Learn About the Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment of Bone and Joint Infections
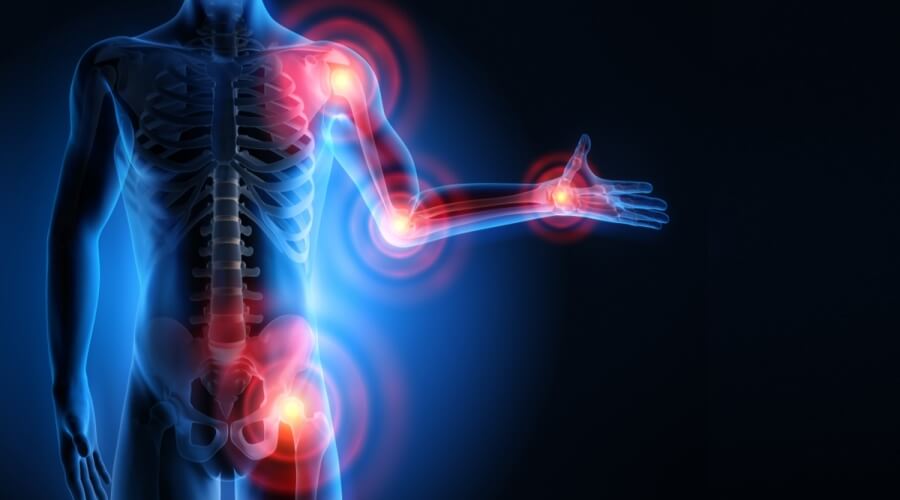
Symptoms of Bone and Joint Infections
Symptoms of bone and joint infections can vary and may differ from one case to another, but there are some common symptoms that may indicate the presence of inflammation in the bones and joints. Here is a list of the most prominent of these symptoms:
- Severe Pain: Patients may experience severe pain in the affected joints, and the pain can be continuous or intermittent, increasing during movement or when touching the affected joint.
- Swelling and Redness: Bone and joint inflammation may be accompanied by swelling and redness in the affected area, and the swelling can be noticeable and painful.
- Difficulty in Movement: Patients may have difficulty moving the affected joint and may feel stiffness and rigidity in the joint, affecting their ability to perform daily activities easily.
- Warmth and Heat: Patients may feel warmth and heat in the affected joint, and the skin around the joint may be redder than other areas.
- Unusual Sounds: Patients may notice an unusual sound or crackling when moving the joint, which may result from the bones in the affected area rubbing against each other.
- Muscle Weakness: In some cases, patients may experience weakness in the muscles surrounding the affected joint, affecting the strength and mobility of the joint.
- Bone Swelling: In cases of severe bone inflammation, swelling may occur in the bone itself, and this swelling can be noticeable and painful.
It is important to consult a doctor if any of these symptoms appear, as the doctor can diagnose the patient’s condition and prescribe the appropriate treatment. Proper diagnosis and treatment of bone and joint infections are essential to avoid complications and the progression of the condition.
How to Get Rid of Bone Inflammation:
Taking Care of Nutrition: Consume balanced meals rich in vitamins and minerals essential for bone health, such as calcium and vitamin D. Eat foods rich in omega-3 fatty acids, such as fatty fish and nuts, to maintain bone health. Exercise Regularly: Engage in appropriate exercises for bone health, such as walking, cycling, and weight lifting. Consult a doctor or fitness trainer to determine suitable exercises for your condition. Maintain an Ideal Weight: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces the pressure on the bones and lowers the risk of bone inflammation. Eat healthy, balanced meals and exercise regularly to maintain an ideal weight.
Avoiding Smoking: Smoking has a negative impact on bone health and increases the risk of bone inflammation. Quit smoking and consult a doctor for the necessary support to achieve that.
Getting an Adequate Amount of Sleep: Good sleep helps in the renewal and rejuvenation of cells and tissues, including bones. Try to get 7-8 hours of good sleep every night to support bone health.
Consulting a Doctor: In case of recurrent or worsening symptoms of bone inflammation, it is essential to consult a specialized doctor for diagnosis and the appropriate treatment. Treatment may include anti-inflammatory medications, pain relievers, and physical therapy.
Maintaining Movement and Physical Activity: Avoid sitting for long periods and move your body regularly to maintain muscle and joint flexibility. Regularly perform stretching and muscle strengthening exercises to strengthen the bones and improve their mobility.
What Are the Causes of Bone and Joint Pain?
Here is a long list of causes of bone and joint pain:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the most common joint diseases and causes swelling and pain in the joints.
- Gouty Arthritis: It occurs due to the accumulation of uric acid in the joints and results in severe pain and swelling in the joints.
- Osteoarthritis: It occurs due to the erosion of joint cartilage and causes continuous pain and stiffness in the joints.
- Autoimmune Arthritis: It occurs due to an immune system reaction and causes pain and swelling in the joints.
