Spinal scoliosis surgery success rate and what to do after it
Scoliosis or scoliosis operation is one of the medical procedures that are performed in cases of curvature of the spine and exposure to scoliosis, and there is a lot of important medical information that you should know about what scoliosis is and how to treat it, and this is what we explain in the following article.
scoliosis
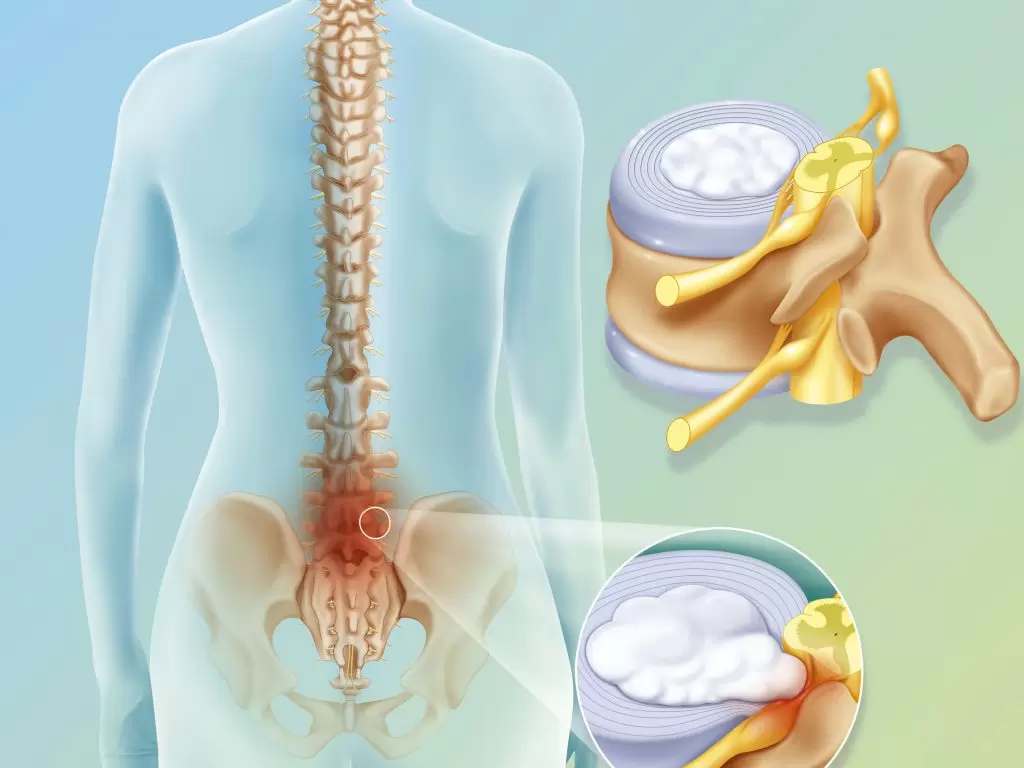
The spine is the main component of the moderation of the body shape, which gives it the ability to move and connects the lower and upper parts of the body, and thus the person is able to change from one position to another or practice sports and the usual daily activities, and the spine consists of several vertebrae in which scoliosis can occur.
