How do you know if you have a herniated disc? And does it heal on its own?
How do you know if you have a herniated disc?
To determine if you have a herniated disc, you would typically look out for certain symptoms. These may include:
- Pain that radiates to your arms or legs.
- Increased pain when bending or twisting.
- Pain that worsens after sitting or standing for long periods.
- Unexplained muscle weakness.
- Tingling, aching, or burning sensations in the affected area.
As for self-healing, some herniated discs may indeed heal on their own over time. The body can initiate a healing response, and symptoms can improve through a combination of rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy. However, the healing process is different for each individual and some cases may require more intervention, including medical procedures or surgery. It is essential to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
How do you know if you have a herniated disc?
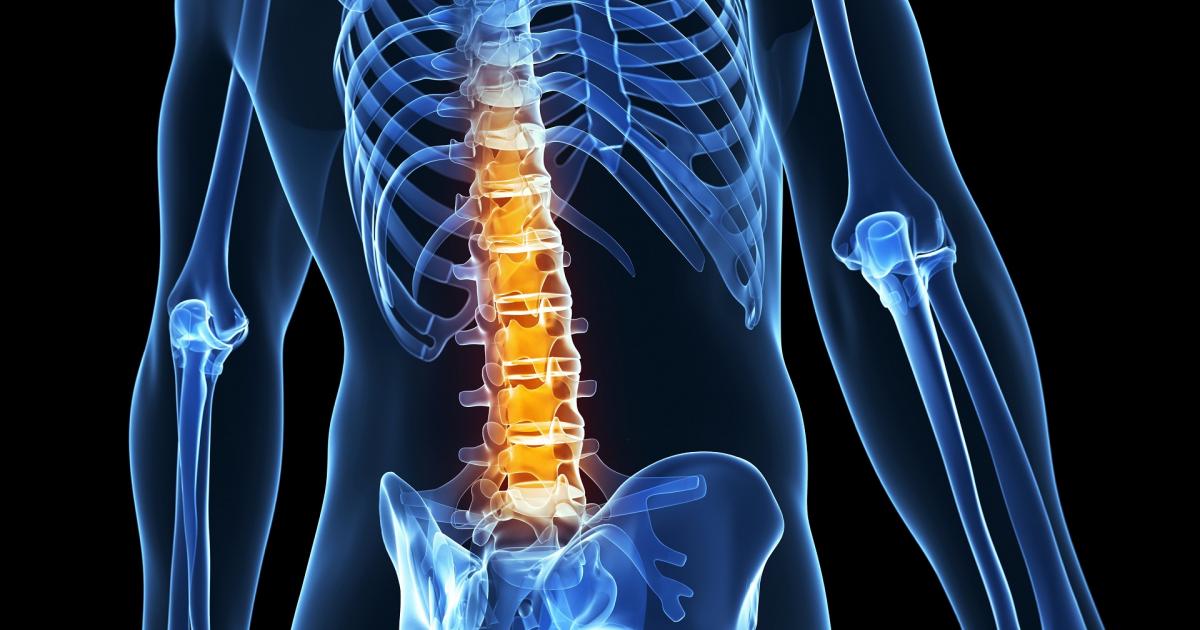
A herniated disc is a condition that occurs when the disc, which acts as a shock absorber between the vertebrae in the spine, slips out of its normal place. This slippage can result from excessive pressure on the spine or due to an injury or tear in the disc. A herniated disc can lead to vertebrae compression and pressure on the nerves, causing multiple health problems.
Here are some symptoms that may indicate you have a herniated disc:
- Back pain: You may experience persistent pain in the back area, especially in the lower part of the spine.
- Numbness or tingling in the legs: You may feel numbness or tingling in your legs due to pressure on the nerves in the spine.
- Difficulty moving: You might find it difficult to move or experience stiffness in your legs, due to the effect of the herniated disc on the normal functioning of the muscles and nerves.
- Pain in the buttocks and thigh: If the herniated disc is in the lower part of the spine, you may feel pain in the buttocks and thigh.
- Pain when moving: You may feel pain when performing certain movements, such as bending, kneeling, or sitting for long periods.