- Overexertion: Overexertion from intense activities or excessive use of joints can result in temporary pain and swelling in the joints.
- Physical Injury: Fractures or bruises can cause pain in the bones and joints.
Bone Diseases: Conditions such as bone inflammation, gout, and advanced bone diseases can cause bone and joint pain.
Infectious Diseases: Bacterial and viral joint inflammation can lead to joint pain.
Genetic Factors: Some genetic diseases like juvenile arthritis can result in joint pain.
Hormonal Changes: In some cases, hormonal changes like menopause can cause bone and joint pain.
Psychological Factors: Psychological stress and tension can exacerbate bone and joint pain.
Environmental Factors: Prolonged exposure to cold or humidity can increase bone and joint pain.
Dietary Factors: Certain foods like red meat and high-fat foods can exacerbate joint inflammation and cause joint pain.
Age-Related Factors: As you age, the likelihood of developing bone and joint issues such as arthritis and cartilage erosion increases.
Genetic Factors: Some genetic diseases like hereditary rheumatoid arthritis can result in bone and joint pain.
It’s best to consult a specialized doctor for diagnosing the cause of pain and determining the appropriate treatment.
Does Bone Inflammation Show Up in Blood Tests?
Bone inflammation is a condition that affects the bones and causes inflammation in them. Bone inflammation is usually diagnosed through a patient’s medical history and a comprehensive physical examination. However, blood tests may also be used to detect signs of bone inflammation and identify the organisms causing the inflammation.
Blood tests can measure the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) in the bottom of a specialized tube. The levels of this protein in the blood rise when the body is affected by a condition that causes inflammation. Therefore, the C-reactive protein (CRP) blood test can be used to detect inflammation in the body due to a serious health condition.
However, it’s important to note that a blood test alone is not conclusive for diagnosing bone inflammation. Additional tests such as X-rays or laboratory blood tests may be required to determine the cause of inflammation and confirm the diagnosis.
Therefore, if you suspect you have bone inflammation, it’s essential to consult a doctor for the necessary diagnosis. Treatment depends on the cause and severity of bone inflammation and may include medication, physical therapy, and in some cases, surgery.
Feel free to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan for your condition.
What Is the Difference Between Bone Inflammation and Joint Inflammation?
Causes: Bone Inflammation: Occurs due to roughness of the bones themselves and can result from aging and cartilage damage. Joint Inflammation: Occurs due to inflammation of the joints themselves, causing swelling and pain in the joints, potentially affecting their movement and function.
Symptoms: Bone Inflammation: Characterized by joint pain and stiffness, worsening with age. Joint Inflammation: Characterized by swollen and tender joints, potentially accompanied by redness and warmth in the affected joints.
Types: Bone Inflammation: Includes osteoporosis, ankylosing spondylitis, reactive arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and thumb arthritis. Joint Inflammation: Encompasses rheumatoid arthritis, infectious arthritis, gouty arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and reactive arthritis.
Impact on Mobility and Function: Bone Inflammation: May affect joint mobility and reduce flexibility, leading to difficulties in performing daily movements. Joint Inflammation: Can significantly impact joint mobility and function, causing movement difficulties and hindering daily activities.
Treatment: Bone Inflammation: Typically requires a treatment focused on pain relief and improved mobility, which may include taking pain-relieving medications and undergoing physical therapy. Joint Inflammation: Requires a comprehensive treatment plan that includes pain relief, inflammation reduction, and improved joint mobility. This may involve taking anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and appropriate exercises.
In conclusion, while there may be some similarities between bone inflammation and joint inflammation, they differ in causes, symptoms, types, and treatment. Therefore, it’s essential to consult a specialized doctor for an accurate diagnosis and the appropriate treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of Arthritis and Its Treatment?
Many people suffer from arthritis, a condition that causes swelling and joint pain. Arthritis symptoms can appear in any joint in the body, including the hands, feet, knees, hips, and shoulders.
Arthritis symptoms include continuous pain in the affected joints, which worsens with movement. Stiffness in the joints and difficulty moving them can also be experienced. The affected joints may be swollen, red, and warm to the touch. Arthritis can also be accompanied by general weakness in the body and a feeling of fatigue.
There are several ways to treat arthritis, and the options vary depending on the type and severity of the disease. Non-surgical treatment may include taking pain-relieving medications like non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), which help alleviate pain and swelling. Selective cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) inhibitors can also be used to relieve pain without affecting inflammation.
In addition to medications, physical therapy can be beneficial for some types of arthritis. Exercise can help improve range of motion and strengthen the muscles around the joints. The doctor may also recommend applying ice or localized heat to alleviate pain and swelling.
