Learn about the causes of rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis, or as it is called rheumatoid arthritis, is an autoimmune disease and has many causes and symptoms, as well as several prevention methods, and all details will be mentioned in the following.
Rheumatoid causes
Rheumatoid arthritis, or as it is known as rheumatoid arthritis, is one of the diseases that women are exposed to more often than men, at a rate of two to three times that it occurs mostly in middle age, and rheumatoid arthritis is one of the autoimmune diseases that occur as a result of the body attacking its cells.
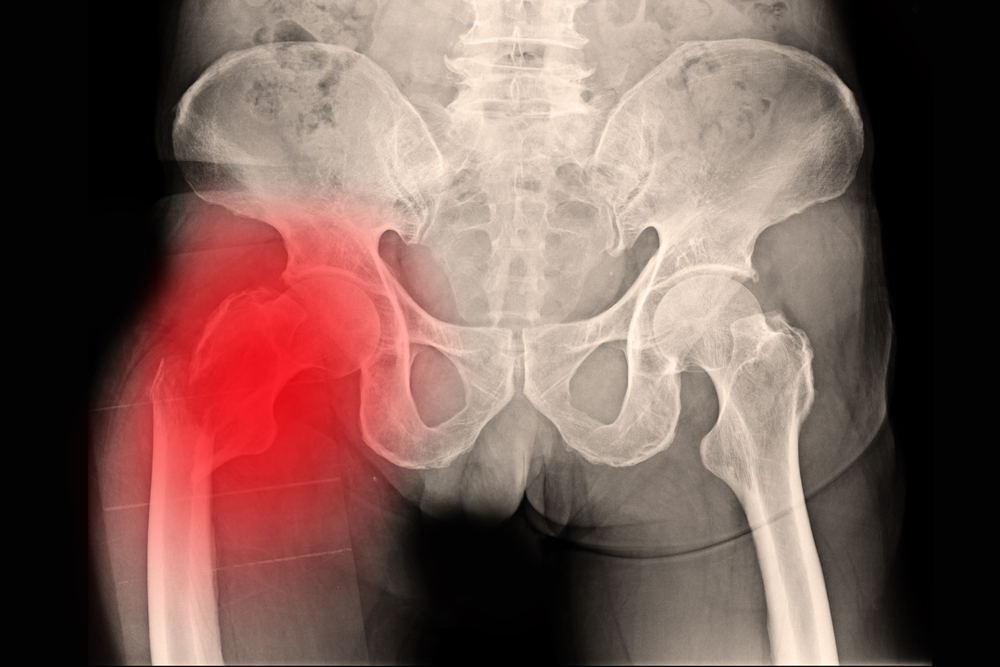
Rheumatoid arthritis causes pain in the joints, and it may affect more than one organ at the same time, including the heart and lungs. It may also reach the eye and cause severe inflammation and redness. However, rheumatoid arthritis often affects joints, especially small ones, such as fingers, which makes the patient unable to perform simple daily activities.
What are the causes of rheumatoid disease?
Rheumatoid arthritis occurs as a result of the presence of white blood cells responsible for attacking foreign bodies attacking the cells of the body and the membranes that surround the organs, causing erosion and damage to them, especially in the synovial membrane of the joints, and thus resulting in protrusion and deformities in the joint.
There are more than one cause and a risk factor that increases the possibility of a person developing rheumatoid arthritis, including:
- Age: A person’s age, especially those between the ages of 40 and 60, may be more susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis.
- Family history: You may be at risk of rheumatoid arthritis if someone in your family has had rheumatoid arthritis before.
- The gender of the person: Scientific research has shown that women are more susceptible to rheumatoid arthritis than men, and the infection can be in the works of young people or older people.
- Smoking: If you are a smoker or you mix with them, the lungs may be affected a lot, which increases the chance of rheumatoid arthritis and resulting deformities.
- Obesity: a person’s weight gain negatively affects more than one organ in the body, which makes the person face the risk of rheumatoid arthritis.
How is rheumatoid arthritis diagnosed?
There is more than one way to know whether rheumatoid arthritis is positive or negative, including the following:
- The doctor begins with a clinical diagnosis of the patient and asks about symptoms that have appeared in the past few weeks.
- The specialist doctor requests blood tests for the erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
- Perform a blood test for rheumatoid factor.
- Perform MRI and x-rays.
- Conducting analyzes of the immune system.
How do you know that you have rheumatoid arthritis?
A rheumatoid sufferer shows some symptoms that inform him of his infection and quickly communicate with an orthopedist, especially if he finds that the symptoms are getting worse or persist with him for more than several weeks, and the speed of discovering the disease and starting treatment contributes greatly to the body’s response to treatment and increase the chances of recovery.
What are the symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis?
Rheumatoid symptoms appear on the person gradually, especially if the injury is in the joints and usually occurs in the joint of the hand, knee, or foot, and rheumatoid affects the general activity of the person and his ability to carry out daily activities such as walking or standing.
There are more than one sign and symptom that appears on rheumatoid arthritis, including the following:
- A feeling of general fatigue and stress in the body.
- A feeling of pain in the joint in the early morning periods.
- The presence of swelling and swelling in the rheumatoid-affected area lasts for a while.
- An increase in the redness of the affected part and the appearance of some dark spots.
- Difficulty moving the affected joints and severe pain when moving between sitting and standing.
- Difficulty breathing and a feeling of constant pain that starts mild and then intensifies.
- If the previous symptoms persist for up to 6 weeks, you should refer to a specialist doctor immediately.
Are there complications of rheumatoid arthritis?
In some cases, the diagnosis of which is delayed, or some non-benign complications may occur, so it is important to refer to your specialist doctor in the event of swelling, redness, and pain in the joints that lasted for more than a month.
Here are some complications for a rheumatoid patient:
- The presence of osteoporosis and great weakness in the joints.
- The appearance of some rheumatic nodes and deformities in the joints as a result of their inflammation and erosion.
- The feeling of dryness in the eyes and mouth is a result of Sjögren syndrome, which modifies the level of moisture in the body.
- The presence of heart problems affects the arteries and may cause them to harden.
- Rheumatoid arthritis also affects the lung, especially in smokers, and may lead to infections and deformities in the lung tissue.
How to avoid rheumatoid disease?
The American Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) provided some guidelines and tips that help avoid rheumatoid arthritis and limit its spread, especially in women, who are most at risk of rheumatoid arthritis, and the instructions were as follows:
- Completely avoiding smoking or mixing with smokers (passive smoking) because it is one of the risk factors that increase the rates of rheumatoid arthritis due to its negative impact on the body.
- Maintaining normal body weight is one of the tips that reduce rheumatoid arthritis, and a healthy, balanced diet can help maintain weight.
- Exercising can help avoid rheumatoid disease because continuous exercise increases the body’s efficiency in dealing with diseases.
- Periodic follow-up for rheumatoid check-ups, especially if you have a person with the disease in the family because prevention at an early stage pays off better.