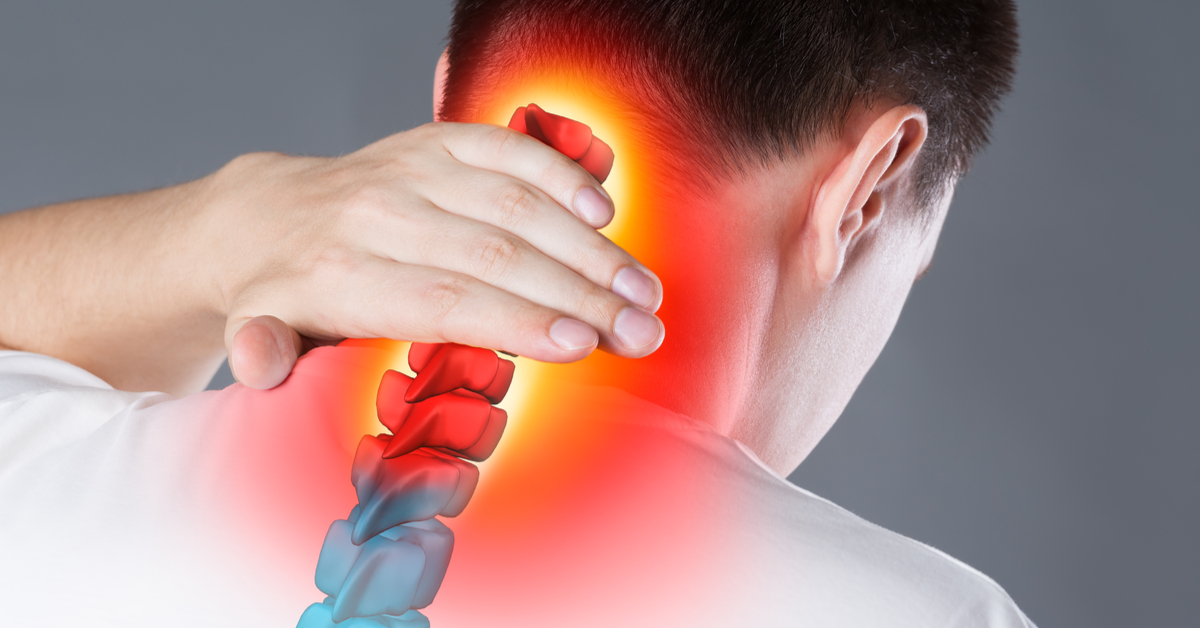
- Numbness or tingling in the upper limbs: If the herniated disc is in the neck area, you might feel numbness or tingling in the arms and hands.
- Muscle weakness: You may experience weakness in the muscles served by the affected nerves, which affects your ability to lift or carry objects.
- Difficulty controlling bladder function: A herniated disc can affect bladder function, causing difficulty in controlling urination and frequent visits to the bathroom.
To prevent herniated discs, some preventive measures can be followed. Among these measures:
- Regular and proper exercise, especially exercises that strengthen the back and abdominal muscles.
- Maintaining a healthy weight, avoiding obesity which puts extra pressure on the spine.
- Sitting properly and using appropriate back supports to support the spine.
- Avoiding sitting for long periods without movement, and doing stretching and muscle strengthening exercises.
- Avoiding heavy lifting and following correct lifting and carrying techniques.
- Maintaining a good posture while sleeping, and using suitable pillows to support the spine.
- Getting enough rest and good sleep.
In conclusion, people who suffer from symptoms similar to those of a herniated disc should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Treatment can include physical therapy, muscle strengthening, medication, and in some severe cases, surgery may be necessary.
Is a herniated disc a serious condition?
A herniated disc is a condition in which the soft cartilage that sits between the vertebrae in the spinal column protrudes out. Although it is not considered a serious illness in itself, it can lead to serious complications if not treated correctly.
Among the serious complications that can occur as a result of untreated herniated discs is permanent nerve damage. A herniated disc can put pressure on the nerves in the spinal column, causing pain and a burning sensation in the extremities of the body. If this nerve pressure is not treated, permanent nerve damage can occur, and it becomes difficult to recover normal neural functions.
Additionally, a herniated disc can lead to other repercussions such as muscle spasms and loss of sensation in the affected part of the body. This can affect the ability to move and perform daily activities normally.
