What is the difference between flexible and rigid Flatfoot?
In this article, we explain a number of questions that were received regarding flatfoot.
What is the difference between flexible and rigid flatfoot?
Flatfoot is the occurrence of flattening in the arch of the foot, which often occurs as a result of a genetic factor or a defect in the growth of the foot and others, and in many cases, it does not affect the movement of the person and does not cause pain when moving, but if symptoms of pain or difficulty walking appear, the person can start the appropriate treatment for his condition.
There is the most common type of flatfoot, which affects the person’s speed when walking or playing sports, and other types with which the person may not feel any pain, and here are the two main types of flat feet and the difference between them:
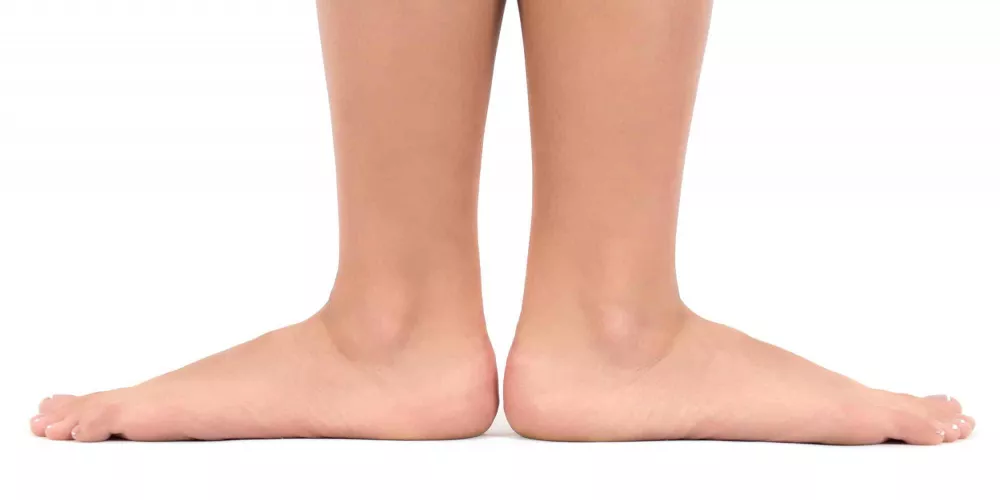
Flexible flatfoot: This type is the flattening of the flexible foot, that is, it appears when a person presses on the foot, but in the case of sitting or resting, the natural curvature appears.
Rigid Flatfoot: It is a solid flat foot, and the name is due to the fact that it appears continuously, whether when walking or sitting.
When do flat feet appear?
Mostly a person can be exposed to flat feet as a result of genetic factors that can affect the infection, but sometimes some reasons can increase the chances of flat feet, which are:
- Achilles tendon injury.
- A rupture of the calf muscle.
- Having Down syndrome.
- Being pregnant or being obese.
- Inflammation of the joint.
- diabetic.
How to diagnose flatfoot
Diagnosis of the flatfoot condition can be done through a medical or physical examination of the affected person, and the necessary x-rays begin to be performed that determine the impact that occurred to the foot, and the patient can begin treatment after the diagnosis, and the treatment may continue for several weeks, and the person begins to feel recovered.
Does flatfoot cause back pain?
Flatfoot is one of the injuries that can occur in the foot, but it often does not have symptoms of pain or affects movement, and sometimes when the flatness increases or the infection of the foot develops symptoms of pain and inability to walk properly.
If the affected person suffers from the symptoms of flatfoot and does not start treatment or the treatment method is not appropriate for him, he may face complications of flatfoot, including the presence of pain in the leg that extends to the lower back as a result of the weight not being distributed normally on the body and thus begins to feel pain in the foot.