Learn About the Degrees of Herniated Disc and Tips for Those Suffering from It
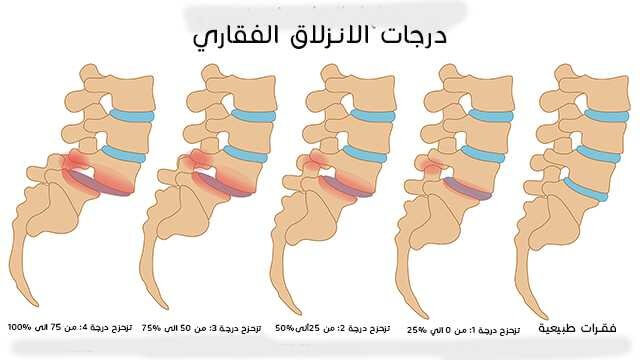
Degrees of Herniated Disc
- First Degree:
Herniated disc in this degree occurs when the disc slightly shifts from its natural position. No significant symptoms may appear in this degree, and the pain may be mild and intermittent. This degree can be diagnosed through clinical examination and the patient’s medical history.
- Second Degree:
Herniated disc in this degree occurs when the disc shifts further from its natural position. The patient may experience back pain that worsens with certain movements such as bending or kneeling. Numbness or tingling in the lower limbs may occur. This degree can be diagnosed through clinical examination and MRI scans.
- Third Degree:
Herniated disc in this degree occurs when the disc significantly displaces from its natural position. The patient may experience severe and continuous pain in the back and legs. Weakness in the muscles and difficulty in movement may occur. Surgical intervention may be needed to treat this degree of herniated disc.
- Fourth Degree:
Herniated disc in this degree occurs when the disc displaces very significantly from its natural position. The patient may experience extremely severe and continuous pain in the back and legs. Severe muscle weakness and loss of sensation in the lower limbs may occur. Urgent surgical intervention is required to treat this degree of herniated disc.
- Fifth Degree:
Herniated disc in this degree occurs when the disc completely displaces from its natural position. The patient may experience extremely severe and continuous pain in the back and legs, along with severe muscle weakness and loss of sensation in the lower limbs. Urgent surgical intervention is required to treat this degree of herniated disc.
Please note that this list provides general information about the degrees of herniated disc and does not replace consulting a specialist to accurately diagnose your condition and determine the appropriate treatment.
When is a Herniated Disc Patient at Risk?
Herniated disc, also known as slipped disc or disc herniation, is a common condition that affects the spinal column and can lead to health complications in patients. It is important to understand when a patient is at a high risk of developing this condition, as it can help take necessary precautions and initiate appropriate treatment early. Here is a list of factors that increase the risk of herniated disc:
- Age: The risk of herniated disc increases with age. As a person gets older, the spinal discs become less flexible and more susceptible to damage and tearing.
- Genetic Factors: There may be genetic factors that make some individuals more predisposed to herniated discs. If you have relatives with herniated discs, you may have a higher risk of developing one.
- Previous Injuries: If you have had a previous spinal injury, it can increase your risk of herniated disc. Past injuries can lead to disc damage and weakening, which raises the likelihood of herniation.
- Heavy Physical Activity: Engaging in strenuous physical activities and lifting heavy objects can increase the risk of herniated disc. The discs undergo additional pressure and stress during such activities, increasing the chances of damage and herniation.
- Lifestyle: Lifestyle factors can also play a role in raising the risk of herniated disc. For example, prolonged sitting in front of a computer or constant exposure to stress and mental tension can increase the likelihood of herniation.
- Obesity: Excess weight is a contributing factor to the risk of herniated disc. Excess weight places extra pressure on the spinal column, increasing the chances of disc damage and herniation.
It’s important to note that these factors are not strict rules, and individuals can develop herniated discs without any of these risk factors. They are merely factors that increase the likelihood of occurrence. If you are experiencing symptoms suggestive of a herniated disc, it is advisable to consult a doctor for a proper evaluation and determination of appropriate treatment.
When Does a Herniated Disc Heal Completely?
When it comes to herniated discs, many people suffer from severe pain and restricted spinal movement. It is important to know when a person can fully recover from this condition. Here is a list that explains when a herniated disc can heal completely:
Recovery Period: Typically, the treatment of a herniated disc usually takes a period ranging from four to six weeks. During this time, the patient undergoes the appropriate medical treatment and follows the advice of the treating physician.
Appearance of Recovery Signs: In some cases, signs of recovery may begin to appear within a few days of starting treatment. These signs may include an improvement in pain and better mobility.
Return to Normal Activities: After the recovery period, the individual can gradually return to their daily and sports activities. This should be done cautiously and gradually to avoid the recurrence of herniated disc.
Complete Rest: Initially, patients are advised to rest completely as a first measure in the treatment of a herniated disc. Patients should relax and avoid strenuous physical activities and heavy lifting.
Surgical Treatment: In some severe cases, surgical treatment may be necessary. The necessity of surgery is determined based on the evaluation of the condition by the specialist doctor.
Preventing Recurrence of Herniated Disc: After recovery, individuals should follow a healthy lifestyle and engage in appropriate exercises to strengthen the back muscles and maintain spinal health.
In summary, a herniated disc can heal completely, but it depends on several factors, including the severity of the condition and the commitment to treatment and self-care. Patients should consult with specialist doctors regarding their specific condition for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
What Is the Recovery Rate for Herniated Disc?
The recovery rate for a herniated disc is an important topic of concern for many individuals dealing with this health issue. Here are some facts and figures about the recovery rate for herniated discs:
Complete Recovery is Possible: Yes, it is possible to achieve a complete recovery from a herniated disc, especially for lumbar and cervical disc herniations, through non-surgical interventions in the vast majority of cases.
Rate of Complete Recovery: Several studies have shown that the rate of complete recovery from herniated disc pain can be as high as 90% within just 12 weeks.
Recovery Time: Of course, the time required for full recovery varies from person to person. The severity of the herniated disc is not necessarily an indicator of recovery time. There are cases of severe herniations, and if the symptoms are not severe, doctors typically start with medications and physical therapy for 6-8 weeks. Most doctors consider the recovery time for a herniated disc to be around 6 to 12 weeks, depending on the severity and location of the herniation.
Surgical Treatment: If symptoms do not improve or are very severe to the point of hindering daily activities, surgical treatment may be resorted to. The success rate of minimally invasive herniated disc surgery can reach up to 90%.
Treatment Approaches: To treat a herniated disc, doctors usually begin with pain-relieving medications and physical therapy as a first step. Nerve root injections can also be used to alleviate pain.
Recovery Duration: Recovery from herniated disc surgery may take approximately 3 to 4 months, with some cases recovering faster as pain, numbness, and weakness improve within a few weeks after treatment.
Based on realistic data, it can be said that the recovery rate for a herniated disc is high, and many individuals can achieve complete recovery from the pain and associated symptoms of this condition. However, it’s important to consider that treatment and recovery depend on several factors, including the severity of the herniation and the guidance of the treating physician.
Can You Live with a Herniated Disc?
Many people suffer from the problem of a herniated disc in the spine, and some may wonder if they can live with this health issue. The answer is yes, of course, you can live with a herniated disc. A herniated disc can occur without any symptoms or pain, and sudden pain can occur without any warning. In general, a herniated disc can return to its place on its own over time when following the treatment plan specified by the specialist doctor.
To help prevent disc herniation, the following guidelines can be followed:
Engage in appropriate exercises to strengthen the core muscles and support the spine. Avoid lifting heavy objects incorrectly and repeatedly, and avoid sitting in incorrect positions for extended periods. Avoid prolonged driving, as sitting for extended periods can exert significant pressure on the spine and increase the risk of herniation. Quit smoking, as smoking reduces the amount of oxygen available to the tissues and increases the risk of disc herniation. Avoid activities that involve manual lifting or handling of heavy bags or vibrations, as these activities can increase the pressure on the spine and lead to herniation.
Although a herniated disc can cause some pain and discomfort, it is typically temporary and can be managed long-term by following the mentioned guidelines and the specific medical treatment prescribed by the doctor. Therefore, individuals with a herniated disc can live with this health issue and maintain their quality of life by following the necessary guidelines.
Is Herniated Disc Considered a Disability?
Herniated disc is a common condition that affects the spine and causes severe back and spine pain. However, the debate about whether a herniated disc is considered a disability or not is still ongoing. Here is a list of factors that affect the classification of a herniated disc as a disability:
Impact of Pain: Individuals with a herniated disc suffer from acute and persistent pain in the back and spine. This pain can lead to a restriction of movement and the ability to perform daily activities normally.
Impact on Mobility: Herniated discs can affect the ability to move and perform routine activities such as walking and sitting for extended periods. Herniated disc can be a limiting factor for mobility and the ability to work.
Psychological and Social Impact: Herniated disc can affect the psychological and social well-being of patients. They may experience depression and anxiety due to constant pain and the restrictions imposed by the herniated disc on their lives.
Impact on Functional Capacity: Patients with a herniated disc often have limited functional capacity, making it difficult for them to perform daily activities normally. They may need assistance in performing some basic tasks.
Continuous Treatment and Care: Patients with a herniated disc require continuous treatment and care to alleviate pain and improve their overall condition. Treatment may include physical therapy, medications, and in some cases, surgery.
Although there are arguments in favor of classifying a herniated disc as a disability, there is no global consensus on this issue yet. Classification may vary depending on the legal and medical criteria in each country. It is essential to evaluate each case individually based on the individual circumstances of the patient.
It is important to provide appropriate support and care for individuals with a herniated disc, whether it is considered a disability or not. Doctors and specialists should collaborate in providing the appropriate treatment and guiding patients in effectively managing their condition and improving their quality of life.
Tips for Those with a Herniated Disc
- Proper Sitting: A person with a herniated disc should ensure proper sitting posture. They should keep their back as straight as possible and avoid sitting on deep couches or un-padded chairs for extended periods.
- Regular Exercise: Exercise is an excellent way to prevent back pain, especially pain caused by a herniated disc. Regular exercise helps strengthen the back and core muscles and promotes proper sitting and standing posture.
- Avoid Prolonged Bed Rest: Prolonged bed rest should be avoided, as it can increase pressure on the disc and exacerbate symptoms. It is advisable to perform muscle-strengthening exercises and light movement instead of complete rest.
- Use Cold and Hot Packs: Cold packs can be used to reduce inflammation and pain in the affected area, while hot packs can help relax tense muscles and improve blood circulation.
- Avoid Lifting Heavy Objects: Patients should avoid lifting heavy objects or excessive exertion, as it can increase disc pressure and worsen symptoms.
- Rest and Relaxation: Taking regular rest breaks during prolonged sitting is recommended. Relaxation techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help reduce tension and calm the muscles.
- Consult a Doctor: Patients should continue to consult with a specialist doctor to monitor their condition and receive appropriate treatment. The doctor can provide additional advice and guidance based on their individual health status.
By following these tips, individuals with a herniated disc can alleviate pain and improve their quality of life. However, patients should adhere to their doctor’s instructions and seek medical attention if their symptoms worsen or persist for an extended period.
How Does a Herniated Disc Patient Sleep?
Here’s how a herniated disc patient can sleep properly:
Use a Reclining Chair: A reclining chair is considered a suitable option for sleeping for herniated disc patients. This chair provides better back support, helping to alleviate pain and reduce pressure on the spinal discs.
Use Appropriate Pillows: It’s preferable for the patient to sleep in a comfortable back position, which can be achieved by placing a pillow under the legs when sleeping on the back. Additionally, a pillow can be placed between the legs and knees when sleeping on the sides.
Avoid Incorrect Positions: The patient should avoid positions that worsen the condition of the herniated disc during sleep. Sleeping on the stomach and sitting in incorrect positions for extended periods should be avoided. Instead, it is recommended to sleep on the back or sides.
Ensuring Relaxation and Rest: Sleep is an important time for recovery and regaining strength. Therefore, the patient should ensure they get an adequate amount of rest and relaxation during sleep.
Engaging in Appropriate Exercises: Proper exercises can be beneficial in strengthening the back muscles and improving their flexibility. However, the patient should consult with a doctor before starting any physical activity and choose suitable exercises.
Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Excess weight gain can increase pressure on the spinal column and raise the likelihood of exacerbating a herniated disc. Therefore, the patient should maintain a healthy weight through regular physical activity and a balanced diet.
Consulting a Doctor: The patient should consult a specialist doctor for an accurate diagnosis and a suitable treatment plan. The doctor can provide guidance on the best sleeping positions, appropriate exercises, and necessary medical treatment.
It is important for patients suffering from a herniated disc to follow proper sleeping advice to alleviate pain and improve their daily quality of life. Sleep should be in a comfortable and supportive environment, and consultation with a specialist doctor is necessary.
Does a Herniated Disc Progress?
Herniated disc is a common condition that affects the spinal vertebrae and can cause severe pain. But does this condition progress over time? In this article, we will discuss in detail whether a herniated disc progresses or not.
Initial Symptoms: Initially, there may be no symptoms of a herniated disc, and it may be discovered incidentally during another medical examination. However, when symptoms start to appear, they often include neck or back pain, tingling, or weakness in the limbs.
Progression of Symptoms: Generally, a herniated disc can progress over time. Pain may gradually increase in intensity and extend from the neck or back to the limbs, such as the legs or arms. The pain may also be more severe when attempting to move, restricting the person’s movement and affecting their daily life.
Impact on Movement and Mobility: A herniated disc can affect a person’s ability to move. They may have difficulty performing simple movements such as bending or lifting heavy objects. Pain can become more intense when attempting to move, leading to restricted movement and an impact on their daily life.
Factors Influencing Progression: Several factors can influence the progression of a herniated disc. For example, excessive stress on the cervical or lumbar spine can increase the risk of herniation and its progression. Additionally, aging and the long-term effects of aging can affect the development of the condition.
Treatment and Preventive Measures: When diagnosed with a herniated disc, treatment typically involves a comprehensive set of measures. Medications may be prescribed to relieve pain and swelling, and physical therapy may be recommended to strengthen the muscles around the spinal column and improve flexibility. In more advanced cases, surgical treatment may be necessary.
In summary, a herniated disc can progress over time. It is crucial to expedite the diagnosis and treatment of the condition to avoid worsening of symptoms and restricted movement. Consultation with a specialist doctor is essential to assess the condition and provide appropriate treatment.
Can Herniated Disc Cause Frequent Urination?
Many patients, especially young individuals, may experience urinary problems such as frequent urination and lower back pain. This could potentially be the beginning of a herniated disc. Herniated disc is one of the most common causes of cauda equina syndrome and can occur when the disc located between the vertebrae or spinal bones slips out of place.
Symptoms of a herniated disc may include an inability to control urine or bowel movements, a feeling of coldness or numbness in the limbs, difficulty urinating, a burning sensation during urination, and a change in the color of urine. Numbness in the limbs may be one of the symptoms indicating a herniated disc compressing a nerve.
To prevent disc herniation, several measures can be taken. It is recommended to engage in regular physical exercises to strengthen core muscles, which help stabilize and support the spine. Additionally, avoiding excessive stress on the spine and adopting a healthy lifestyle, including maintaining a healthy weight and avoiding prolonged sitting in the same position, is advisable.
However, it’s important to note that herniated disc can also lead to complications that affect the urinary process. Herniated disc may cause weakness in the bladder or bowel muscles, resulting in difficulty urinating or urinary incontinence. Increased pressure on the spine can exacerbate symptoms, and significant compression can lead to muscle weakness and atrophy, affecting the patient’s ability to control urination.
Nevertheless, it should be noted that patients with herniated discs may exhibit symptoms entirely different from those associated with this disorder. Some patients may be unaware of any relationship between their symptoms and a herniated disc.
Therefore, if you suspect a herniated disc and experience symptoms such as frequent urination and difficulty controlling it, it is advisable to consult a specialist doctor for a thorough evaluation and accurate diagnosis. Treatment should be tailored to the specific diagnosis made by the specialist doctor and the patient’s condition.
So, while herniated disc can be one of the potential causes of frequent urination and related issues, an accurate diagnosis is necessary to determine the appropriate treatment.