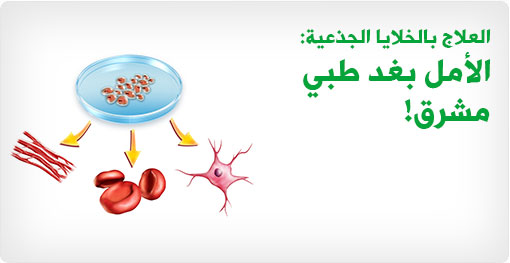
What is the best country for stem cell therapy, and what are the diseases it treats?
Best Country for Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is a promising medical field that offers hope for many patients suffering from serious diseases and injuries. With the expanding scope of this field, patients must choose a treatment destination that provides the best services, advanced technologies, and high-quality medical care. In this article, we will explore the best country for stem cell therapy and the reasons for its recommendation.
- India: India tops our list as the best country for stem cell therapy. It has made significant progress in this field over the years, offering a high level of expertise and advanced technology. India boasts highly qualified doctors and surgeons in the field of stem cell transplantation, and it has medical facilities equipped with the latest technologies. Additionally, India has relatively low treatment costs compared to other countries, making it a preferred destination for patients seeking an affordable solution.
- Turkey: Turkey is among the top destinations for stem cell therapy. It has a long and successful history in this field, providing advanced technology and highly experienced hospitals. Turkey is a renowned destination for patients in need of stem cell transplantation in blood, bone marrow, heart, liver, and other organs. Turkey also stands out for its competitive cost packages and quality medical services.
- Germany: Germany is considered one of the best countries in the world for stem cell therapy. The German state is a global hub for research and development in this field, with a strong international reputation for healthcare quality. Germany offers patients access to the latest technologies and clinical trials, along with treatment opportunities in various regions of the country.
- South Korea: South Korea is known for offering advanced technology and innovations in the field of medicine, especially in stem cell therapy. South Korea is famous for providing modern and effective treatment methods that meet international standards. Additionally, South Korea has specialized and qualified medical teams working in the field of stem cell transplantation.
- United States of America: The United States of America enjoys a global reputation in the field of stem cell therapy. It houses highly specialized medical facilities and distinguished medical teams. The country conducts a wide range of clinical trials and research, contributing to the development of techniques and treatments in this field. However, it should be noted that the overall treatment costs in the United States can be high, which may impact accessibility for many patients.
When choosing the best country for stem cell therapy, patients should consider several factors such as medical expertise, the availability of advanced technology, ease of access, and treatment costs. By turning to the mentioned countries above, patients can receive suitable treatment and the necessary professional care.
Is stem cell therapy available in Egypt?
Despite ongoing developments in the field of stem cell therapy in Egypt, it is still in the research and development stage. Therefore, stem cell therapy services may not be widely available at this stage. However, there is no doubt that this treatment has a promising future and may become a solution for many patients in Egypt and around the world in the future.
If you are looking for stem cell therapy in Egypt, you may have these questions in mind. This is an interesting and current topic in the field of medicine. Can we really rely on this treatment in Egypt? If so, where can patients access this service? What are the techniques used in extracting and transplanting these cells? We will answer these questions and more in this informative article.
Introduction to Stem Cells:
Stem cells are a type of cells that are characterized by their ability to self-renew and transform into other cell types in the body. They are essential cells used in the processes of tissue renewal and replacement in the body.
Uses of Stem Cells in Treatment:
Stem cells are used in various fields of treatment. They can be used to treat chronic and stubborn diseases such as heart diseases and cancer, neurological diseases such as Parkinson’s disease and muscular dystrophy, as well as autoimmune diseases that involve immune system dysfunction.
The Evolution of Stem Cell Therapy in Egypt:
In recent years, Egypt has witnessed significant progress in the use of stem cells in treatment. Many studies and research have been conducted in this field, along with the development of techniques used in cell transplantation and their use in treatment.
Stem Cell Treatment Centers in Egypt:
There are several specialized centers for treating diseases using stem cells in Egypt. These centers offer a variety of services, including the extraction, storage, and transplantation of stem cells into the desired areas for rejuvenation.
The Stem Cell Transplantation Process:
The process of stem cell transplantation involves a series of steps to ensure the success and effectiveness of the treatment. These steps include extracting the cells, whether from the patient’s blood, bone marrow, or fatty tissues, purifying them, and then transplanting them into the affected area.
Potential Side Effects and Challenges:
Despite the benefits of stem cell therapy, it may face some challenges and side effects. Some stem cells have the ability to abnormally replicate tissues, which can lead to the abnormal growth of tissues or even the development of tumors.
