Lumbar Spinal Discs: Everything You Need to Know to Ensure Your Back’s Safety! What is the lumbar spinal disc?
Lumbar Spinal Discs
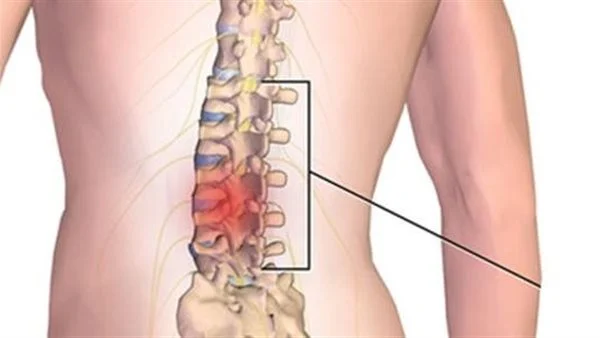
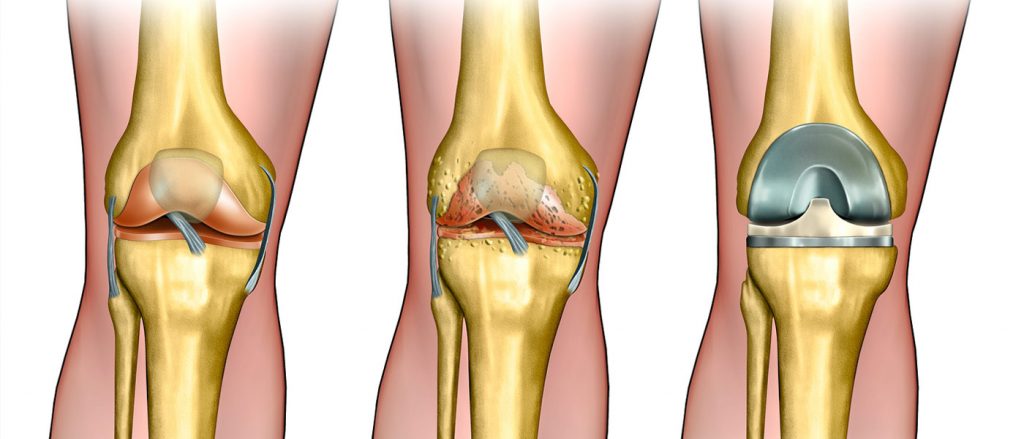
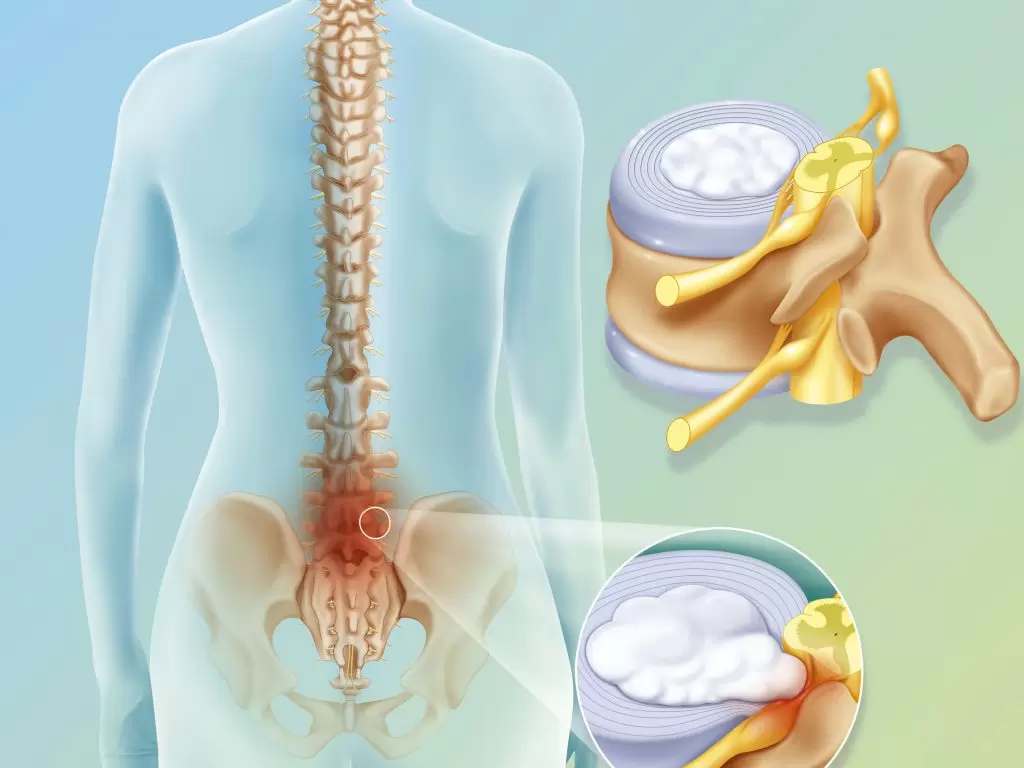
The lumbar spinal disc is a type of common and widespread disc herniation. This herniation occurs when there is a protrusion of the cartilaginous discs that are located between the lumbar vertebrae in the spine. The symptoms of this herniation vary in severity, where they can range from moderate back and buttock pain to severe pain that requires immediate medical intervention in some cases.
