Symptoms of Lumbar Disc Herniation and Who is the Best Doctor for Minimally Invasive Lumbar Disc Surgery?

Symptoms of a Lumbar Disc Herniation
A Lumbar Disc Herniation is a common problem that affects the spine. This slippage causes several symptoms that indicate a problem with the disc cartilage that separates the vertebrae in the spine and helps absorb shocks and distribute pressure on the spine.
Among the most important symptoms that we can mention:
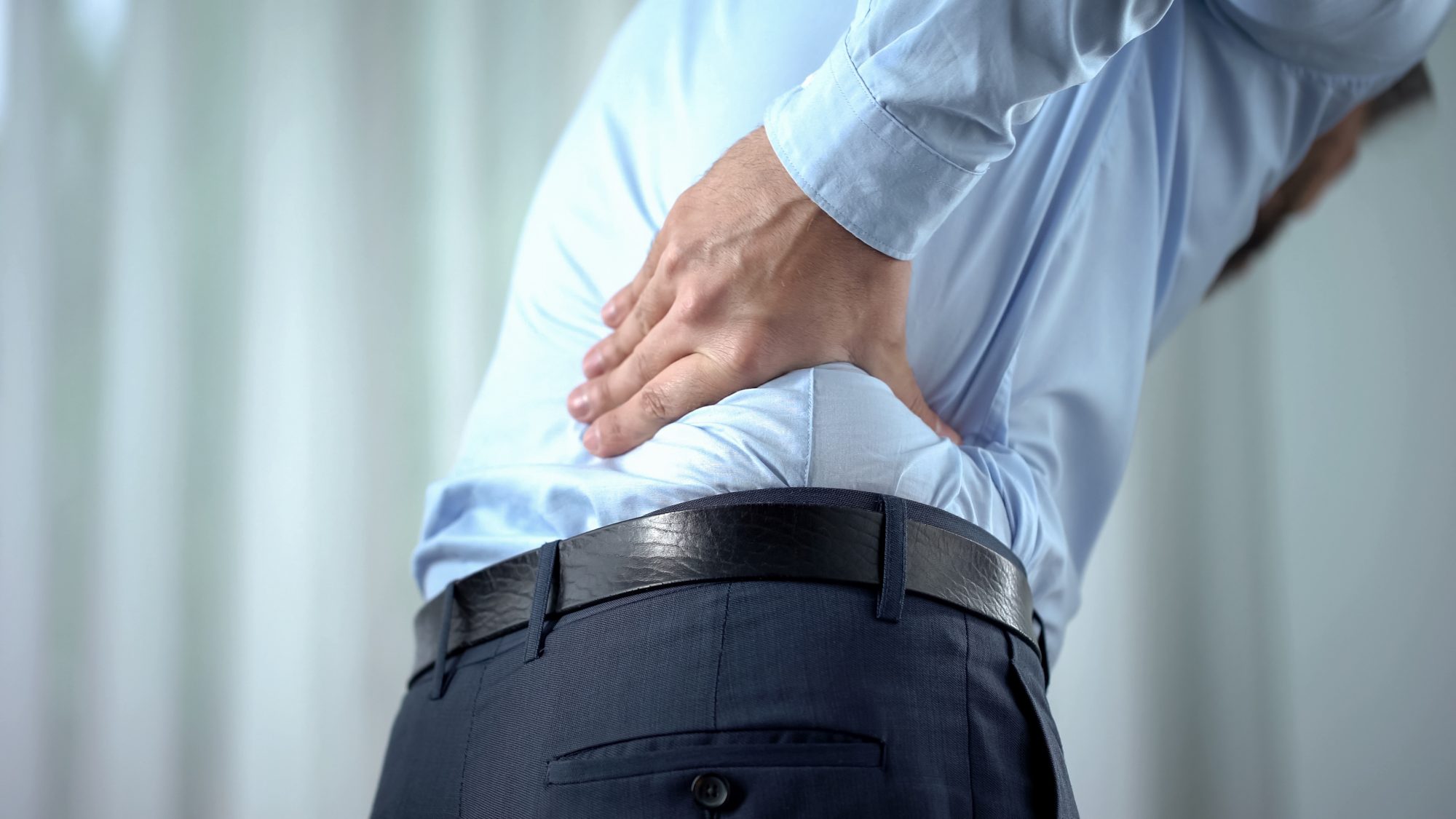
Continuous lower back pain: The patient may feel severe pain that spreads to the lower back area and lasts for long periods. Stiff legs or lower back stiffness: The patient may feel that his legs have become heavy and feel stiff and difficult to move. Feeling pain when pressure is placed on the lower back area: When pressure is placed on the spine in the slip area, the patient can feel sharp pain. Pain in the thigh: Pain may move from the back area to the thigh when a slip occurs. Difficulty moving: The patient may have difficulty bending or changing body position due to pain and stiffness.