Future Developments in Stem Cell Therapy in Egypt:
Studies and research in the field of stem cells continue in Egypt, with the cultivation and release of cells to develop new and more effective treatments. It is hoped that this development will bring about a medical transformation in the field of treatment and open new doors for patients to access innovative treatments.
Awareness and Future Research:
It is important to raise awareness of the importance and benefits of stem cell therapy and expand the scope of research to understand how these cells can be used in treating various diseases in Egypt. Encouraging the government, healthcare institutions, and academia to fund research and develop related technologies is crucial.
What is the Success Rate of Stem Cell Therapy?
Stem cells are one of the most significant medical innovations in modern times. They have the ability to renew and regenerate damaged tissues in the body and have garnered significant interest from researchers and medical professionals worldwide. One of the ways to utilize these remarkable cells is for medical treatment.
However, the discussion revolves around the success of this treatment and its ability to fully restore the functions of damaged tissues. Does this process guarantee complete healing?
The available research so far shows that the success rate of stem cell therapy is subject to improvement depending on the circumstances and the type of medical condition the individual is dealing with. The matching of transplanted stem cells with the body’s natural cells is of great importance in the success of the treatment.
In the case of a 50% match, stem cells can be sufficient for treatment and stimulate regeneration and repair processes in damaged tissues. Consequently, significant improvements can occur in the patients’ condition. However, a 100% match between the transplanted stem cells and the white blood cell antigens of the body provides a better chance for optimal results and complete healing.
Diseases that can be treated using stem cells:
Stem cells have shown the potential to treat chronic diseases and long-term injuries. They have the ability to stimulate the specialization of new cells and the regeneration of damaged tissues. Some examples of diseases that can be treated using stem cells include:
Parkinson’s Disease: Stem cells may be able to repair damaged parts of the brain and replace lost nerve cells, resulting in a significant improvement in the accompanying symptoms of this disease.
Diabetes: Using stem cells is believed to repair damaged pancreatic cells, enhance insulin production, and improve blood sugar control in patients.
Spinal Cord Injuries: Spinal cord injuries involve severe structural damage that affects bodily functions. Stem cells are a promising candidate for treatment, as they can contribute to replacing damaged tissues and rewire them.
Scientific Research and Future Improvements:
Scientists and researchers are currently focused on improving the success rate of stem cell therapy. They aim to enhance the matching of transplanted cells with natural cells in the patient’s body. They also look forward to developing ways to stimulate stem cells to specialize and transform into specific cells for therapeutic purposes.
Gene editing technology is one of the future techniques that may lead to improving the success rate of this treatment. Gene editing is used to activate specific genes in stem cells, enhancing their ability to specialize and regenerate.
In summary, the success rate of stem cell therapy is a multifaceted issue. It is influenced by individual patient circumstances and the type of medical condition they are suffering from. Nevertheless, a 50% match between transplanted cells and natural cells is sufficient to achieve good results and significant healing. With the improvement of techniques and future research, the success rate of this treatment is expected to increase, particularly for stubborn diseases.
What are the risks of stem cells?
Stem cells are an exciting field of research and development in medical science. These cells have the potential for unlimited proliferation and are capable of transforming into various cell types in the body. This potential has led to their possible benefits in treating various diseases and injuries. However, there are also some risks and challenges that we need to be aware of.
Abnormal Proliferation: Stem cells can rapidly proliferate, which may lead to the formation of cancerous tumors. If these cells acquire the ability to proliferate abnormally or uncontrollably, they can cause the growth of malignant tumors.
Host Rejection: Stem cell therapy from an external source carries the risk of host rejection, where the immune system may reject these cells as foreign entities. Many doctors, therefore, resort to using autologous stem cells, known as hematopoietic stem cells, derived from the patient’s own body to avoid this risk.
Subclonal Cancer Issue: Specific subtypes of stem cells may contain subclonal cancer cells. When these cells are used for therapeutic purposes, it may lead to the transformation of these subclonal cells into new cancers. This is why researchers are concerned with regulating factors that affect the growth of subclonal cells and preventing their transformation into cancer.
Ethical Concerns: There is a significant ethical debate surrounding the use of stem cells, especially when it involves stem cells derived from human embryos. Some people consider the use of these cells unethical because they view it as exploitation of early life. Therefore, many researchers turn to using stem cells derived from non-embryonic sources, such as preserved embryos or cord blood.
Resource Limitations: The use of stem cells for medical treatments can be highly costly. These cells require a specific environment in advanced laboratories and advanced technical skills to be suitable for therapeutic applications. Therefore, future studies need to ensure the availability of sufficient resources for research and development in this field.