Therefore, it is necessary for a herniated disc to be treated correctly to avoid these serious complications. Patients should start early treatment and follow the appropriate medical guidance.
In addition to conventional medical treatment, there are some measures that can be taken to prevent a herniated disc and reduce the risk of its occurrence. It is advised to maintain a healthy body posture when standing and sitting, and avoid wearing high heels. Also, one can regularly perform stretching exercises, especially after sitting for long periods. People should avoid lifting objects improperly and ensure bending their knees and keeping their back straight while doing so.
Furthermore, it is recommended to practice some physical exercises that strengthen the back and legs. These exercises include swimming, walking, and cycling. Such exercises can enhance muscle strength and improve the flexibility of the spine, which reduces the risk of a herniated disc.
In conclusion, a herniated disc is not a serious disease in itself, but it can lead to serious complications if not treated properly. Therefore, people should start early treatment and follow the right medical advice to avoid these complications and maintain the health of the spine.
Does a herniated disc heal on its own?
A herniated disc is a common condition that affects many people around the world. When someone is diagnosed with a herniated disc, the first question that comes to mind is whether it can heal on its own or not.
Unfortunately, complete recovery from a herniated disc is very rare. A herniated disc occurs when the intervertebral disc, which acts as a cushion between the vertebrae in the spine, is damaged. When the intervertebral disc undergoes excessive pressure or stress, it can slip out of place and press on surrounding nerves, causing pain, swelling, and numbness.
In mild cases, a herniated disc may heal over time on its own. Symptoms can improve and disappear gradually without the need for special treatment. However, in many cases, a herniated disc can be painful and bothersome and requires proper treatment and care.
Many treatments are available to alleviate the symptoms of a herniated disc. Non-surgical treatment may include taking pain relief medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Massage and physical therapy can also be used to relieve pain and improve movement and flexibility.
In more advanced cases or severe pain, surgical treatment may be necessary. Surgical treatment involves the removal of the affected part of the intervertebral disc or its replacement with an artificial disc. Surgery is considered a last resort and is used only in severe cases that cannot be managed by other treatments.
Generally, symptoms of a herniated disc can be alleviated and the quality of life improved by following a healthy and suitable lifestyle. It is advised to engage in exercises that strengthen the core muscles and improve the flexibility of the spine. It is also important to avoid heavy physical activities and excessive strain on the spine.
Thus, although a herniated disc does not usually heal by itself, symptoms can be controlled and pain can be relieved, improving the quality of life through necessary treatment and following a healthy lifestyle. It is important to consult a specialist doctor to evaluate each individual’s condition and determine the appropriate treatment.
What are the prohibited exercises for a herniated disc?
A herniated disc is a common condition that occurs when the cartilaginous disc between the spinal vertebrae moves and presses on the surrounding nerves. Many people suffer from this condition and look for ways to relieve pain and improve their health. One effective way to treat a herniated disc is to engage in appropriate exercises. However, there are some exercises that should be avoided to prevent exacerbating symptoms and further injury. In this article, we will look at the exercises prohibited for a herniated disc.
First and foremost, it must be mentioned that before starting any type of exercise or sports programs, it is necessary to consult a doctor or medical specialist before performing any exercise. An experienced doctor will be best at providing appropriate advice and guiding you towards the most suitable exercises for your health condition.
Among the exercises prohibited for a herniated disc are those that require strong bends and twists of the spine. For example, avoid lifting heavy weights or engaging in high-impact exercises like heavy squats and exercises that require deep back bends. These exercises may increase pressure on the spine and lead to the worsening of symptoms and further injury.
Exercises that require strong and sudden movements like jumping and sprinting should also be avoided. These exercises cause a significant shock to the spine and put extra pressure on the damaged disc.
It is also advisable to avoid exercises that require strong forward bending such as toe touching or sitting on the floor and trying to touch the toes. These exercises put significant pressure on the spine and cause irritation to the damaged nerves.
In general, any exercises that cause an increase in pain or exacerbate symptoms should be avoided. Exercises should be gentle and light on the spine and help in strengthening the muscles around it. A medical specialist can guide you towards the most appropriate exercises for your health condition and provide you with a customized exercise program to improve your condition.