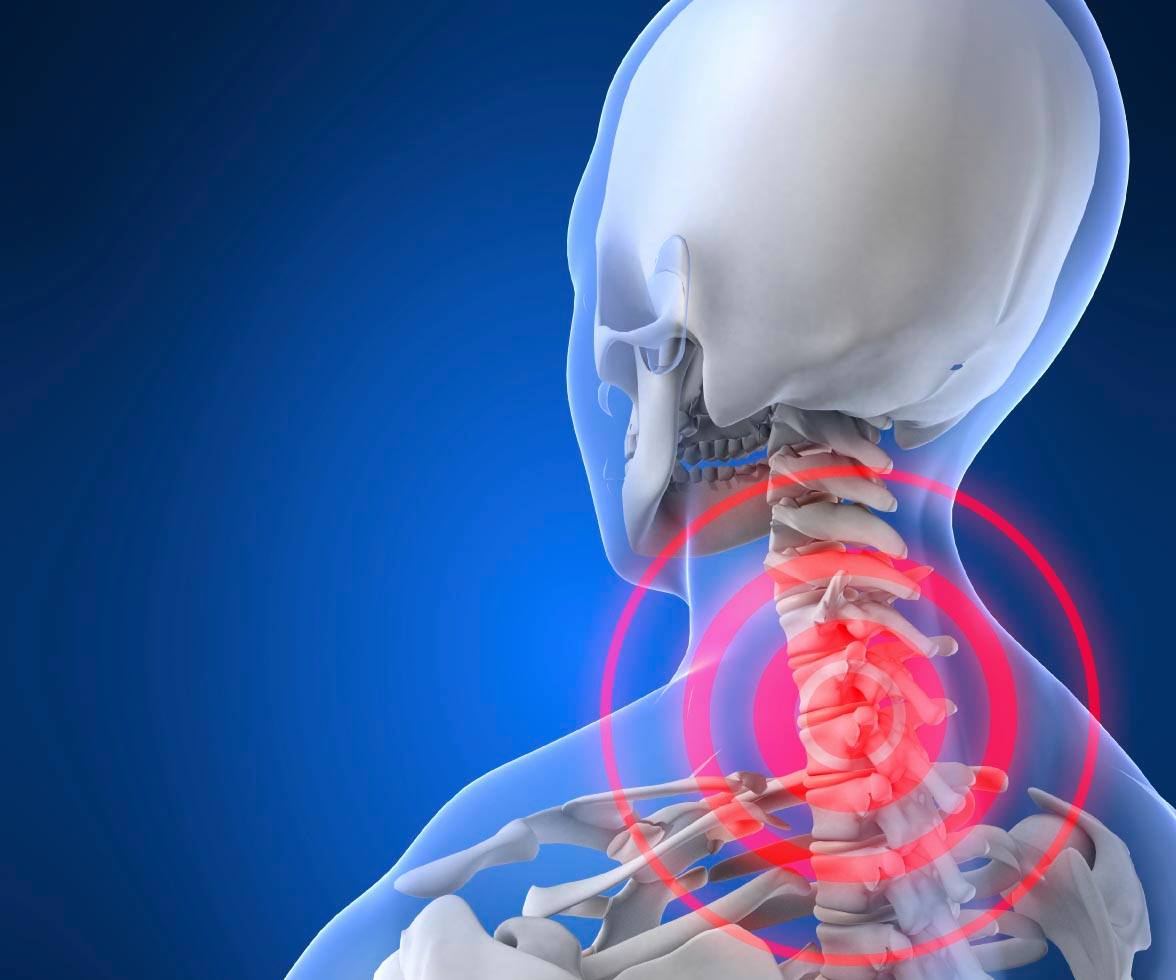
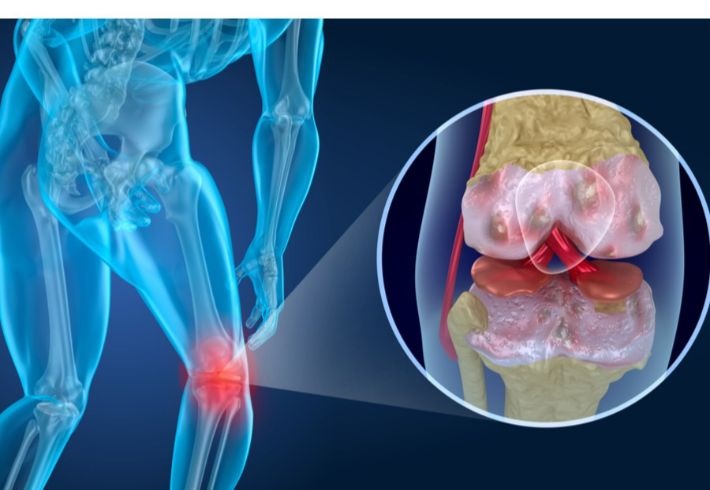
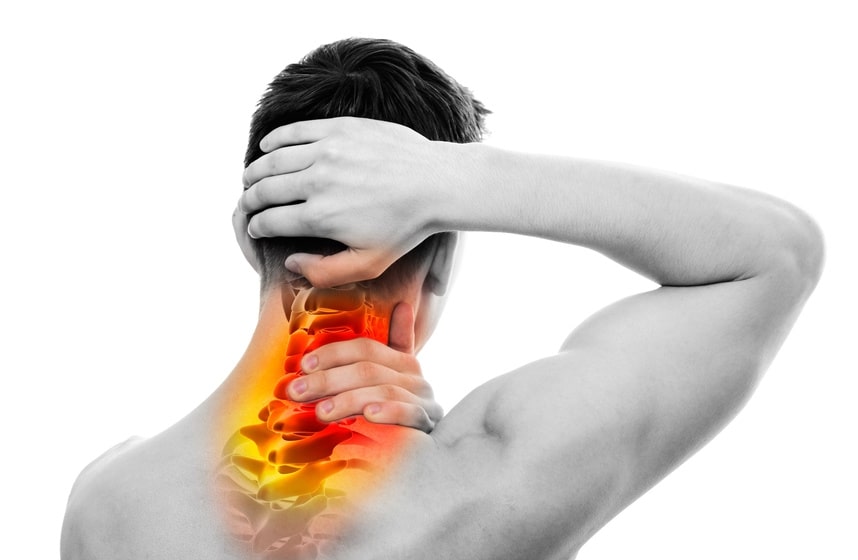
Scoliosis or scoliosis is one of the diseases that affect the back and leads to a tilt or deviation in the natural shape of the spine, and this scoliosis is mostly in the lumbar vertebrae in the lower back or in the cervical vertebrae at the beginning of the back and is more common in the elderly than in children.
Scoliosis affects the shape of the back as a result of the presence of an internal curvature in the vertebrae, which sometimes causes pain to the person, and this curvature is apparent, and the effect can reach the thigh, and the person’s movement is unstable and limp.
What are the causes of scoliosis?
A person can be exposed to scoliosis as a result of scoliosis in the vertebrae, whether lumbar or cervical, in the back, and the deviation is the result of more than one reason, including what is related to daily activity and others as a result of disease, and the condition of the most common causes of scoliosis in the spine can be identified, which are:
- Excessive weight gain (obesity): People who are overweight can be at a higher risk of scoliosis due to overloading the abdomen and buttocks.
- Lack of physical activity: Not doing exercise or lack of daily movement, in general, is one of the reasons that can lead to muscle weakness and lack of support for the spine, and thus the back is vulnerable to scoliosis.