The lumbar disc can cause many painful problems and symptoms. When the disc protrudes and presses on the nerves and spinal cord, sharp pain in the back and limbs can occur, and may also cause numbness and tingling in the limbs. Lumbar disc herniation can affect a person’s movement and ability to perform daily activities normally.
To treat lumbar disc herniation, artificial disc is used as a substitute for the natural cartilage. The artificial disc works to protect the spine from further degeneration and ensure its stability in the long term. Spinal fusion surgery can also be performed to stabilize the vertebrae affected by disc herniation, where the vertebrae are permanently fused to achieve spinal stability.
Possible causes of lumbar disc herniation include incorrect movements during work or exercise. Excessive stress on the spine and the cartilaginous discs can damage them and cause a protrusion. In addition, the meniscal cartilage in the knee can be affected by disc herniation, leading to increased knee roughness and exacerbation of associated problems.
Overall, lumbar disc herniation is a common health issue that affects many people. Patients with degeneration of the spinal vertebral discs should adhere to appropriate treatment and medical guidelines to alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life. Other treatments may include physical therapy, strengthening the muscles surrounding the spine, and conservative treatment techniques.
In summary, lumbar disc herniation is a common and painful health problem that affects many people. Patients should adhere to the appropriate treatment and medical guidelines to alleviate symptoms and improve their quality of life.
Is Lumbar Disc Herniation Dangerous?
Lumbar disc herniation is a common condition that occurs when the discs between the vertebrae in the spine get compressed in the back region. This herniation is a real danger and can negatively impact the life of the patient and their daily activities.
It is one of the most common causes of back and spinal pain and can lead to complications in the patient. A lumbar disc herniation occurs when one of the vertebrae moves forward (slips) over the vertebra below it, which can cause pressure on the spinal cord and the nerves emerging from the spinal cord. This pressure may cause acute pain in the back, and the pain may extend down one leg.
Certain factors contribute to the risk of lumbar disc herniation, such as performing routine activities in the wrong ways repeatedly, like lifting heavy objects improperly, or sitting in incorrect postures for extended periods. Also, having excess weight increases the pressure on the vertebrae in the lower back, which increases the risk of lumbar disc herniation.
For the treatment of lumbar disc herniation, the patient must seek appropriate treatment methods. This may include physical therapy to strengthen the back muscles and improve flexibility, using pain relief medications, heat or cold treatment, and in some severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to relieve pressure on the nerves and spinal cord.
In general, it can be said that lumbar disc herniation is a serious condition that should be dealt with seriously. People should take the necessary precautions to avoid this condition, such as maintaining good posture while sitting and standing, and avoiding lifting heavy objects incorrectly. It is also advisable to practice appropriate exercises to strengthen the back muscles and maintain overall physical fitness.
In summary, lumbar disc herniation is considered a real danger and can significantly affect the life of the affected person. Therefore, individuals should adhere to the necessary precautions and stay physically active to maintain spinal health and avoid this condition.
What are the symptoms of lumbar disc herniation?
Lumbar disc herniation is a common condition that affects the back and buttocks area, and its symptoms vary in intensity and impact on the individual’s daily life. Symptoms can range from moderate pain in the back and buttocks to severe pain that requires immediate medical intervention.
One of the symptoms of lumbar disc herniation is pain in the back and buttocks area, which may be accompanied by a feeling of numbness or tingling in the affected area. The person may feel pain that extends from the waist to the leg if the herniation is in the lumbar area below the back, whereas if the herniation is in the cervical area, they may experience persistent pain in the lower back region.