In conclusion, we must mention that physiotherapy and exercise can be an effective way to deal with herniated discs. However, this should be done under the supervision of a medical specialist to avoid any problems or worsening of symptoms. Consult your doctor before starting any exercise program and ensure that you follow the correct guidelines to achieve the best results.
What is the difference between a herniated disc and sciatica?
A herniated disc and sciatica are two disorders that affect the back and leg, causing pain and numbness in these areas. Although the symptoms may sometimes be similar, there are clear differences between the two conditions.
A herniated disc, also known as a disc, is the protrusion of the gel-like fluid inside the spinal discs. This occurs when the gelatinous cartilage separates from its natural place and presses on the surrounding nerves. A herniated disc causes sharp pain in the back area and can extend this pain to the leg. A herniated disc can develop into sciatica, but not the other way around.
Sciatica, on the other hand, is typically used to describe pain felt by a person in the lower back and spreading to the leg. The most common cause of sciatica might be a herniated disc that presses on the sciatic nerve root. However, sciatica can have other causes such as inflammation of the sciatic nerve or compression of the sciatic nerve by tumors or spinal stenosis.
The symptoms of a herniated disc and sciatica are quite similar, which makes correct diagnosis difficult sometimes. The affected person may feel a sharp pain in the back and leg area, and there may be numbness and tingling in the leg and foot. The pain may develop or worsen when sitting for long periods or when making certain movements like bending or kneeling.
It is essential that the condition is diagnosed by a specialist doctor, by inquiring about the patient’s medical history and conducting a comprehensive examination of the back and nerves. Additional examinations such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging may also be required to determine the extent of damage to the spine and nerves.
For the treatment of a herniated disc, this may involve physiotherapy and strengthening the muscles around the back and leg, in addition to taking pain-relieving medications. In more advanced cases or when other treatments do not respond, surgery may be necessary to remove the damaged part of the disc.
As for the treatment of sciatica, it depends on the cause of the condition. If the cause is a herniated disc, it may be treated using the same methods used for treating a herniated disc. It may also require pain-relieving medications and preventive measures such as avoiding heavy loads and maintaining good posture while sitting and sleeping.
Overall, people who suffer from pain in the back and leg should consult a doctor to get an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The treatment may be multi-faceted and may include physiotherapy, medication, sports exercises, and in some cases, surgery.
Can a herniated disc lead to paralysis?
A herniated disc is a condition that occurs when the intervertebral disc, located between the vertebrae in the spinal column, slips out of place. This slippage may be due to excessive pressure on the disc or damage to it. Although a herniated disc can cause severe pain and numbness in the limbs, it rarely leads to paralysis.
The most common symptoms of a herniated disc occur in the neck and back. In the case of a herniated disc in the neck, the patient may experience sharp pain in the neck that extends to the shoulder, stiffness of the neck muscles, and restricted movement. The pain may increase when bending the neck or during sneezing or coughing. In the case of a herniated disc in the back, the patient may feel pain in the lower back that extends to one or both legs, which may be accompanied by numbness and tingling.
Although a herniated disc can be painful and cause a restriction in the movement of the spine, it rarely leads to paralysis. In the case of paralysis, a person loses the ability to move or properly use the muscles. Although a herniated disc can cause muscle weakness and numbness in the limbs, it rarely leads to a loss of the ability to walk or move.
However, patients who suffer from severe symptoms of a herniated disc or symptoms that last for a long period should contact a doctor to evaluate their condition and guide them to the appropriate treatment. In some rare cases, surgical treatment may be necessary to remove the damaged part of the disc or to stabilize the vertebrae.
To prevent a herniated disc, some preventive measures can be followed. These measures include maintaining good body posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping, avoiding sitting for long periods, and doing exercises to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding lifting heavy objects improperly.
In general, patients should stay active and exercise regularly, avoid excessive strain on the spine, and visit the doctor regularly to examine the spine and detect any early problems that may occur.