In conclusion, stem cells have tremendous potential in treating various diseases and injuries. However, their use requires significant attention to side effects and potential risks. It is important to continue research and innovation in this field to find safe and effective ways to use these cells in disease treatment.
What are the diseases that can be treated with stem cells?
Stem cells are one of the most important modern techniques in regenerative medicine, offering promising opportunities for tissue renewal and repair. They have the potential to revolutionize traditional treatment concepts. Here is a list of some diseases and conditions that can be treated with stem cells:
Spinal Cord Injuries: Spinal cord injuries are among the most challenging cases in modern medicine, but stem cells can provide hopeful prospects for recovery. Transplanting stem cells derived from bone marrow can help replace damaged cells and compensate for the injured tissues in the spinal cord, allowing for improved function, movement, and sensation.
Type 1 Diabetes: Type 1 diabetes is a chronic condition that requires daily insulin injections to control blood sugar levels. By using stem cells, pancreatic cells can be transplanted, either derived from the patient’s own body or from an external source, to replace the destroyed cells in the pancreas. This represents a significant step in the treatment of type 1 diabetes and may lead to more effective and permanent therapies in the future.
Parkinson’s Disease: Parkinson’s disease is a neurological disorder resulting from a deficiency in the balance of the neurotransmitter dopamine in the brain. Stem cell transplantation is considered an opportunity to replenish the dopamine-deficient nerve cells, improving motor control and other symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): This disease, also known as lateral Alzheimer’s disease, is characterized by the degeneration and loss of nerve cells in the area of the brain responsible for motor control and cognitive functions. Using stem cells, it is possible to rebuild and repair the damaged parts of the brain, improving the symptoms of this devastating disease.
Alzheimer’s Disease: The damage to brain cells and the loss of future cognitive cells are part of the effective path for Alzheimer’s disease. Stem cells provide an opportunity to rebuild tissues and replace cells destroyed by the disease, which may contribute to improving symptoms and cognitive function.
Heart Diseases: Thanks to stem cell technology, engineered cells from the laboratory or from an external source, such as bone marrow, can be used to renew and regenerate damaged heart cells. This technique allows for the replacement and repair of damaged heart tissues, opening the door to treating chronic heart diseases.
Stroke: Using stem cells to treat stroke is a promising technique. This technique allows for the transplantation of stem cells to damaged blood vessels in the brain after a stroke, restoring oxygen and nutrient flow to the affected parts, thereby reducing stroke symptoms and promoting brain recovery.