- Sitting incorrectly: Sitting is one of the positions that must be paid attention to in order not to cause muscle spasms and tightening, and thus it is difficult for the spine to remain in its correct position, and scoliosis can occur in the back over time.
- Infection with a disease in the spine: There is more than one disease that can lead to scoliosis or curvature in the spine, including osteoporosis, herniated discs, dwarfism, as well as inflammation or tumor of the spine.
Symptoms of scoliosis
A person can suffer from scoliosis or scoliosis for more than one reason, as we mentioned, scoliosis has visible signs of a change in the shape of the body, and others that affect the joints and the person’s ability to move in general, and the doctor begins to identify these symptoms during the physical examination of the injured person.
Here are some of the symptoms that appear in a person with scoliosis, as follows:
- One shoulder higher than the other.
- Hip discrepancy.
- Stiffness in the muscles.
- Constant back pain.
- A tilt to one side.
- A change in the shape of the buttocks and their protrusion outwards.
- The presence of pain in the leg and foot.
- Inability to sit or stand upright.
What is the risk of scoliosis?
The danger of scoliosis lies in the complications that a person may suffer from in the event of scoliosis and failure to start treatment early or the diagnosis is delayed, and thus the symptoms become clearer and there is an impact on the person’s ability to walk and the apparent shape of the back in general.
A person may be exposed to some risks as a result of scoliosis in the back vertebrae, and these complications are:
- The occurrence of lung problems is a result of weakness in the rib cage, and thus the person is not able to breathe normally.
- The heart is weak and does not pump blood well, which affects the extremities and the blood supply to the rest of the body.
- The occurrence of severe back pain continues, and the person is unable to bend, and there are sitting and standing positions that he cannot do.
- One of the shoulders is higher than the other, there is a significant change in the appearance of the hip, and the torso leans to one side.
Can scoliosis be cured?
Yes, there is a treatment for scoliosis, and in some cases, the patient does not resort to treatment, and this is in the case of a mild injury that does not affect the body or cause complications that cannot be controlled, and also in the event that the patient’s condition does not develop for the worse, but in the event that the symptoms began to increase The injured person should be returned to the attending physician immediately.
How can scoliosis be treated?
Scoliosis can be treated by working to improve the patient’s condition, and this is by working on some steps that help the patient to be in a better condition, namely:
- Take appropriate analgesics that relieve pain.
- Work on doing the physiotherapy prescribed by the doctor.
- Commitment to exercises that help return the back vertebrae to normal.
- It is possible to work on reducing weight because obesity negatively affects the vertebrae and weakens the muscles, thus increasing scoliosis in the back.
- The use of auxiliary tools and devices improves the state of bending in the back, especially when the smaller dental work is affected.
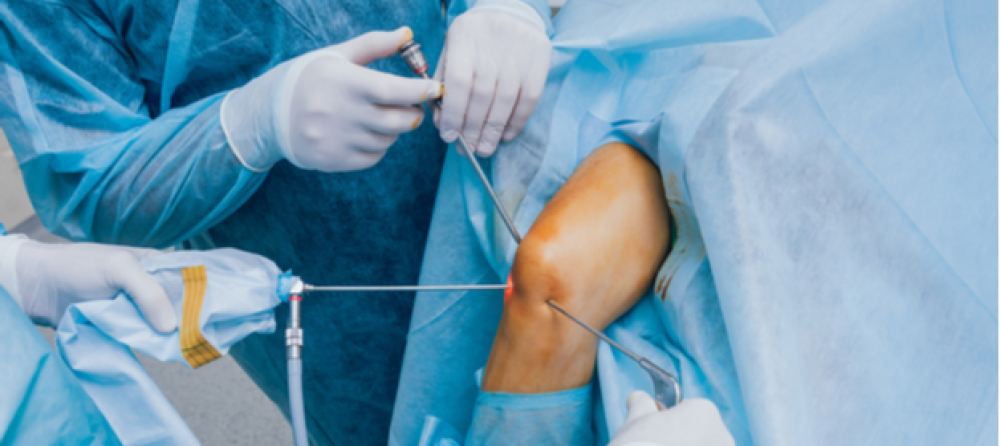
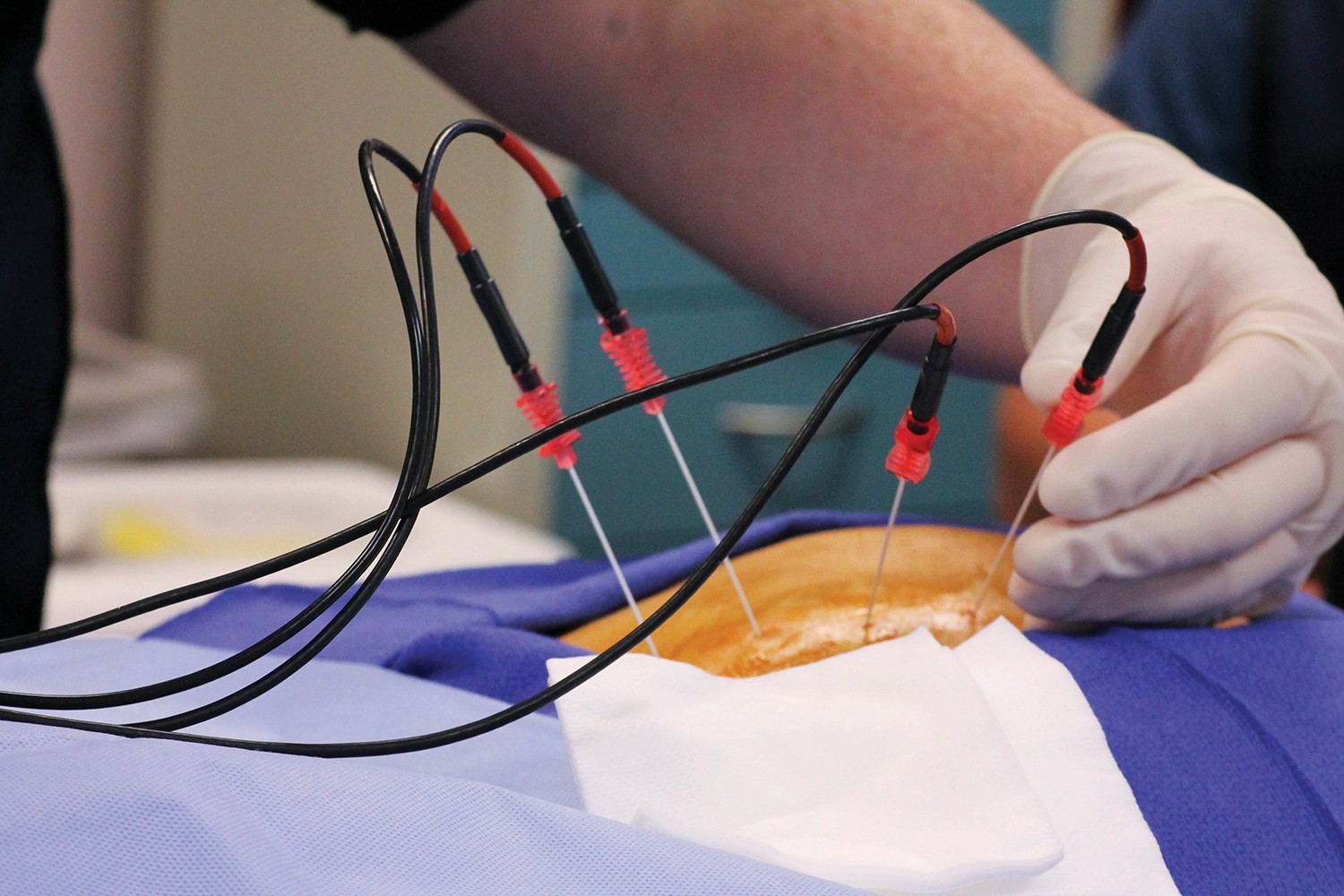
- Performing surgery in case of failure to respond to other steps in treatment and the effect of scoliosis on the vertebrae and nerves.
Spinal scoliosis exercises
The patient must do some exercises, including squats or “plank” exercises, which mainly work to strengthen the muscles of the abdomen and back and thus give the necessary support to the spine to return to its normal shape.
