Learn more about the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid disease is one of the most famous autoimmune diseases, which is more common in women than in men, and it has a set of symptoms that we talk about in detail in the following article.
You should first know what rheumatoid disease is, the causes that help a person get sick with the disease, and other detailed information about the disease, which are:
What is rheumatoid?
Rheumatoid arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis is one of the diseases that has spread widely, and it falls under immune diseases because the body, in the case of rheumatoid arthritis, attacks its own cells and destroys them, causing inflammation in one or more parts of the body.
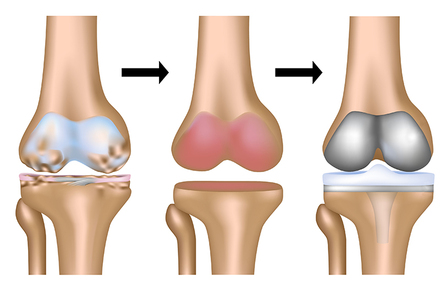
Rheumatoid arthritis usually affects the joints, and inflammation occurs in the protective cartilage and the synovial fluid surrounding the joint, which makes it erode and atrophy, and the rheumatoid patient suffers from pain in the joint towards infection, and bumps and deformities appear in it that are noticeable.
The rheumatoid disease damages the joints and infects them with severe tissue inflammation that results in joint pain and stiffness that leads to difficulty in movement and imbalance in a person’s steps. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect more than one organ in the body, including the eyes, heart, and kidneys.
Rheumatoid causes
Rheumatoid arthritis disease (rheumatoid) occurs to a person due to several factors, and there is more than one cause, including:
- Age group: In many kinds of research, it has been indicated that the elderly are more susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis due to weak immunity and also the presence of a defect in the joints.
- Gender of the person: Rheumatoid arthritis is more common than in men.
- Family history: The heredity factor can affect a person’s chances of developing rheumatoid arthritis, meaning that someone in the person’s family may be exposed to arthritis.
- Obesity: Being overweight is a risk factor that may affect a rheumatoid arthritis patient because it directly affects the joints and their health.
- Smoking: Smokers and those who come into contact with them are more likely to develop the rheumatoid disease.
Complications of rheumatoid disease
Neglecting the symptoms in cases of rheumatoid arthritis often leads to major complications, especially to the spread of the disease in more than one joint in the body, and we explain some of the complications that may occur to a rheumatoid patient when neglected:
- The patient may develop osteoporosis as a result of the increase in the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis without following appropriate medications.
- Erosion and deformity of the bones as a result of rheumatoid arthritis lead to hard, nodule-like bumps at the site of the injury.
- Sometimes a rheumatoid patient develops carpal tunnel syndrome as a result of pressure on the nerve in this part and affects the hand and fingers.
- If rheumatoid arthritis affects the lung, damage to the lung tissue is followed by major health problems such as difficulty breathing.
Rheumatoid symptoms
There is more than one symptom that appears in a patient with rheumatoid arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. It mostly affects the smaller joints in the body such as the fingers, followed by the larger joints such as the wrist and the knee. After that, rheumatoid arthritis may affect other organs of the body such as the kidneys, eyes, and lungs.
Doctors explained that the symptoms of the rheumatoid disease appear on the person as follows:
- pain in the joints.
- The appearance of swelling in the affected part.
- Feeling of stiffness in the joint, especially in the early morning.
- High body temperature and loss of appetite.
How to detect rheumatoid disease
Detecting and diagnosing rheumatoid disease may be difficult in the initial stages of the disease because the symptoms that a person feels are similar to other diseases, but there are some procedures that the doctor follows to diagnose a rheumatoid patient, which are:
- Clinical examinations
The doctor examines the initial symptoms that appear on the patient, such as pain in the joints and difficulty in moving them, especially when waking up, and there is a high temperature and general fatigue in the body. A rheumatoid patient may also develop redness and stiffness in the joints.
- Blood tests
The attending physician can ask the patient to do blood tests that show the rate of erythrocyte sedimentation, and there are other tests for rheumatoid factor, or to measure the level of C-reactive protein (CRP).