Therefore, it can be said that a herniated disc rarely leads to paralysis, but it can cause pain and restriction in the movement of the spine. Patients who suffer from severe or persistent symptoms should communicate with a doctor to evaluate their condition and receive the appropriate treatment. Appropriate preventive measures should be followed to maintain the health of the spine and avoid a herniated disc.
Where does a herniated disc come from?
A herniated disc is a common condition that can affect the lower vertebrae of the spinal column. A herniated disc occurs when an intervertebral disc moves or slips out of its natural position. This slippage can put pressure on the spinal cord and surrounding nerves, causing symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the legs.
There are multiple causes of disc herniation, which may include:
Aging: Aging is one of the main factors that increase the risk of disc herniation, as the cartilage deteriorates over time. Stress and excessive pressure on the spine: Disc herniation may occur as a result of continuous stress on the spine, such as lifting heavy weights improperly or making sudden movements. Previous injuries: Exposure to prior spinal injuries may increase the risk of disc herniation. Genetic factors: Some people may be more prone to disc herniation due to genetic factors.
There are several methods for treating disc herniation in the lower vertebrae, which include:
Conservative treatment: Conservative treatment involves avoiding activities that exacerbate symptoms such as bending or lifting heavy objects. Pain relief medications can also be used to reduce pain and swelling. Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the spine and improve flexibility. This includes stretching exercises, muscle strengthening, and rehabilitation techniques. Injection therapy: The doctor may recommend a localized injection to alleviate pain and inflammation in the affected area. Surgery: If symptoms do not respond to conservative treatment and physical therapy, surgery may be the last option. Surgery involves removing the damaged disc and fusing the adjacent vertebrae.
It is important to consult a doctor if symptoms persist or worsen, as they can assess the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Does walking help in treating disc herniation?
Walking is a simple, low-impact activity that can have a significant impact on the health of the cartilage. Cartilage is an essential part of the musculoskeletal system and contributes to protecting the bones and absorbing shocks. Many people suffer from cartilage problems such as disc herniation, a condition that occurs when the cartilage moves away from its normal position in the spine. Can walking help in treating cartilage issues? This is the topic we will discuss in this article.
It is known that cartilage suffers from a lack of blood supply, which affects its ability to regenerate and heal. Some believe that walking can increase blood flow and oxygen to the cartilage, promoting healing processes and reducing pain. Some studies also suggest that walking can improve the flexibility of the cartilage and help restore its normal functions.
One of the main benefits of walking in treating cartilage is the reduction of pressure on the spine. When walking, weight is evenly distributed across the spine, reducing the pressure on the cartilage and decreasing the likelihood of disc herniation. In addition, walking helps strengthen the muscles around the spine, enhancing its stability and reducing the likelihood of cartilage tear.
In practical terms, walking should be done regularly and in moderation. It is preferable to start with a short duration and then gradually increase it. It is recommended to walk for 30-60 minutes daily at a moderate pace. Walking can be done outdoors or on a treadmill. Walking on hard or uneven surfaces should be avoided as it can increase the impact pressure on the cartilage.
In addition to walking, swimming, cycling, or other forms of exercise can have similar benefits for cartilage treatment. It is also important to maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can increase the pressure on the cartilage and exacerbate symptoms.
However, it is important to consult a doctor before starting any exercise program for cartilage treatment. The doctor should assess the overall health condition of the individual and provide guidance accordingly. It may be necessary to consult a physical therapist to develop a customized exercise program for cartilage treatment.
In conclusion, walking can be effective in treating cartilage and alleviating associated pain. However, it should be done correctly and under the supervision of a specialized doctor. The individual health condition and necessary precautions should also be considered to avoid any complications.
Can a herniated disc be treated without surgery?
A herniated disc, also known as disc herniation, is a common condition that causes pain in the lower back. This slippage occurs when the gel-like structure of the spinal disc breaks through a weak area in the outer wall. This slippage usually occurs due to disc degeneration, a natural process that can occur due to age-related issues and stress on the spine as one ages.