Burns: Stem cell transplantation holds promise in the treatment of acute and chronic skin burns. Stem cells can be collected from the patient or from other sources, such as placental membranes, and planted in damaged skin areas. These cells promote the regrowth of skin cells and the creation of new tissues, enhancing wound healing and reducing burn scars.
Cancer: Cancer treatment using stem cells is an active research field. This technique is primarily used to transfer engineered stem cells that target cancer cells and restrict their growth. This process is very promising and may be key to cancer treatment in the future.
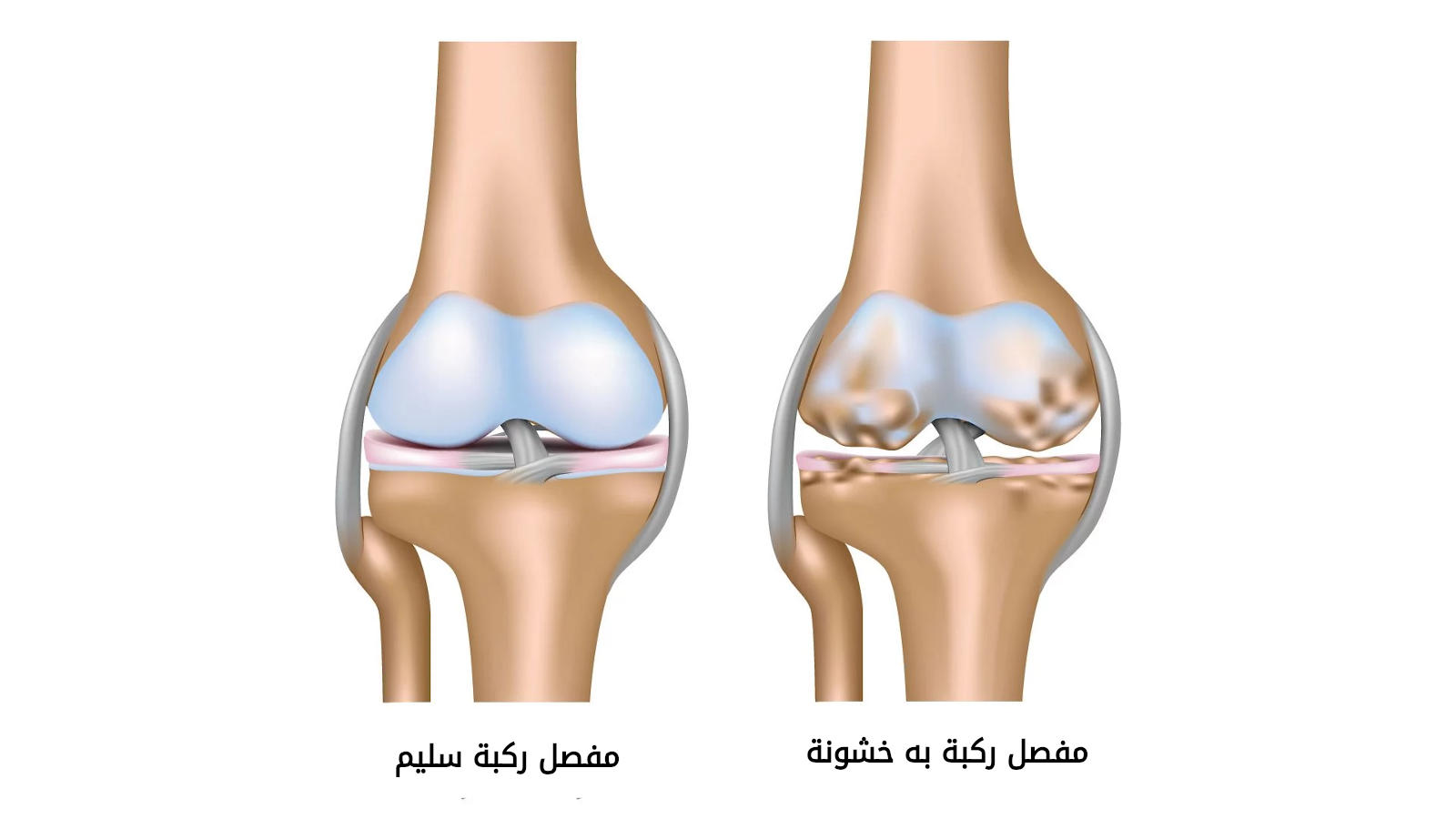
Osteoarthritis: Stem cells can be one of the options for treating osteoarthritis. Stem cells can be collected from bone marrow and planted in the damaged joints, promoting tissue repair and regeneration, improving joint movement, and reducing painful symptoms.
The use of stem cells for the treatment and prevention of diseases and medical conditions represents a revolutionary breakthrough in the field of medicine. Over the coming years, it is expected that new treatments will be discovered using this technology. However, proper precautions must be taken, and full consideration of ethical and legal regulations should be made before using this technique.
Where Do Stem Cells Come From?
Scientists have developed several methods to obtain stem cells, which are considered one of the most important modern techniques in the field of regenerative medicine. Stem cells can come from various sources, and among the prominent sources are:
- Umbilical Cord Blood: Umbilical cord blood from a newborn baby is considered a rich source of stem cells. This blood is collected by extracting it from the umbilical cord after it is cut, then it is processed to extract the stem cells from it. Umbilical cord blood is preferred as a source of stem cells over bone marrow because this process is less complicated and the natural blood cell count recovers more quickly.
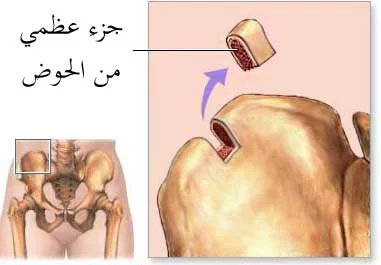
- Bone Marrow: Bone marrow is another common source of stem cells. These cells are extracted from the bone marrow, which is the soft material found in the center of bones. This source requires a small surgical procedure where a thin needle is used to draw from the bone marrow of a donor, typically from the hip or thigh bone.
- Adipose Tissues (Fat): Adipose tissues are also considered a potential source of stem cells. These cells are extracted by transplanting them from specific areas within adipose tissues, such as the abdomen or buttocks. These cells are then converted into stem cells.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): There is another type of stem cells known as “induced pluripotent stem cells” (iPSCs). These cells are obtained by converting adult cells, such as skin cells or fat cells, into stem cells. This process requires complex laboratory procedures using cell reprogramming techniques.
Stem cells can be used in various medical applications and research. Researchers can direct stem cells to specialize and transform into specific types of cells, such as nerve cells, muscle cells, bone cells, and more. This opens up broad prospects for using these cells in disease treatment and tissue regeneration.