Other symptoms of lumbar disc herniation include pain in the buttocks, thigh, and leg. Patients suffer from what is known as “sciatica,” which is intense pain that extends from the buttocks to the back of the knee in one leg. This pain occurs as a result of the pressure on the intervertebral discs in the spine. The pain may also be accompanied by numbness in the legs or feet, in addition to muscle weakness in these areas.
The symptoms of lumbar disc herniation should be taken seriously, as they can significantly affect an individual’s life and their ability to perform daily activities. Immediate medical consultation and initiation of appropriate treatment are advised to alleviate pain and improve the patient’s overall condition. Treatment may include medication, physical therapy, and in some severe cases, surgery may be required to correct the herniation.
In conclusion, lumbar disc herniation is a condition that affects the spine and causes varying degrees of pain in the back, buttocks, and legs. For proper diagnosis and treatment of this condition, it is essential to consult a specialist to assess the condition and determine the appropriate treatment that suits the patient’s needs.
Does walking affect the lumbar vertebrae?
Walking is a simple and accessible activity for everyone, and numerous studies have shown that it has a positive effect on the lumbar vertebrae. When performed regularly and correctly, walking can have a significant impact on strengthening the muscles surrounding the spine and improving its health.
One of the main benefits of walking is the improvement of the strength of the muscles surrounding the lumbar vertebrae. When these muscles are strong, the vertebrae are better supported, and the risk of back problems such as disc herniation decreases. These muscles include the abdominal, back, hip, and buttock muscles. With regular walking, these muscles are activated and strengthened, contributing to better spinal alignment and reduced pressure on it.
Additionally, walking is considered a low-impact activity on the lumbar vertebrae. It does not cause harmful effects on the cartilage or discs between the vertebrae. On the contrary, walking helps improve blood circulation and provides nutrition and oxygen to the tissues surrounding the vertebrae, which promotes their health and contributes to cell regeneration and tissue strengthening.
Studies also indicate that walking can help relieve the pain of disc herniation and reduce swelling and inflammation in the affected area. When the vertebrae and muscles move regularly, the body is stimulated to release chemicals that relieve pain and improve the overall condition of the body.
It is worth mentioning that one should not forego consulting a specialist before starting any sports activity after undergoing lumbar spine stabilization surgery. There may be special recommendations for your health condition and personal medical history. The doctor may be able to guide you on the appropriate level of physical activity and exercises that you can perform.
Overall, walking is a simple and beneficial physical activity for the health of the lumbar vertebrae. It can help in strengthening muscles and improving the alignment of the spine.
Is There a Treatment for Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Lumbar disc herniation is a common condition that affects the spine and causes back pain and spasms. A lumbar disc herniation occurs when the cartilage that serves as a cushion between the vertebrae tears and slips out of place. This condition can be a significant nuisance for those who suffer from it and affects the quality of their daily life.
Historically, surgery was the primary option for treating lumbar disc herniation. However, advances in medicine and physical therapy have made other options available to patients. Is there an effective treatment for lumbar disc herniation? The answer depends on the individual’s condition and the degree of disc herniation.
In cases of simple lumbar disc herniation that do not cause severe symptoms, physical therapy may be the best option. Physical therapy includes exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine, stretching and elongation exercises. These exercises help strengthen the muscles and improve the flexibility of the spine, which reduces the pressure on the damaged lumbar cartilage.
In addition to medical exercises, there are some manual folk remedies that can help align the spine and relieve pain. These manual folk remedies include massage, regular use of thermal frequency, and caring for the body and a healthy diet.
However, in cases of severe lumbar disc herniation that causes persistent pain and restriction of spinal movement, surgical treatment may be the best option. Lumbar disc herniation surgeries involve removing the damaged part of the cartilage and stabilizing the adjacent vertebrae with screws or plates.
Ultimately, the appropriate treatment for lumbar cartilage should be determined based on an individual assessment of each patient’s condition. It is advisable to consult with specialists in spine surgery and physical therapy to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan.
How to Get Rid of Lumbar Spine Pain?
Getting rid of lumbar spine pain requires attention to many factors and implementing a comprehensive strategy for treatment and prevention. Here are some tips that can help reduce and eliminate pain in the lumbar vertebrae:
- Rest and Massage: After a long period of activity or stress, rest can play a significant role in relieving pain. Take some time to rest and give your body a chance to rejuvenate. Massage can also help relieve muscle tension and increase blood circulation.