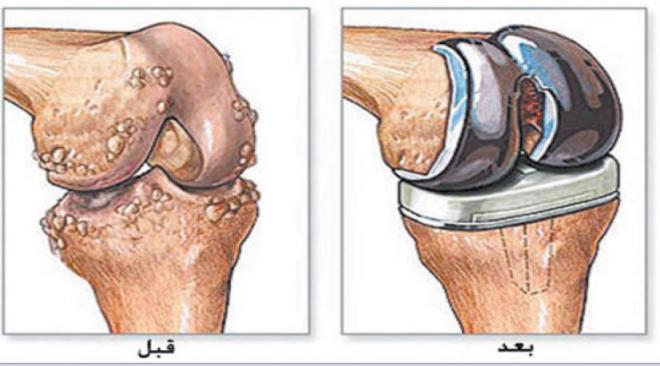
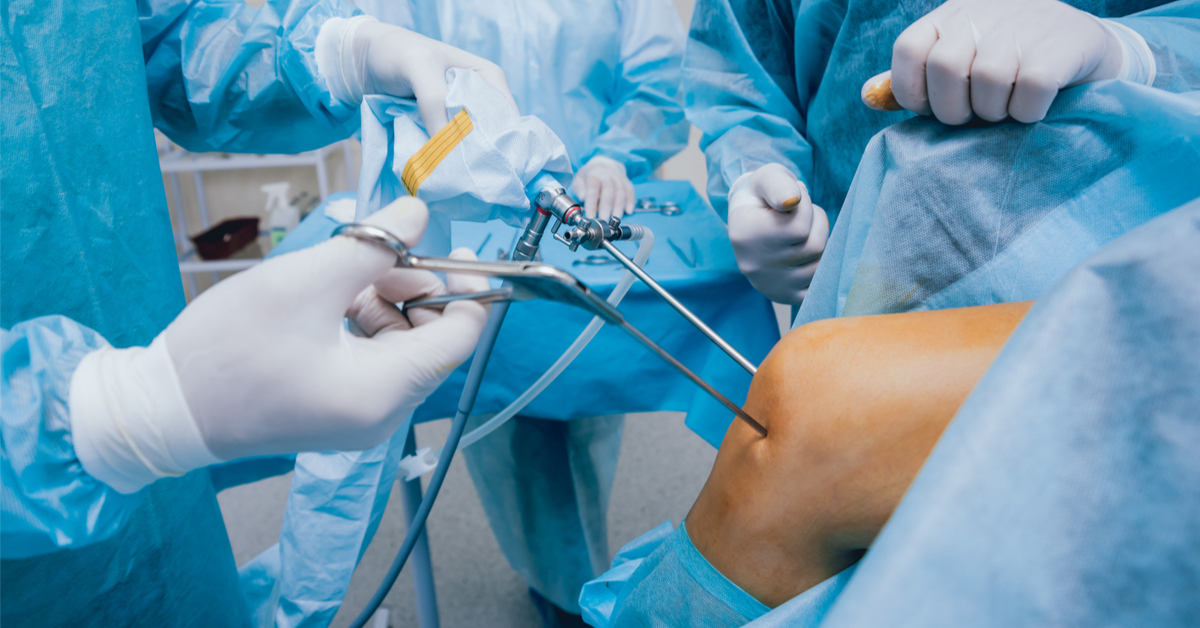
In cases of severe and chronic arthritis, surgical treatment may be required. Surgical treatment can involve repairing the affected joint or replacing it with an artificial joint. The decision for surgery is based on the doctor’s evaluation of your condition and the impact of arthritis on your daily life.
It’s essential to collaborate with your healthcare team to determine the best treatment options for your condition. Don’t hesitate to ask questions and discuss any concerns you may have. Proper treatment can help alleviate symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Does Vitamin D Deficiency Cause Joint Pain?
Vitamin D is an essential nutrient for bone and muscle health. It plays a crucial role in calcium absorption and regulation in the body. However, vitamin D deficiency can have a negative impact on joints and may cause joint pain and muscle cramps.
Here is a list of possible symptoms of vitamin D deficiency and its effect on joints:
- Joint Pain: Joint pain is considered one of the common symptoms of vitamin D deficiency. The pain can be continuous or intermittent and can affect different joints in the body.
- Joint Inflammation: Vitamin D deficiency may increase the risk of joint inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis and gouty arthritis. Joint inflammation can lead to pain, swelling, and difficulty in movement.
- Weak Muscles: Vitamin D deficiency can affect muscle function and cause muscle weakness. Individuals with vitamin D deficiency may have difficulty in performing daily activities and moving freely.
- General Pain: Vitamin D deficiency may have an impact on the immune system, increasing the risk of widespread pain and continuous fatigue.
- Osteoporosis: Vitamin D deficiency is one of the contributing factors to osteoporosis. When there is a deficiency of vitamin D in the body, it becomes challenging for bones to absorb calcium properly, leading to weakened bones and an increased risk of fractures.