- Imaging examinations
The doctor can ask you to do an x-ray, which helps determine the condition of the joint affected by rheumatoid arthritis, and an MRI can also be used in order to know the condition of the body as a whole and its impact on the disease.
What are the rheumatoid symptoms?
The rheumatoid disease attacks the body slowly, starting from smaller joints such as the joints of the fingers, and some symptoms begin to appear in them, such as pain and mild swelling, especially in the morning period, and it increases in its spread in the body to reach larger joints such as the wrist and knee.
The severity of the symptoms increases slowly in the patient with rheumatoid arthritis gradually, and it may affect more than one joint at the same time, and the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis can begin as follows:
- The person begins to feel general pain in the body that may last for several weeks.
- The onset of a feeling of stiffness in the affected joint may last for up to an hour, especially in the morning.
- Mild swelling in the joint and difficulty in normal activities such as walking.
Early rheumatoid symptoms
Rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease that causes the body to attack its own cells, such as foreign bodies, and damage occurs. It has a number of early symptoms, which are:
- General stress: A rheumatoid patient may begin to feel excessively tired from daily exertion, which affects the performance of his activities in general.
- Fever: In cases of rheumatoid arthritis, a person may have a high fever and a feeling of fatigue as a natural reaction of the body to the inflammation in it.
- Body weakness: The person with rheumatoid arthritis gradually loses his appetite, his body begins to lose part of his weight, and he feels that he is unable to do his daily work normally.
- Stiffness: The patient may begin to feel stiffness in the joints when waking up, and it may last for more or less than an hour, and the joint will return to normal, and these symptoms may last more than 6 weeks.
Negative rheumatoid symptoms
Negative rheumatoid means that the result of the analysis of the rheumatoid factor was negative in the blood, but the doctors indicated that this does not mean that the person does not have rheumatoid arthritis because other factors are taken into account, including the patient’s clinical examinations, red blood cell sedimentation rate analyzes, and other procedures that doctors follow to accurately detect rheumatoid arthritis.
There are some symptoms that the doctor can check for in a negative (hidden) rheumatoid patient:
- The patient may suffer from pain in the joints, which may become more severe at times and less at other times.
- Swelling appears around the affected joint in the early morning hours when waking up and decreases during the day.
- The presence of visible redness on the skin surrounding the joints, accompanied by soreness when pressed.
- Difficulty moving the joint normally and pain when moving the joint from one position to another.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the hand
Rheumatoid arthritis can affect one or more joints in the body, and it usually begins at small joints such as the fingers of the hand and then moves to the wrist, and the onset of symptoms is as follows:
- The onset of pain in the joints of the hand, especially the fingers, whether right or left.
- The joint can begin to swell due to fluid pooling around it.
- Feeling hot when touching the joint and increasing redness around it.
- Difficulty fully bending the joints of the hand.
- The intensity of the pain varies from severe to mild.
- The appearance of deformation and bumps near the joint.
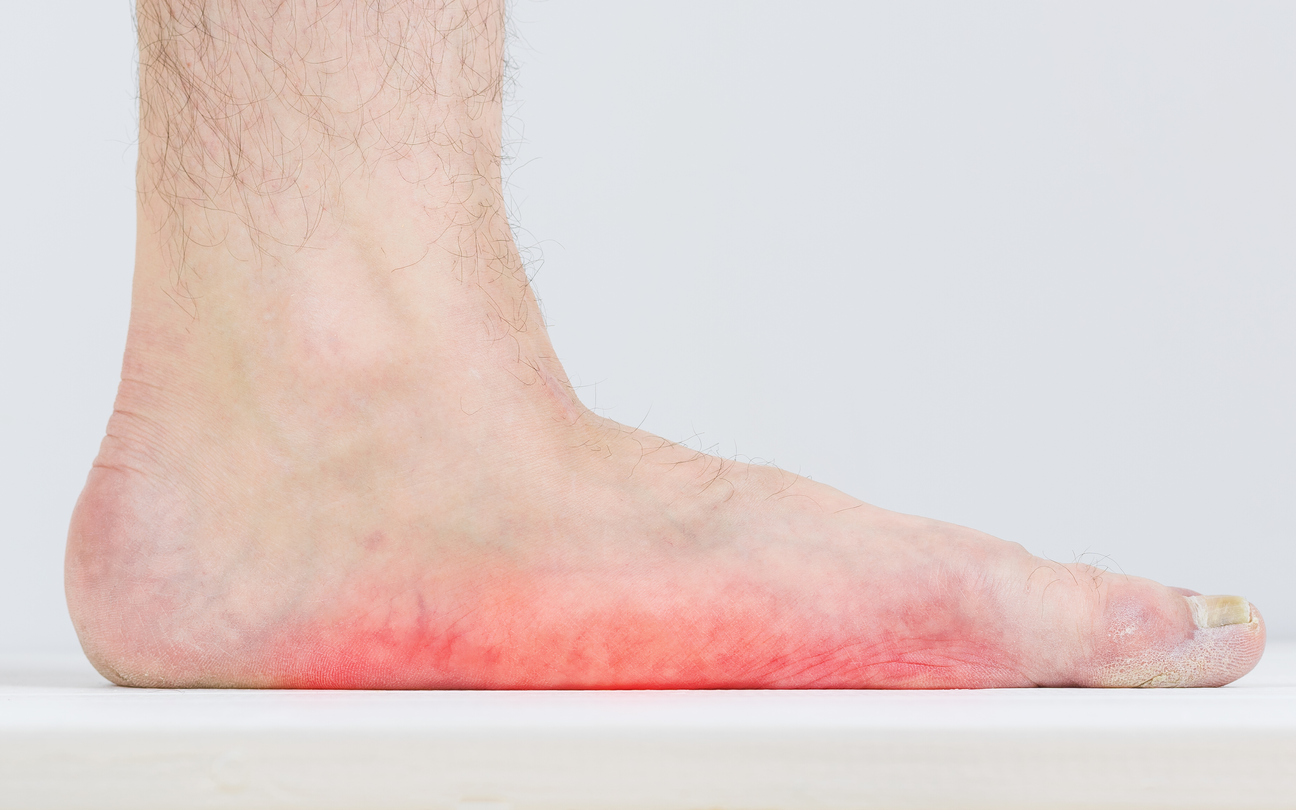
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the foot
There is more than one part of the body that is more susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis or rheumatoid arthritis, including the joints of the feet, which show symptoms of infection as follows:
- A feeling of fatigue and general weakness in the body without much effort.
- The patient may feel excessive pain in the joint of the foot, which increases in the morning.
- As a result of inflammation, a person loses appetite, and this affects body mass.
- The patient feels stiffness in the foot and it becomes difficult to move it normally.
- In advanced cases of the disease, the person gets numbness in the foot.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the fingers
The fingers of the hand are among the smaller joints that rheumatoid disease targets when infected and affects them, and several symptoms appear, which are:
- A feeling of pain when moving the fingers of the hand between flexion and extension.
- Increase in size and swelling in the morning when you wake up.
- A tingling sensation in the fingers that gets worse when moving them.
- The skin around the fingers can become red and irritated.
Rheumatoid symptoms in women
A number of researches have shown that women are more susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis, and there may be more than one symptom that appears on a woman with rheumatoid disease, and they are as follows:
- At the beginning of the disease, general fatigue can appear in the body.
- Dryness and redness of the eyes can appear.
- If inflammation affects a joint in the body, it causes severe pain.
- The woman may develop rheumatic nodules in the advanced stages of the disease.
Symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis in the shoulder
some symptoms or signs affect the shoulder when rheumatoid infection can be recognized by the doctor upon clinical examination of the patient, including the following:
- The presence of pain in the joint lasts for a while, then breaks off, and then returns.
- The appearance of swelling or swelling in the shoulder, resulting in pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis can cause limited movement of the shoulder.
- An increase in body temperature due to infection.