- Heat and Cold Application: Heat packs can be used to warm up the muscles and tissues surrounding the lumbar vertebrae, which helps to relieve pain. Conversely, cold can be used to reduce swelling and inflammation. Remember that applying heat or cold directly to the skin should be done carefully to avoid burns or frostbite.
- Rehabilitation Exercises: After consulting your doctor or a physiotherapist, you can perform specific rehabilitative exercises to strengthen the back muscles and increase the flexibility of the vertebrae. These exercises can be effective in improving support for the vertebrae and reducing pain.
- Breathing and Relaxation Techniques: Learning deep breathing and relaxation techniques can have a positive effect on lumbar spine pain. These techniques can help relieve muscle tension and calm the nervous system.
- Medical Treatment: In more complicated cases or severe pain that does not improve quickly, consulting with a specialist doctor may be necessary. The doctor can offer therapeutic options such as pain-relieving medications, physical therapy, or surgical procedures if necessary.
- Prevention: Once the condition improves, work should be done to prevent the problem from returning by maintaining a healthy weight, maintaining proper body posture, strengthening the back and abdominal muscles, and avoiding sitting for long periods without movement.
In conclusion, it is essential to handle lumbar spine pain carefully and under the supervision of healthcare professionals. Remember that these tips are general guidelines and should not be used without medical consultation, especially if you have chronic pain or a specific condition.
How does a herniated disc heal on its own?
A herniated disc, also known as a “disc slip,” is a condition that occurs when the fibrous cartilage located between the vertebrae in the spinal column moves out of its normal position. A herniated disc is a common problem in the spine and can cause sharp pain and annoying symptoms such as numbness and tingling in the legs or arms.
Although some minor cases of herniated disc may improve on their own over time, the general rule is that spontaneous healing cannot be relied upon. A herniated disc is often a chronic condition that requires proper management and treatment.
The effectiveness of treatment depends on the characteristics and severity of the condition. Treatment can include physical therapy and rehabilitative exercises to strengthen the muscles around the spine and increase its flexibility, as well as pain relief medications and anti-inflammatory treatments. In more severe cases, surgery may be the best option to repair the damaged cartilage.
In conclusion, although some minor cases may improve spontaneously, a herniated disc is a medical condition that usually requires therapeutic procedures and medical supervision. If you suffer from spinal pain or suspect a herniated disc, you should consult a specialist doctor to provide the necessary assessment and treatment.
What is the success rate of lumbar spine surgery?
Lumbar spine surgery is a surgical procedure in which part of the fibrous cartilage between the vertebrae in the spinal column is removed to treat problems such as disc herniation, spinal stenosis, and other conditions that cause pressure on the nerves and surrounding tissues of the vertebrae. The success rate of lumbar spine surgery depends on many different factors.
Firstly, we must take into account the severity of the problem and how far it has progressed. In simple cases where the herniated disc is not serious and does not cause severe pain or significant pressure on the nerves, the success rate is usually high, and the patient can resume daily activities quickly after surgery.
However, in more complex cases where extensive surgery is required to remove a large part of the disc or to correct another structural problem in the spine, the risks of surgery may increase and the success rate may decrease. Success also depends on the surgeon’s skill and experience in performing this type of operation.
In general, the patient should consult their doctor and discuss the expectations and potential risks of the operation before deciding to undergo surgery. The response to treatment and its success depends on each patient’s individual condition. Importantly, other treatments before surgery can sometimes be effective in controlling pain and improving the condition without the need for surgery.
Can disc herniation be treated without surgery?
Disc herniation is one of the common problems in the spinal column, which is a condition where a part of the fibrous cartilage found between the vertebrae slips out. Disc herniation can cause sharp pain and disturbing symptoms that affect the quality of a person’s life. Although surgery is sometimes necessary for treating serious or complicated cases, there are many options for treating disc herniation without surgery.
- Physical Therapy and Exercises: Natural treatments and physical therapy sessions offer significant benefits for patients with disc herniation. Through exercises, massage, and muscle strengthening techniques, medical professionals can provide pain relief and increase strength and flexibility in the affected back areas.
- Medications: Pain relievers and anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to alleviate pain and swelling. The medication treatment can include drugs such as non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and painkillers.