It is worth noting that the symptoms of a Lumbar Disc Herniation vary depending on the location of the herniation. It may occur in the neck area or in the lower spine, and it may be accompanied by other symptoms in advanced cases. The patient should also consult a doctor to determine the accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
To prevent a Lumbar Disc Herniation, it is recommended to avoid exposure to heavy loads, excessive movements, and sitting for long periods without changing the body position. It is also possible to strengthen the back muscles and improve physical fitness by exercising regularly. Before starting any exercise program, it is recommended to consult with a doctor to determine appropriate exercises based on each individual’s condition.
To protect the back and maintain a healthy spine, you must follow a healthy lifestyle and stay away from factors that cause stress on the spine. This means avoiding sitting for long periods without moving and paying attention to the correct posture while sitting and walking. It is also recommended to adjust the diet and eat foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to promote healthy bones and cartilage.
What is the treatment for a Lumbar Disc Herniation?
When the disc in the lower vertebrae slips out of place, it can cause severe pain and muscle spasms in the back area. Fortunately, there are several ways to treat this condition. Below is a list of some of the treatments used to relieve the symptoms of a Lumbar Disc Herniation:
- Physical therapy and therapeutic exercises: Therapeutic exercises and stretching are considered one of the best treatments to relieve the pain of a Lumbar Disc Herniation. These exercises can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine and improve its balance.
- Drug treatment: includes painkillers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. These drugs can help reduce the pain and inflammation associated with a Lumbar Disc Herniation.
- Heat and cold therapy: Applications of heat or cold to the affected back area can provide temporary relief from pain and swelling caused by a Lumbar Disc Herniation.
- Massage therapy: Massage is considered one of the alternative treatments that can be used to relieve the pain of a Lumbar Disc Herniation. Proper massage techniques can relieve muscle tension and improve blood circulation in the affected area.
- Dry needling: Dry needling is part of acupuncture treatment that relies on pricking thin needles at specific points on the body to stimulate the body’s self-healing system. This treatment can help improve blood flow and relieve pain.
These traditional treatments can help relieve the symptoms associated with a Lumbar Disc Herniation. However, people who experience severe pain or have symptoms that do not improve should see a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
How many days does a Lumbar Disc Herniation pain last?
Healing duration: The recovery period from a Lumbar Disc Herniation varies from one person to another and depends on several factors such as the severity of the condition and the type of treatment followed. Healing from a Lumbar Disc Herniation usually takes between 4 and 6 weeks.
Specific treatment: Recovery from a Lumbar Disc Herniation requires adherence to the treatment specified by the specialist doctor. Treatment can include the use of pain relievers, cortisone injections, and physical therapy sessions.
Return to normal activity: After the recovery period ends, a person with a Lumbar Disc Herniation can gradually return to normal activities. This should be done carefully and gradually to avoid re-aggravation of the condition.
Signs of complete recovery: A person must achieve signs of complete recovery from a Lumbar Disc Herniation before fully resuming normal activity. These signs may include the disappearance of muscle spasms and pain in the back and neck.
Severe cases: In some advanced cases or cases that do not improve after the normal recovery period, there may be a need to perform surgery to replace the damaged disc.
Duration of symptoms: The duration of symptoms of a Lumbar Disc Herniation may also vary depending on each case. Some people experience symptoms for only several days, while in others they may last for several months.
Common Symptoms: Common symptoms of a Lumbar Disc Herniation that indicate recovery include pain in the back and neck and numbness in the legs. These symptoms should gradually fade as the condition improves.
What is the difference between a Lumbar Disc Herniation and a Lumbar Sprain?
Although a Lumbar Disc Herniation and a Lumbar Sprain may have similar symptoms, they are two different conditions affecting the lower back.