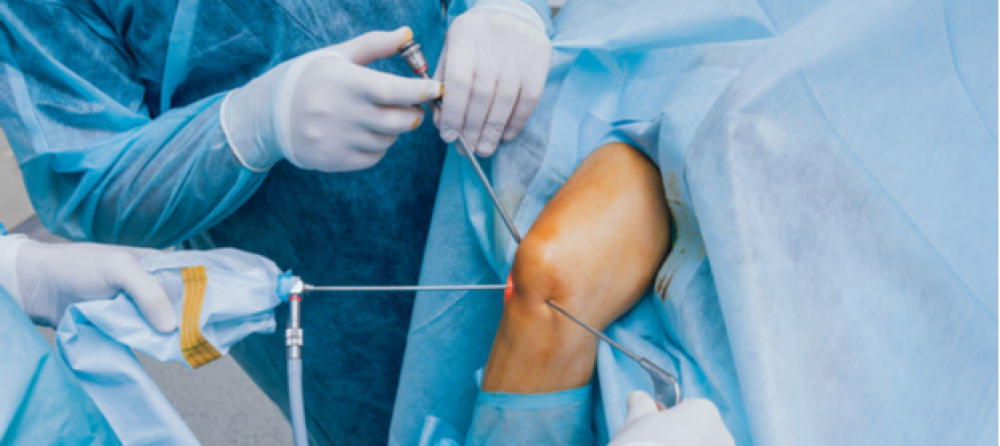
Before the advent of modern and advanced means of treating disc herniation such as interventional radiology and the concept of disc decompression, the patient had only two options: medical and physical therapy or surgery to remove the herniated disc.
Medical treatment and physical therapy are typically used to alleviate temporary pain and strengthen the muscles around the spine. Medical treatment includes taking pain relief and anti-inflammatory medications and using medical aids for mobility. Meanwhile, physical therapy includes physical rehabilitation exercises, muscle massage, and core muscle strengthening exercises.
Nonetheless, some doctors and physical therapists recommend certain home remedies for treating herniated discs without surgical intervention. For instance, warm compression can be used to relieve pain in muscles tense from an associated herniated disc. Warm compression helps to improve the elasticity of connective tissue and enhance blood circulation in the affected muscles. Warm compression should be used before performing any physical exercises. Additionally, cold packs can be used to alleviate pain.
However, it should be mentioned that medical and physical therapy does not cure herniated discs permanently but only serves to alleviate pain and strengthen the muscles. In some cases, surgical treatment may be the only solution to completely eliminate the herniated disc.
Treatment of herniated discs without surgery through disc decompression is another option that can be considered. In this procedure, the herniated disc material causing pain and pressure on the nerve is removed. However, accurate diagnosis of the condition must be made before resorting to this technique by using magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to locate the herniation and assess its size and impact on the nerve. After confirming the diagnosis, a decision to proceed with the operation is made.
In summary, there may be some home, medical, and physical treatments for treating herniated discs without surgery. Nevertheless, it must be understood that these treatments do not cure the herniated disc definitively, and surgical treatment may be the only solution in some cases. Patients should consult a specialist to evaluate their condition and choose the appropriate treatment.
Does a herniated disc progress?
A herniated disc is a condition that affects the spine and is considered one of the most prominent problems threatening young adults in the age stages between 18 and 40 years. A herniated disc results from continuous pressure on the vertebrae and the cartilage between them, due to weak muscles, excess weight, and incorrect movements such as bending or sitting improperly.
The degrees of a herniated disc are divided into five basic levels, and the methods of treatment and management vary according to the degree of herniation. In the first degree, there is a slight protrusion of the disc with weak effects on the nerve, and it can be treated with exercises to strengthen the back muscles only. In the second degree, there is weakening and stretching of the fibrous ring surrounding the disc, and its treatment also relies on therapeutic exercises to strengthen the back.
As for the question of whether a herniated disc progresses, the answer depends on the degree of herniation and the influencing factors. In the first and second cases, the herniation can be managed and symptoms can be reduced through non-surgical treatment and muscle strengthening exercises. In some cases, the herniation may improve spontaneously without the need for surgery.
However, in more advanced cases that involve third, fourth, and fifth degrees, surgery may be necessary. In these cases, the damaged part of the cartilage is removed, or repair of the surrounding fibrous ring is conducted. The need for surgery is determined based on the specialist physician’s assessment, the patient’s medical history, and the impact of the herniation on their daily life.
