Is scoliosis operation dangerous?
More information about scoliosis surgery can be found in the following article.
How can scoliosis be treated?
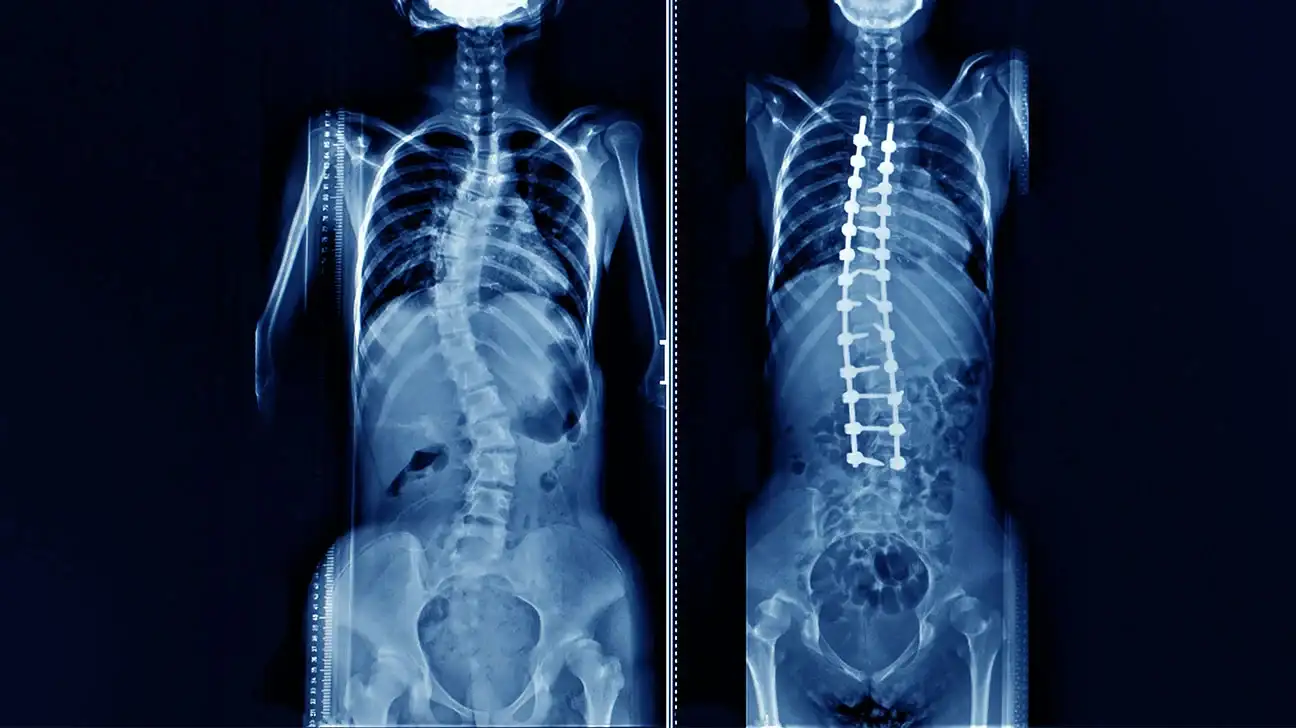
Scoliosis or curvature of the spine is one of the injuries that occur in the spine and affects its shape and appearance and can develop to affect the muscles or nerves in the spinal cord and thus the injured person is unable to bend or walk straight and also causes sharp pain in the lower part from noon.
There is more than one reason that can affect a person and get scoliosis, and the common causes of scoliosis are a birth defect or a neuromuscular disorder, as well as the presence of atrophy in the spinal cord or infection and tumor in the spine and other factors that can increase the chances of developing a curvature in the spine vertebral.
What are the symptoms of scoliosis?
There are some symptoms that appear outwardly on the patient and others that are internal and affect the external shape of the spine. Symptoms associated with scoliosis include:
- Feeling lower back pain.
- An increase in the height of one shoulder.
- The presence of asymmetry in the feet.
- Having difficulty breathing accompanied by chest pain
- A protrusion in one of the hips.
What are the types of scoliosis?
There is more than one type of scoliosis, and it depends on the cause that causes scoliosis in the body, and they can be classified as follows:
- Degenerative scoliosis: It occurs due to aging and mostly affects the lower back.
- Congenital Scoliosis: It is caused by a congenital defect that occurs at birth and is the result of deformities in the spine during growth.
- Unknown Scoliosis: This type of scoliosis does not determine the underlying cause of its infection and represents the largest percentage of cases.
- Neuromuscular scoliosis: This scoliosis occurs as a result of a neuromuscular disorder in the spine that results in a curvature of it and causes a number of other complications.
Scoliosis treatment methods
There are two types of scoliosis, including mild scoliosis, and the symptoms are mild and quickly disappear with growth, and it mostly occurs in children. The other type is severe scoliosis, which is the most severe and has a noticeable effect on the spine and the shape of the back, and it can be treated through the following steps:
- Physiotherapy: The patient should take care of the treatment program that the doctor set for him, which reduces the curvature and limits its increase in the future.
- Brace therapy: Braces can help correct curvature and can be worn while sleeping and awake.
- Surgical treatment: When the patient does not respond to other types of treatment, preparations can begin for the surgical operation that corrects scoliosis and does not develop the injury.
What happens after the scoliosis operation?
After the scoliosis operation, the patient can return to his normal activity within several weeks, and he can return to his full activity, whether at work or school, within a month. Doing exercises.
How to sleep after scoliosis surgery
How to sleep after scoliosis surgery may require some instructions that help the patient feel better and sleep does not affect recovery, and the patient can sleep as follows:
- Sleeping on one side, keeping the knees bent and the arm under the head.
- Sleeping on the back, but lying on the back, bending the knee, and using pillows under the knee should be taken into account.
Does height increase after scoliosis surgery?
Scoliosis can affect the patient’s height and increase it slightly as a result of adjusting the curvature that occurred in the back after scoliosis. Stretching exercises can help improve the patient’s condition, restore the ability to move again, and also obtain normal height.
Is scoliosis surgery serious?
Scoliosis surgery, like other surgeries, can affect the patient and expose him, in rare cases, to risks. Complications associated with scoliosis surgery include:
- The presence of inflammation in the affected part.
- loss of sensation
- Having muscle weakness.
- Difficulty controlling the bladder.
- Partial collapse of the lung.
- The occurrence of clots.