Additionally, stem cells are used in research to understand the causes of diseases and develop new treatments. It’s important to mention the ethical issues related to the use of stem cells, where these procedures must respect stem cell guidelines, as well as local government laws and regulations.
Stem cells represent an important source for developing new treatments and renewing damaged tissues. Using diverse sources to obtain these cells opens up wide avenues for studying diseases and advancing medicine.
What Are Stem Cell Banks?
Stem cell banks are institutions that collect and store stem cells for future use in the treatment of diseases and injuries. These cells represent a significant opportunity to provide innovative and targeted treatments for many diseases that are difficult to treat using conventional methods. In addition, stem cell banks are an important means of studying specific diseases and gaining a better understanding of them.
Dental stem cell banks are among the prominent forms of these institutions. Stem cell preservation services for teeth focus on collecting children’s teeth when they naturally fall out, and then storing the extracted stem cells from the dental pulp. These cells are stored under optimal conditions until they are ready for therapeutic use in the future if the child needs them as they grow up.
The role of dental stem cell banks is not limited to children only. Some individuals undergo dental extraction procedures, such as wisdom teeth or root canals, and choose to preserve stem cells from these teeth in a stem cell bank for potential future use.
The different types of stem cells used in stem cell banks include:
- Embryonic Stem Cells: These cells are derived from embryos in the early stages of development and are characterized by their ability to differentiate into any type of desired cells. However, these cells face ethical and legal issues regarding the use of embryos in research.
- Fetal Stem Cells: Fetal stem cells include those obtained from the fetus during the ninth to the ninth month of gestation, and they have the ability to differentiate into various cells in the body. Despite their effectiveness in many therapeutic applications, their use also faces ethical and legal challenges.
- Adult Stem Cells: These cells are present in various tissues in adults, such as bone, skin, mucous membranes, and blood, and they have the ability to differentiate into specific cell types. These cells have many advantages as they can be efficiently used for therapy and do not face the ethical and legal challenges that other types of stem cells do.
Stem cell banks are an important source for scientific research and future therapies. Utilizing these cells can open up new avenues for treating diseases and injuries that are difficult to treat with traditional methods. With ongoing advancements in this field, the importance of stem cell banks is expected to increase, and their use is likely to expand in the future to improve human health.
What Are the Types of Stem Cells?
Stem cells can offer hope for the treatment of various diseases and injuries due to their unique ability to develop and specialize into different cell types in the body. There are different types of stem cells, each with distinct characteristics and uses.
In this article, we will briefly overview some common types of stem cells that are of significant importance in scientific research and the development of new treatments.
- Embryonic Stem Cells: Embryonic stem cells are among the most well-known and widely used types of stem cells. These cells are derived from the inner cell mass of an embryo at an early stage of development and are characterized by their remarkable ability to self-renew and differentiate into any type of human body cells. This has made them highly valuable in scientific research for disease treatment and the restoration of damaged organ functions.
- Somatic Stem Cells: Somatic stem cells, also known as adult stem cells, are found in various tissues within the human body, such as bones, skin, nerves, and muscles. These cells possess the capacity to reprogram themselves and transform into other cell types within the same tissue. However, they typically have lower capabilities compared to embryonic stem cells. Nevertheless, these cells are of great importance in understanding cellular regeneration and discovering new therapies for chronic diseases.
- Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs): Induced pluripotent stem cells represent a relatively recent innovation in the field of stem cell research. These cells are created by reprogramming mature cells in an individual’s body to become pluripotent stem cells capable of developing functions similar to embryonic stem cells. This process involves complex procedures and modern techniques, opening new avenues for the use of stem cells in research and therapy.
- Multipotent Stem Cells: Multipotent stem cells exist in specific tissues in the human body, such as bone marrow and cartilage. These cells are known for their ability to specialize into specific cell types within the same tissue, making them highly useful in the treatment of diseases and injuries affecting these tissues.
Thanks to technological advancements and scientific progress, stem cells are being used in various fields, including the treatment of heart diseases, neurological disorders, and damaged tissues. While the use of stem cells is still in its early stages, it is expected to significantly contribute to improving the quality of life and treating diseases in the future.
The use of stem cells is a promising technique in the medical field, but it requires strict ethical considerations and ensuring the rights and safety of patients. Therefore, the scientific community, pharmaceutical companies, and legislative bodies must work together to explore the best ways to develop and guide this technology effectively and safely for disease treatment and injury recovery.
There is no doubt that stem cells represent the future in treating many diseases and injuries that were once considered hopeless. With ongoing scientific and technological advancements, we can expect to see more discoveries and innovative applications in this field, providing new opportunities in the world of medicine and improving human quality of life.