It is worth mentioning that a herniated disc may develop over time if not properly managed. The pressure on the vertebrae and cartilages may increase, leading to worsening symptoms and deterioration of the condition. Therefore, it is important to detect the herniation early and begin appropriate treatment to avoid negative progression.
In general, it can be said that the treatment of a herniated disc does not depend on surgery in all cases, but rather on the degree of herniation and its impact on the nerves and muscles. A specialist doctor should be consulted to evaluate the condition of the herniation and to direct appropriate treatment, whether it is non-surgical or surgical, with the aim of improving symptoms and enhancing the patient’s quality of life.
Is there a herniated disc without pain?
A herniated disc is a condition that affects the spine and causes pain in the lower back area, where one of the intervertebral discs slips forward. The main cause of disc herniation is usually damage to the intervertebral discs due to aging, the side effects of excessive load on the spine, or injuries resulting from accidents or sports activities.
However, a herniated disc can also occur without hereditary factors, meaning that anyone can suffer from this condition regardless of their age or physical activity. It is difficult to determine the specific causes of a herniated disc without hereditary factors, but the following factors may play a role in increasing the risk of its occurrence:
Age: With aging, intervertebral discs deteriorate and lose their elasticity, which increases the likelihood of herniation. Hereditary factors: Genetics may play a role in increasing the risk of disc herniation, where the intervertebral discs may have a weak or unhealthy composition making them more prone to damage and herniation. Excessive load: Frequently carrying heavy objects or engaging in activities that require excessive use of back muscles can increase the pressure on the intervertebral discs and increase the likelihood of herniation. Sports activities: Some sports that require excessive movements of the spine, such as weightlifting or jumping, may increase the risk of a herniated disc.
To prevent disc herniation and maintain the health of the spine, the following guidelines can be followed:
- Regular exercise in the correct ways, paying attention to strengthening the muscles of the back and abdomen and improving the body’s flexibility.
- Avoid excessively lifting heavy objects and use correct lifting and carrying techniques.
- Maintain good body posture while sitting and standing, providing necessary support for the spine.
- Avoid sports activities that increase spinal pressure and expose it to injury.
- Maintain a healthy weight and consume a balanced diet, as obesity may increase the pressure on the spine and increase the risk of disc herniation.
In conclusion, it is important to take care of spinal health and follow the above guidelines to prevent disc herniation. In the case of abnormal symptoms such as chronic back pain or bone deformities, it is imperative to consult a doctor immediately to obtain the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Best Doctor for Disc Herniation
Disc herniation is a common disease that affects the spine and requires specialized treatment to achieve excellent results in reducing symptoms and improving the quality of life of patients. Among the specialists in this field, Dr. Amr Amal stands out as one of the best doctors in Egypt for treating disc herniation.
Dr. Amr Amal is a consultant orthopedic surgeon specialized in treating disc herniation in Egypt. Dr. Amr enjoys an excellent reputation and a proven track record of success in performing this surgical procedure. Dr. Amr treats many spine-related issues, such as degenerative disorders, spinal stenosis, spinal curvature, and pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots.
Dr. Amr employs various therapeutic methods to treat disc herniation, ranging from medication and local injections to endoscopic surgery. Dr. Amr relies on the latest surgical techniques and advanced equipment to ensure the success of the surgery and the restoration of the normal function of the herniated disc. In addition to his extensive experience in disc herniation surgery, Dr. Amr Amal has broad knowledge in diagnosing and treating spinal diseases in general, making him an excellent choice for patients suffering from back and neck problems.
The cost of endoscopic disc herniation surgery in Egypt depends on several factors, including the patient’s condition, the advancement of the disease, and the required surgical intervention. It is important to consult with Dr. Amr Amal to assess your case and determine the appropriate cost.
In summary, Dr. Amr Amal is the best doctor for endoscopic disc herniation surgery in Egypt. He has an excellent reputation and a track record of success in this field. He uses the latest surgical techniques and advanced equipment to ensure the success of the operation and the restoration of the normal function of the herniated disc. He possesses extensive experience in diagnosing and treating spinal diseases in general. If you are suffering from issues with a herniated disc, it is recommended to consult with Dr. Amr Amal to receive the necessary treatment and restore the normal function of your spine.