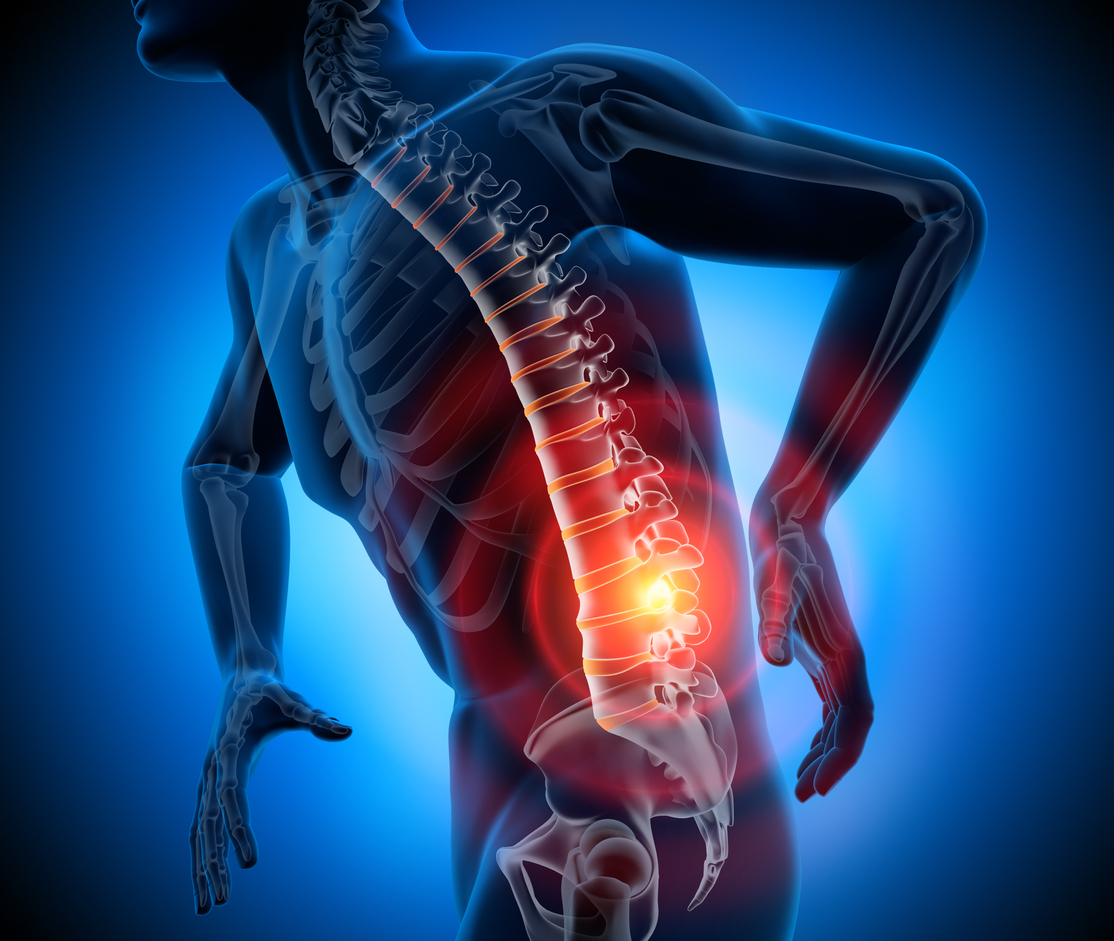
A Lumbar Disc Herniation occurs when one of the discs that cushion the vertebrae in the lower back slips out of place or ruptures. This can cause pain, numbness, and weakness in the lower back, buttocks, and legs.
On the other hand, a Lumbar Sprain occurs when the ligaments that hold the vertebrae together are stretched or torn. This can cause pain, swelling, and stiffness in the lower back.
When is a Lumbar Disc Herniation Dangerous?
When people ask about the danger of a lumbar disc herniation, the answer depends on the degree of the herniation and its effect on the body. In the case of a simple lumbar disc herniation, there may not be a significant risk, and it can be treated with traditional treatments such as rest, applying ice, and taking painkillers. However, there are some conditions that can be serious and require immediate treatment, including:
- Severe and persistent pain: If pain in the back or legs is persistent and severe, it may be a sign of a serious condition. There may be pressure on the nerves or a tear in the cartilage, which requires rapid evaluation and treatment.
- Numbness in the legs or loss of sensation: If there is numbness in the legs or loss of sensation in any area of the body, this may be evidence of pressure on the sensory nerves, which is a serious matter that requires immediate medical evaluation.
- Muscle weakness: If there is muscle weakness or difficulty controlling movement, this may be a sign of pressure on the motor nerves, which calls for immediate action.
- Problems urinating or defecating: If there is difficulty urinating or defecating or loss of control, this may be evidence of significant pressure on the nerves in the pelvic area, and requires immediate evaluation.
Does Massage Help Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Degrees of Lumbar Disc Herniation are conditions in which the layers of cartilage between the vertebrae slip. They are classified according to the severity of the slip into the following three grades:
- Minor Lumbar Disc Herniation: occurs when the herniation is between 0 to 25% of the cartilage length. In this case, there is no significant pressure or friction between the affected spine and the adjacent spine. Common symptoms of a minor lumbar disc herniation include mild pain in the back area, stiffness in movement, and inability to perform daily prep activities.
- Moderate Lumbar Disc Herniation: occurs when the herniation is between 25 to 50% of the cartilage length. In this case, the patient may feel severe pain in the back and legs, tingling, and numbness in the lower extremities. Treatment may require surgical intervention in some cases to stabilize the slip and avoid further damage.