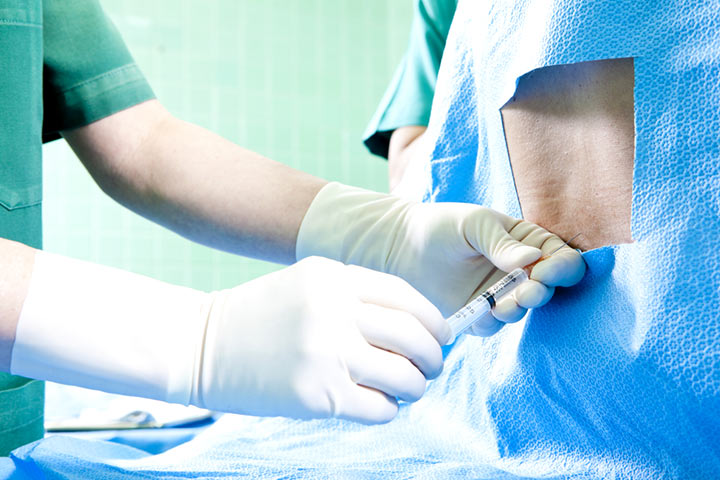
- Anesthetic Injections: Anesthetic injections can be useful in directly targeting treatment to the pain area. These injections include a needle containing anesthetics like cortisone and natural tissues to help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Complementary and Alternative Treatments: There are many complementary treatments that can contribute to improving the condition, such as massage, yoga, heat or cold therapy, herbal therapy, and psychotherapy. In addition, there are alternative techniques such as laser-guided therapy and radiofrequency treatment.
- Lifestyle Changes: Lifestyle changes can be beneficial in improving the condition of the lumbar vertebrae. These include maintaining a healthy weight, eating a balanced diet, refraining from smoking and alcoholic beverages, and maintaining proper body posture while sitting and lifting.
- Local Anesthetic Techniques: These techniques include local anesthesia that can provide temporary numbness to the affected area, helping to reduce pain and improve the condition.
Results vary depending on each person’s case and the severity of the problem. You should always consult your doctor or a physical therapy specialist before starting any type of treatment. In many cases, significant improvement and relief of pain and symptoms can be achieved without resorting to surgery, but commitment to treatment and medical guidance plays a crucial role in the success of non-surgical treatment.
Can lumbar vertebrae pain be treated without surgery?
Lumbar vertebrae pain is a common problem experienced by many people at various stages of their lives. The pain in the lumbar vertebrae can be a result of multiple factors, and understanding these factors can help in identifying the cause and taking necessary actions for treatment and prevention. Here are some common causes of lumbar vertebrae pain:
- Disc Herniation (Slipped Disc): This is one of the main reasons for lumbar vertebrae pain. A disc herniation occurs when a part of the fibrous cartilage between the vertebrae slips out of its normal position, causing pressure on the nerves and surrounding tissues, resulting in severe pain.
- Arthritis: Joint inflammations such as rheumatoid arthritis and degenerative arthritis can lead to pain in the lumbar vertebrae and reduce the flexibility of the spine.
- Muscle Strain and Tears: Excessive strain on the muscles surrounding the lumbar vertebrae can lead to tears and strain, resulting in pain and tightness in this area.
- Fibrous Tissue Tear: A tear in the fibrous tissues surrounding the lumbar vertebrae can be a cause for pain, which may occur as a result of an injury or natural deterioration.
- Age-related Changes: With aging, natural changes in the spine can occur, such as cartilage wear and reduced bone density, which can cause pain and stiffness in the vertebrae.
- Injuries and Accidents: Direct injuries or accidents such as car accidents or falls can cause injuries to the lumbar vertebrae and lead to acute pain.
- Genetic Conditions: Some hereditary diseases like multiple sclerosis and genetic bone and joint diseases can increase the likelihood of experiencing pain in the lumbar vertebrae.
- Poor Posture and Psychological Stress: Psychological stress and pressures can increase the severity of the pain and negatively affect the spine.
To determine the exact cause of lumbar vertebrae pain and to plan for appropriate treatment, it is essential to consult a specialist in orthopedics, a rheumatologist, or a general surgeon. The treatment depends on the cause and severity of the pain and may include physical therapy, anti-inflammatory and pain medications, psychotherapy, and in some rare cases, surgery.