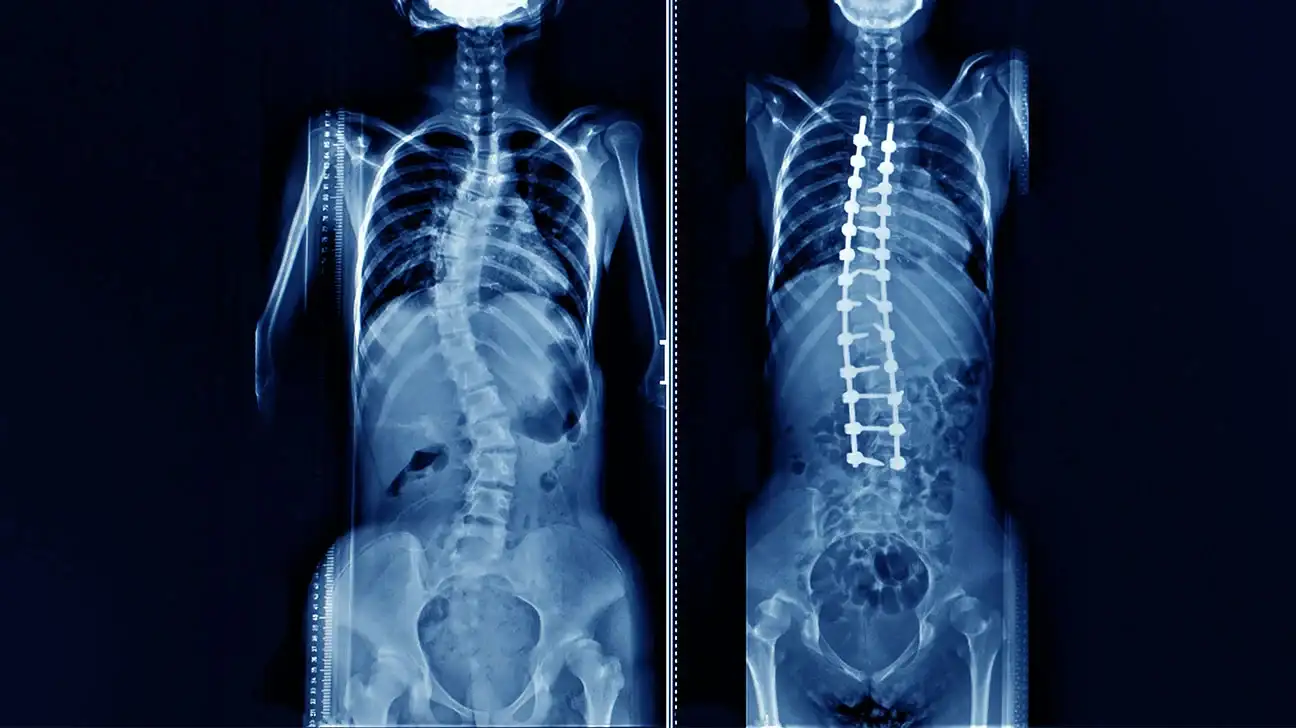
Spinal scoliosis operation
Performing surgery in the spine to fix the scoliosis is sometimes necessary, especially when scoliosis affects a person’s movement and ability to stand, and there is more than one surgery that can be performed to correct scoliosis in the spine, which are:
- Vertebral fusion: Two or more vertebrae can be combined in order to stabilize and strengthen the spine and fix its curvature.
- Removing the vertebral plate: Work is done to remove part of the bone in the spine, which relieves pressure on the nerve as a result of the warp.
- Spinal discectomy: In this case, the surgeon removes one of the intervertebral discs, which reduces the patient’s feeling of pain as a result of pressure on the spinal cord.
What happens after the scoliosis operation?
After the scoliosis operation, the patient must follow some steps and instructions that the doctors explained in order for the recovery to be faster and to avoid complications, and these instructions are:
- Pay attention to the patient’s diet and work to improve its quality.
- Attention to medical follow-up after the operation so that no complications occur.
- Reducing the activities of the patient in the first weeks of surgery.
- Some patients may need a back brace after the process, which is removed when improving.
- The patient can return to work or study about a month after the surgery.
- Do appropriate exercise and physical therapy for the person some process.
What is the success rate of spinal curvature surgery?
Many recent studies have confirmed that the success rate of spinal curvature is high, reaching 100% in many cases, and the patient can return to his activity after about 4 weeks of surgery, depending on his health condition, age, and the extent of adherence to the instructions set out by the doctors.
Is spinal adjustment surgery dangerous?
Spine surgeries in general are considered among the important surgical procedures that require the experience of the doctor, and the patient must be careful when choosing the surgeon who will undergo the scoliosis operation, so that he is not exposed to the risks that follow the surgery, including the following:
- Bleeding at the site of injury.
- Back pain back again.
- A bacterial infection in the back.
- Numbness in the lower extremities.