- Severe Lumbar Disc Herniation: occurs when the herniation is more than 50% of the cartilage length. In this case, there can be severe pressure on the nerve roots and spinal cord, leading to severe pain and disturbances in movement and sensation. Treatment in this case may require immediate surgery to release pressure on the spinal cord and restore spinal function.
What Exercises are Prohibited for a Lumbar Disc Herniation?
A lumbar disc herniation is a painful and annoying injury that can affect the lives of people who suffer from it. Cases of lumbar disc herniation require special care and adherence to special exercises to avoid complications and worsening of symptoms. Patients with a lumbar disc herniation should avoid certain exercises that can cause irritation of the disc and increase pain. Below is a list of exercises prohibited for patients with a lumbar disc herniation:
- High-difficulty jumps: Exercises that require high-difficulty jumps such as long jumps or high jumps can increase traumatic pressure on the spine and lead to worsening symptoms and increased pain.
- Lifting heavy weights: Patients with a lumbar disc herniation are advised to avoid lifting heavy weights or performing heavy lifting exercises. This is because these exercises can compress the spine and increase pressure on the damaged disc.
- Front board: Exercises that involve the front board should be avoided, as the patient must support the body weight on his hands and feet. This can increase traumatic pressure on the spine and worsen symptoms.
- Rolling on your back: Exercises that involve rolling on your back should be avoided, as this puts pressure on the spine and may cause increased pain.
- Twisting: Exercises that involve severe twisting movements of the spine should be avoided. These exercises may cause excess pressure on the damaged disc and increase pain.
What are the Degrees of Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Lumbar Disc Herniation is divided into 4 grades or stages that become more severe and worse with each stage. Grades include the following:
- Disc Protrusion: This degree occurs when the nucleus pulposus bulges into the annulus without interrupting the outer part of the annulus fibrosus. The effect of this type of lumbar disc herniation is weak and may result in mild numbness when standing or sitting for long periods.
- Disc Bulge: This degree occurs when there is weakness and stretching in the fibrous ring surrounding the cartilage, but the ring is not cut. Treatment for this type of lumbar disc herniation includes therapeutic exercises to strengthen the back.
- Disc Herniation: This degree occurs when the herniation is characterized by the impression of part of the nucleus pulposus through the annulus fibrosus, resulting in pressure on the adjacent nerve. Symptoms of this type of slip include severe pain in the back and extremities and may be accompanied by numbness and numbness.
- Sequestrated Disc: This degree occurs when part of the nucleus pulposus separates from the annulus fibrosus due to its rupture. This type of slip can cause severe pain and pressure on surrounding nerves.
What is Cartilage Food?
In many cases, this term refers to supplements that contain ingredients that are beneficial for cartilage health and promoting the rebuilding process or maintaining its health.
Popular supplements that claim to help support cartilage health include:
- Glucosamine: Glucosamine is believed to help rebuild cartilage and maintain its elasticity.
- Chondroitin: Usually used with glucosamine, it is thought to help reduce pain and improve joint function.
- MSM (methylsulfonylmethane): It is thought to improve joint health and reduce pain.
- Fish oil and omega-3 fatty acids: May help reduce arthritis.
- Collagen: Unbroken type 2 collagen is used in some supplements to support cartilage health.
Can Cartilage Damage be Treated with Physical Therapy?
Physical therapy is considered one of the appropriate options for treating a lumbar disc herniation. Doctors usually recommend physical therapy as the first step in treating this condition. A physical therapist has the ability to treat a lumbar disc herniation by applying customized exercises or using special devices. He or she can also train the patient on how to do exercises at home to strengthen the muscles that support the lower back and help prevent recurrence of the injury.
According to what was stated by Dr. Maher Al-Qiblawy, Professor of Physical Therapy at Cairo University and President of the Middle East Alternative Therapy Association, physical therapy is considered an important role in treating a lumbar disc herniation, as it aims to control pain, restore movement, and return the patient to normal life by strengthening the back and abdominal muscles, and restoring the body’s strength. vertebral column. It is worth noting that treatable surgery may cause severe pain that is not relieved by pain medications, and also leads to compression of sensory nerves, leading to loss of sensation in some limbs or pressure on connective nerves to control urine and stool.
The best doctor for arthroscopic Lumbar Disc Herniation surgery
Dr. Amr Amal is ranked among Egypt’s elite doctors in treating Lumbar Disc Herniation using arthroscopy. His clinic is located in Al-Fouad Medical House, fourth floor, in room No. 418. He is recognized for his high experience and good reputation in this specialty.
The problem of Lumbar Disc Herniation is one of the annoying issues that may prevent people from continuing their daily lives efficiently. In this context, the importance of laparoscopic operations appears as an effective solution to this problem.
Although there are many distinguished doctors in this specialty, Dr. Amr shows exceptional ability and profound knowledge in treating spinal problems, including degenerative issues, spinal narrowing, and sprains, in addition to treating problems of pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots.