Is a herniated disc surgery serious? What is its success rate?
Is a herniated disc surgery serious?
Herniated disc surgery is one of the surgical procedures used to treat back pain and its troublesome symptoms. When patients ask this question, they need to learn more about this procedure and its level of seriousness. Therefore, in this article, we will provide a simplified answer to this question.
Symptoms of a herniated disc: Before discussing the seriousness of herniated disc surgery, it is important to mention the symptoms experienced by patients. If a patient is suffering from severe back or neck pain, difficulty in movement and walking, these may be signs of a herniated disc. Other typical symptoms of this condition may include pain in the upper or lower limbs, numbness or tingling in the limbs, and muscle weakness.
The seriousness of herniated disc surgery: When the question arises whether herniated disc surgery is serious, it is important to remember that any surgical procedure has some potential risks and side effects. The same applies to herniated disc surgery. While this procedure is considered largely safe, it may lead to some potential complications.
Potential complications of herniated disc surgery may include:
- Surgical site inflammation: Inflammation may occur at the surgical site, causing pain, redness, and swelling.
- Bleeding: Mild bleeding may occur at the surgical site and may require medical intervention to stop it.
- Infection: The surgical site may become infected, requiring additional treatment.
- Nerve damage: In rare cases, nerve damage may occur in the surrounding area, leading to loss of movement or sensation in the affected area.
Postoperative measures: To minimize side effects and potential complications after undergoing herniated disc surgery, patients should follow some guidelines, such as:
- Engaging in light exercises recommended by the doctor.
- Avoiding prolonged driving or sitting and bending.
- Avoiding heavy lifting.
- Complying with regular visits to the doctor for evaluating the condition and detecting any potential complications.
Is minimally invasive surgery the best option:
In the end, it should be clarified that minimally invasive surgery is the best option for treating herniated discs. This type of procedure is less invasive and more effective, as it is performed through a small incision in the patient’s skin instead of a complete skin cut.
Herniated disc surgery can be largely safe, but it may lead to some potential complications. The patient should follow postoperative guidelines to avoid complications. However, minimally invasive treatment is considered the best option for herniated disc treatment.
What is the success rate of herniated disc surgery?
Many people seek surgical procedures as a solution for treating herniated discs. However, do you know the extent of the success rate of this surgery? It is important to separate between many factors that affect the success rate.
Factors affecting the success rate of the surgery:
Herniation size: Smaller herniated disc cases are more likely to successfully recover, while larger cases can be more challenging to treat.
Duration of the injury: The duration of the herniation may affect the success rate. Cases with a shorter duration of herniation may respond better to surgery.
Patient’s health: The patient’s overall health may affect the success rate. Individuals with other conditions such as spinal curvature or a history of previous spinal problems may be more prone to complications.
Surgical technique: The success rate also depends on the surgical technique used. Doctors may differ in choosing a specific technique for herniated disc treatment, and as a result, the surgery’s outcomes may vary.
Success Rate of Herniated Disc Surgeries:
According to specialized doctors, the success rate of herniated disc surgeries reaches 80-90%. However, it should be noted that this percentage may vary depending on the patient’s symptoms and the severity of the condition.
It is important to emphasize that surgeries in general require some logistical care to ensure their success. Hospitals excel in providing the necessary physical therapy and rehabilitation after the surgery and offering proper guidance to patients.
Patients are required to adhere to a specific program of physical therapy and exercises aimed at strengthening the back muscles and improving the overall flexibility of the spine. Following medical advice and supervision after the surgery can reduce the likelihood of complications or recurrence of the herniation.
Overall, the success rate of herniated disc surgeries is considered high. However, patients should cooperate with doctors and follow medical guidance to ensure a full recovery and prevent future setbacks. It is important to consult individually with your doctor before deciding to undergo surgery and assess the chances of success based on the patient’s individual case.
What Is the Recovery Time After Herniated Disc Surgery?
Herniated discs are a common health issue that affects many people worldwide. When dealing with this condition, there may be several questions on the patient’s mind, one of the most important being, what is the recovery time after herniated disc surgery?
Fortunately, we can answer this question based on doctors’ opinions and information available online. It should be understood that each case is individual, and the recovery time may vary from person to person, depending on several factors such as the severity and location of the herniation. In this article, we will provide you with detailed information about the possible recovery time after herniated disc surgery.
Potential Recovery Time
Most doctors indicate that the recovery time after herniated disc surgery can take approximately 6 to 12 weeks. However, it should be mentioned that this duration may vary depending on the complexities of the case and other factors. To better understand this timeframe, it can be divided into stages:
Early Stage (1-2 weeks): During the first two weeks after surgery, the patient should rest and avoid overloading the affected spine. The use of supports and assistive walking tools is recommended to aid in mobility.
Intermediate Stage (2-6 weeks): During this stage, the patient can start performing some simple exercises to strengthen the back muscles. Physical therapy can be used to improve mobility and alleviate pain.
Late Stage (6-12 weeks): In this stage, the patient can return to routine activities they engaged in before the surgery, with the need to avoid heavy lifting and excessive strain.
Factors Affecting Recovery Time
In addition to the severity and location of the herniated disc, several other factors can affect the recovery time after herniated disc surgery. These factors include:
- Age: Younger individuals tend to recover more quickly than older adults.
- General Health: The patient’s overall health plays a role in the recovery time. Individuals with chronic illnesses or other medical conditions may require a longer recovery period.
- Adherence to Doctor’s Instructions: Following the doctor’s instructions after surgery can accelerate the recovery process and reduce complications.
Adherence to Prescribed Treatment
Adhering to the prescribed treatment by the doctor is an important part of the recovery process after herniated disc surgery. The prescribed treatment may include:
- Medication: The doctor may prescribe pain relieving and anti-inflammatory medications to alleviate pain and swelling. Patients should follow the prescribed medication doses according to the doctor’s instructions.
- Physical Therapy: A specialized physical therapist may be appointed by the doctor to guide the patient in performing exercises to strengthen back muscles and improve spinal mobility.
- Follow-Up Medical Visits: It is important for the patient to schedule regular follow-up visits with the doctor to assess recovery progress and address any issues that may arise.
In summary, the recovery time after herniated disc surgery can typically range from 6 to 12 weeks. However, patients should remember that this duration can vary from person to person and depends on several factors. It is important to adhere to the doctor’s instructions and follow the prescribed treatment to ensure a successful recovery in the shortest possible time.
When Is Surgical Intervention Needed for Herniated Discs?
Many individuals suffer from herniated discs, a condition that can cause severe pain and significantly impact their daily lives. The severity of herniated disc cases varies, and the decision to undergo surgical intervention depends on how much this condition affects the patient’s life and its progression. In this article, we will discuss surgical intervention and when it is considered necessary for herniated discs.
- Acute and Chronic Symptoms: Some individuals may experience severe spine pain as a result of a herniated disc. If the patient is suffering from severe pain that does not respond to traditional treatments such as medication and physical therapy, surgical intervention may be the most appropriate option.
- Lack of Response to Conservative Treatment: In some cases, the pain caused by the herniated disc may not respond to non-surgical treatments, such as physical therapy and strengthening the muscles around the spine. If the patient does not significantly improve after trying traditional treatments for an extended period, doctors may recommend surgery.
- Deterioration of Health: If the herniated disc is causing a deterioration in the patient’s condition and additional damage to the spine, surgical intervention may be necessary to prevent further harm and improve the overall condition.
In conclusion, surgical intervention for herniated discs may be necessary in cases of acute and chronic symptoms, lack of response to conservative treatment, and deterioration of the patient’s health. The decision to undergo surgery should be made in consultation with a medical professional based on the individual patient’s condition and needs.
Depending on the patient’s occupation and daily activities, some individuals may require a swift recovery to regain strength and normal back mobility. In these cases, doctors may recommend surgery to ensure a quick return to work and daily life.
Neurological Complications: In rare cases, a herniated disc can lead to nerve compression and damage. If there are chronic symptoms such as numbness, tingling, limb numbness, or muscle weakness related to the herniated disc, surgical intervention may be necessary to improve these symptoms and prevent further nerve damage.
It is essential that the treating physician assess whether surgical intervention is necessary for each patient individually. This requires a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, symptoms, test results, and radiological imaging. Patients should also be confident in the necessity of the surgery and be prepared for a prolonged recovery and rehabilitation period following the surgery.
Can a Herniated Disc Return After Surgery?
Patients should understand that herniated disc surgery does not guarantee the absence of a recurrence, and the possibility of additional surgery should be considered in case of symptom recurrence. Patients should communicate with their doctor to discuss options and necessary consultations before making any treatment decisions.
A herniated disc occurs when the intervertebral disc, a natural cushion between the vertebrae of the spine, undergoes excessive pressure, leading to irritation of the surrounding nerves. Herniated discs are a common condition, and disc surgery is the primary treatment for this condition.
However, many people may wonder if a herniated disc can return after undergoing surgery. In this article, we will explore the answer to this question and shed light on some related issues.
Herniated Disc Surgery:
During herniated disc surgery, the protruding portion of the intervertebral disc that compresses the nerve root is excised. Pain typically improves immediately after the surgery, or symptoms gradually improve in the days or weeks following the procedure.
Reverting to Previous Symptoms After Surgery:
One of the possible reasons for the return of symptoms related to herniated disc after surgery is the incomplete removal of the herniated disc during the operation. This means that a portion of the disc may remain attached and improperly compress the nerve after the surgery, leading to a recurrence of the symptoms the patient experienced before the surgery. The patient should consult the follow-up doctor if they feel a recurrence of symptoms to determine the correct diagnosis and the suggested treatment steps.
Factors Affecting Surgical Success:
Several factors can affect the success of herniated disc surgery and the prevention of recurrence. Among these factors are the surgical team’s experience and skill, the condition of the herniated disc before surgery, and the patient’s commitment to post-surgery instructions, such as performing necessary exercises and maintaining a healthy lifestyle.
Post-Surgery Condition of the Disc:
One common and important question about disc surgery is whether the procedure leads to the formation of new disc tissue. Patients should be aware that disc surgery does not result in the growth of new disc tissue; rather, its goal is to repair the damaged portion of the disc. The recovery process after surgery takes time for the damaged disc to heal and regain its natural functions.
Can Cervical Disc Herniation Cause Paralysis?
Cervical disc herniation is considered one of the conditions that can cause various problems in the back and neck, and many people wonder if it can lead to paralysis. In this article, we will explore these questions and discuss the impact of cervical disc herniation on movement and muscles.
What Is Cervical Disc Herniation?
Cervical disc herniation is a condition in which there is a bulging or tearing of one of the intervertebral discs located between the vertebrae of the spinal column. This typically occurs in the cervical spine region, which is the lower back area, and sometimes it can happen in the cervical spine region in the neck.
Impact of Cervical Disc Herniation on Movement:
When cervical disc herniation occurs, the affected disc can compress the nerve roots in the spinal column. This compression affects the transmission of nerve signals and can result in chronic back pain and weakness in the muscles surrounding the herniated area.
Can Lumbar Disc Herniation Cause Permanent Paralysis?
In rare cases, lumbar disc herniation can cause long-term damage to the nerve roots. This nerve damage can lead to the interruption of nerve signals responsible for controlling muscles involved in urination and, in some rare cases, even paralysis.
Consequences of Lumbar Disc Herniation:
If lumbar disc herniation is not properly treated, it can lead to long-term complications. It may result in spinal cord dysfunction and the development of partial paralysis in some cases. Additionally, the tear in the disc can extend from the lower back to the middle of the spine, increasing the severity of the condition.
When Is Lumbar Disc Herniation Serious?
The severity of lumbar disc herniation depends on the extent of its impact and the degree of symptoms it causes. If there are severe symptoms such as intense pain, severe muscle weakness, numbness, or tingling in the extremities, lumbar disc herniation may be serious and require immediate surgical intervention.
Treatment for Lumbar Disc Herniation:
Various treatment methods for lumbar disc herniation include physical therapy, targeted exercises, and pain relievers to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. In more severe cases, surgical treatment may be recommended to remove the damaged portion of the disc and relieve pressure on the nerve roots.
It’s important to understand that lumbar disc herniation can lead to mobility and muscle problems, and in some rare cases, paralysis. Therefore, consulting with a specialist doctor and early detection are essential for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Is It Possible to Treat Disc Herniation Without Surgery?
Disc herniation is a common condition where a portion of the disc in the spine slips, causing pressure on the surrounding nerve and resulting in pain. In the past, surgical treatment was the usual approach to address this issue, but in recent years, several non-surgical methods have been developed to manage disc herniation. In this article, we will take a look at some non-surgical treatments available for disc herniation.
- Medical Treatment: Medical treatment is one of the conventional ways to treat lumbar disc herniation. It involves taking medications to relieve pain and reduce inflammation in the affected area. These medications may include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), pain relievers, muscle relaxants, and muscle relaxants.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is another effective method for treating lumbar disc herniation without the need for surgery. Physical therapy includes a set of exercises and physical techniques aimed at strengthening the muscles and improving the flexibility of the spine. Physical therapy may include stretching and muscle strengthening exercises, manual manipulation, and guidance on proper sitting and sleeping posture.
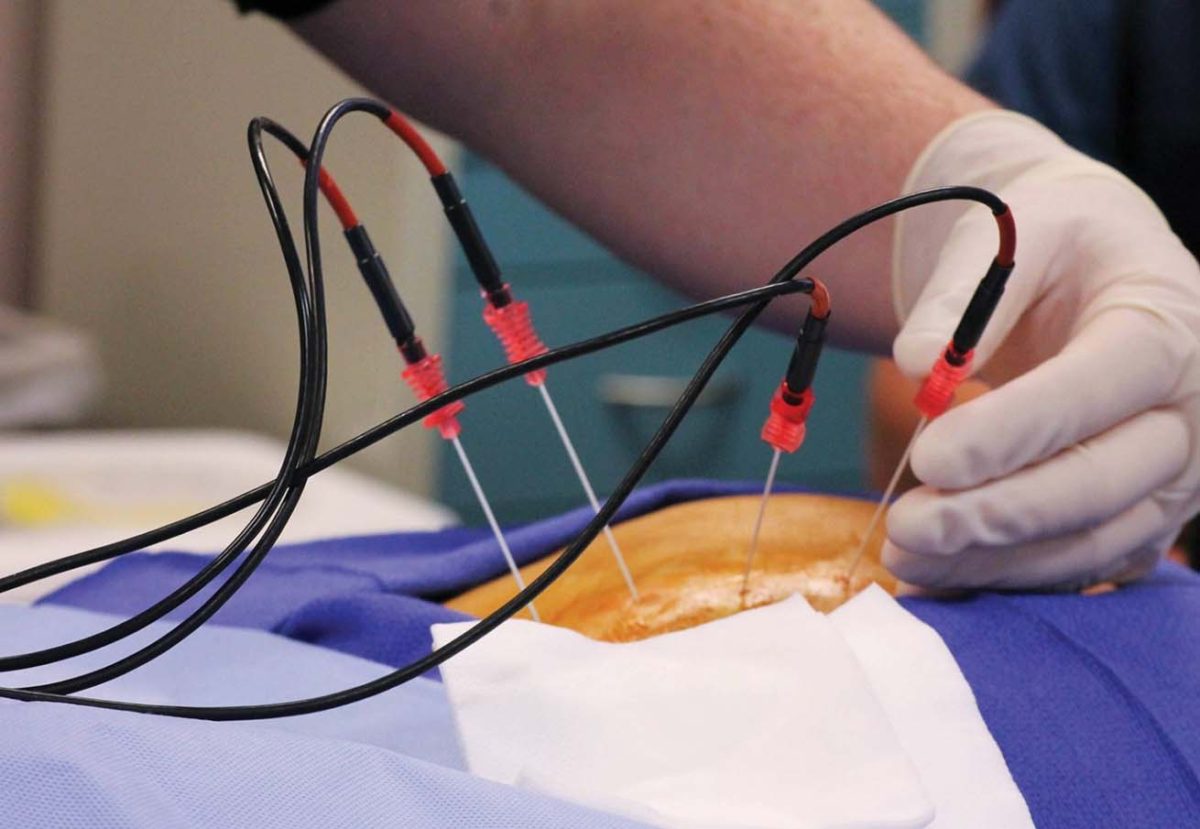
- Electrical Interference: Electrical interference techniques are a common method for treating lumbar disc herniation. These techniques involve applying electrical current through electrodes to the affected area. Electrical interference works to relieve pain, improve blood circulation, and reduce swelling in the spine.
- Laser Therapy: Laser therapy is a modern and effective method for treating lumbar disc herniation. Laser therapy uses lasers to direct light rays to the affected area, stimulating the healing process and reducing inflammation and pain.
- Electrical Fork Therapy: Electrical fork therapy is another method for treating lumbar disc herniation without the need for surgery. This treatment involves using a device that generates electrical currents to stimulate muscles, reduce inflammation, and improve mobility.
In the end, the appropriate treatment for lumbar disc herniation should be determined based on each individual’s condition and the severity of the problem. Individuals with lumbar disc herniation should consult a specialist doctor to assess their condition and guide them towards the best treatment method for their specific case. It’s also important to remember that non-surgical treatment may not be sufficient in some severe cases, and surgery may be required to achieve full recovery.