To avoid vitamin D deficiency and maintain joint health, it is recommended to consume foods rich in vitamin D, such as fatty fish, egg yolks, vitamin D-fortified milk, and regular exposure to sunlight.
It is essential to consult a doctor if you experience troublesome symptoms and suspect vitamin D deficiency. The doctor may conduct tests to determine your vitamin D levels and prescribe appropriate treatment if necessary.
Please note that this information is for reference purposes only and does not substitute for consulting a specialized physician.
Can Arthritis Be Cured?
Yes, arthritis can be managed and symptoms can be alleviated. Below is a detailed list of ways that can help improve symptoms and enhance the quality of life for arthritis patients:
- Consuming Vitamin K-Rich Foods: Spinach and broccoli are vegetables rich in this vitamin, which promotes bone health and reduces the progression of osteoporosis.
- Consuming Vitamin C-Rich Foods: Oranges, grapefruits, strawberries, pineapples, kale, papaya, lemons, cauliflower, turnips, and beans all contain vitamin C, which supports joint health and reduces arthritis symptoms.
- Drinking Green Tea: Green tea contains antioxidants and nutrients that can help reduce inflammation in the joints. Eating Oats: Oats are whole grains that contain compounds that can reduce joint inflammation.
- Following a Balanced Diet: It is recommended to follow a diet similar to the Mediterranean diet, which includes consuming fiber-rich vegetables, omega-3 fatty acid-rich fish, and healthy fats.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can strengthen the muscles surrounding the joints and improve their mobility.
- Maintaining an Ideal Weight: Weight management reduces the pressure on the joints and minimizes deterioration.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen muscles and improve joint flexibility.
- Heat and Cold Therapy: The localized application of heat or cold can help alleviate pain and swelling in the joints.
- Relaxation and Stress Reduction: Psychological stress can exacerbate symptoms, so practicing relaxation and meditation techniques is advised to reduce stress.
By adhering to these guidelines and recommendations, recovery from arthritis may be possible. However, patients should consult a specialized doctor to assess their health condition and receive appropriate treatment.
Is Numbness a Symptom of Arthritis?
Arthritis is a health condition that leads to inflammation and pain in the joints. While numbness may not be a common symptom of this condition, it can occur in some cases. In this extensive list, we will explore the possibility of numbness being one of the symptoms associated with arthritis.
- Vitamin B12 Deficiency: Vitamin B12 deficiency is one possible cause of numbness in the body. Some studies suggest that individuals with arthritis may be prone to this deficiency. Patients experiencing numbness and arthritis should check their vitamin B12 levels and seek appropriate treatment.
- Vitamin D Deficiency: Another potential cause of numbness in the body could be vitamin D deficiency. Some studies indicate that individuals with arthritis may be at risk for this deficiency. It is advisable to undergo tests for vitamin D levels and consult a doctor for proper treatment.
- Physical Fitness Weakness: Numbness in the body may result from physical fitness weakness. Individuals with arthritis often struggle to engage in physical exercise and maintain their physical fitness. Physical fitness weakness can lead to reduced blood flow and oxygen supply to the nerves, causing numbness.
- Sleep Disturbance: Many arthritis patients experience sleep disturbances such as insomnia and frequent awakenings during the night. Sleep disturbances may contribute to an increased sense of numbness in the body.
In summary, numbness can be one of the symptoms associated with arthritis. However, patients should consult a doctor for a precise diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Treatment may involve taking dietary supplements and engaging in suitable exercises to improve physical fitness and reduce numbness.
Is There an Antibiotic for Bones?
Bones are one of the most crucial parts of the human body, playing a vital role in supporting the skeletal structure and protecting vital organs. While bones are not easily susceptible to infection, inflammation in the bones can occur due to injury or other factors.
In the case of bone inflammation, antibiotic treatment is necessary to combat the infection and eliminate accumulated pus. However, there is no specific antibiotic used exclusively for bones. The choice of the appropriate antibiotic depends on the type of infection and the bacteria causing it.
Among the antibiotics that may be used to treat bone infections and eliminate pus, some examples include:
Penicillin: Penicillin is one of the oldest antibiotics used and is effective against various bacterial infections. Cephalosporins: This category of antibiotics includes several varieties such as cefazolin, cephalexin, and others, and they are effective in combating bacterial infections. Clindamycin: This antibiotic is used in some cases to treat bacterial infections in the bones. Vancomycin: This antibiotic is considered an option for treating bacterial infections in the bones.
It should be noted that the use of antibiotics requires a prescription from a qualified doctor, and they should not be used without medical consultation. Antibiotics should also be used according to prescribed dosages and treatment durations.
In conclusion, individuals suffering from bone inflammation or any other infection should consult a specialized orthopedic surgeon to evaluate the condition and provide appropriate treatment, including the use of antibiotics if necessary.