone’s effects may vary from one injection to another based on the number of injections used.
The duration of cortisone injection effects can range from a few minutes or hours to more than a week. However, there is no set timeframe for everyone, as the duration can be longer in some cases depending on the health issue, dosage, and number of injections used. It’s advisable to consult with the treating physician to determine the duration of cortisone injection effects in your specific case and to determine the appropriate dosage and number of injections.
What Are the Side Effects of Cortisone Injections?
- Pain at the Injection Site: You may experience pain at the site of the cortisone injection, a phenomenon known as “cortisone flare.” This pain may last for a few hours or a few days and may be accompanied by redness and swelling.
- Appearance of Bruises or Pimples: Among the side effects of cortisone injections are the appearance of bruises or pimples at the injection site. This can occur as a result of the direct effect on blood vessels in the surrounding area.
- Change in Skin Color and Pallor: After a cortisone injection, you may notice a change in skin color around the injection site, with the skin becoming paler and showing changes in color. This is due to the drug’s effect on melanin in the skin.
- Risks of Cortisone Injections: The risks of cortisone injections include adrenal gland insufficiency, which occurs due to the suppression of natural cortisol production by the adrenal glands, leading to the need for synthetic cortisone replacement. It can also cause an abnormally high heart rate, swelling in different areas of the body, and other side effects.
- Other Side Effects: Some patients may experience warmth in the chest and face, along with redness, after receiving a cortisone dose. It can also cause stomach irritation with the development of gastric ulcers, weight gain, and mood changes such as depression or anxiety.
It’s important to note that the above-mentioned side effects of cortisone injections are common and transient, usually resolving after a short period. However, there are some rare and serious side effects that individuals planning to receive cortisone injections should be aware of and should follow up with their treating physician.
The benefits of cortisone injections are numerous in the treatment of various chronic conditions and inflammations, but they should be taken under the supervision of a specialist and according to prescribed dosages to minimize the occurrence of side effects and potential complications.
When Does the Effect of Cortisone Injection in the Shoulder Begin?
Cortisone injections are a common solution for treating inflammation in the shoulder, but when does their effect start, and when does it end? In this article, we will provide an overview of the duration of cortisone’s effect in the shoulder and the factors that may influence it.
When Does the Effect of Cortisone Injection Begin?
Generally, the effects of cortisone take about five days to become noticeable, but this depends on the individual’s condition and the nature of the inflammation.
When cortisone is injected into the shoulder, the medication is delivered directly to the inflamed area. Cortisone works to reduce swelling and inflammation in the surrounding tissues of the joint, which helps alleviate pain and improve shoulder movement.
While the effect of cortisone injection may start within a few days, some individuals may feel improvement more quickly, while others may take longer to notice any changes.
When Does the Effect of Cortisone Injection End?
Typically, the effect of cortisone injection in the shoulder lasts for a limited period. This can vary from person to person and depends on the type of inflammation and individual characteristics.
In general, the effect of cortisone injection in the shoulder can last anywhere from weeks to several months. Some individuals may experience continuous improvement during this period, while others may find that their symptoms return after some time.
Regardless of the duration of the injection’s effect, it is usually recommended to take rest and avoid strenuous activities that may exacerbate the inflammation. After a cortisone injection, some individuals may experience relief lasting for weeks when treating conditions like shoulder and knee inflammation.
These pieces of information should not serve as a substitute for consulting with a specialist. It is always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to assess your specific condition and the expected duration of the cortisone injection’s effect in your case.
How Long Does the Treatment for Shoulder Tendonitis Take?
Shoulder tendonitis is a common injury experienced by many individuals. Tendons can become inflamed due to partial or complete tears in the tendons in the rotator cuff area or the biceps tendon. If you are dealing with this condition, you may be wondering about the duration of symptom relief and effective treatment.
In this article, we will provide some information on how long it takes to alleviate the symptoms of shoulder tendonitis and effectively treat it. Keep in mind that there are various influencing factors in each case, and it’s essential to seek specialized medical advice and consult with an orthopedic or sports medicine physician to assess your personal condition.
Before beginning treatment, you may need a precise diagnosis to determine the cause of the pain and the possibility of tendon tears or inflammation. It is crucial to obtain specialized medical advice and consult with an orthopedic or sports medicine physician to evaluate your condition and guide you to the appropriate treatment.
Initial Treatments:
Doctors initially recommend primary treatments to reduce symptoms and expedite recovery. These may include:
- Using ice packs to reduce swelling and inflammation. Apply ice to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day.
- Taking aspirin or ibuprofen, which work to relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
Physical Therapy:
The doctor may also recommend physical therapy sessions to strengthen and stabilize the muscles surrounding the shoulder, increase shoulder range of motion, and improve balance and stability. Physical therapy often includes rehabilitation exercises, warm-up and stretching techniques, as well as massage and heat therapy.
Medication:
If symptoms do not improve with primary treatments and physical therapy, a specialized physician may prescribe different medications to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. These medications may include pain relievers containing aspirin or ibuprofen, which may require a prescription.
Surgery:
In cases of severe tendon tears or when other treatments do not yield improvement, surgery may be the last resort. The type of surgery depends on the condition of the tendons and the severity of the tear, and patients typically require a recovery period ranging from several weeks to several months.
Recovery Period:
The recovery period varies from case to case and depends on the severity of the injury and the patient’s adherence to treatment and prescribed exercises. In general, patients typically fully recover within two to four weeks from the start of treatment, but complete recovery may take longer in some cases.
Can Shoulder Tendonitis Be Prevented?
To prevent shoulder tendonitis, you can follow some preventive measures, including:
- Exercising correctly and under the guidance of a qualified trainer.
- Regularly training and strengthening the muscles surrounding the shoulder.
- Avoiding improper heavy lifting techniques.
- Being cautious of sudden movements and excessive stress on the shoulder.
- Using supportive pillows when sitting or sleeping to reduce pressure on the shoulder.
It is essential to consult a doctor before starting any treatment or preventive program to assess individual conditions and ensure necessary steps. Always remember that prevention is better than cure, and preserving the health of tendons and shoulders from injuries is the most important thing.