Learn More About Bone and Muscle Inflammation and How to Differentiate Between Them?
Bone and Muscle Inflammation
5 Things You Should Know About Bone and Muscle Inflammation
- Bone and muscle inflammation is a medical condition that results in the inflammation of bone and muscle tissue in the body. It often occurs in older individuals and may worsen over time.
- Common symptoms of bone and muscle inflammation include muscle weakness, joint pain, and difficulty in movement. These symptoms can suddenly appear in some children. There are no specific treatments for bone and muscle inflammation, and if the symptoms are mild, supportive measures such as applying warm compresses, taking aspirin, or using basic muscle-strengthening exercises may be sufficient to alleviate temporary inflammation.
- Some people may require alternative treatments or physical therapy. Some tips to alleviate the symptoms of bone and muscle inflammation include engaging in appropriate exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility, following a healthy diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, and applying ice or heat to the painful areas.
- It is important to consult with a doctor if you have persistent and severe symptoms of bone and muscle inflammation. They can provide an accurate diagnosis and suggest an appropriate treatment plan.
How Do I Know If I Have Bone Inflammation?
Bone inflammations are a serious medical condition that should be recognized, and the possible symptoms should be known. If you experience unexplained pain in a part of your bone, you may have bone inflammation. Here are some symptoms to watch for:
Unexplained Pain: If you have persistent pain in a part of your bone, especially if it is accompanied by redness and a fever, it may indicate bone inflammation. Sensitivity and Swelling: You may feel sensitivity and swelling in the inflamed area, so observe if there is a noticeable change in the size of the painful area. Weight Loss and Fatigue: You may notice a decrease in your weight and constant fatigue without a known cause, which could be a result of bone inflammation.
If you notice any of these symptoms, here’s what you should do:
Consult Your Doctor: When you are concerned about symptoms that indicate bone inflammation, visit your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Request a Blood Test: Doctors can take a blood sample to examine potential markers of inflammation, such as the erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), to determine the presence of inflammation in your body. Undergo Comprehensive Evaluation: Your doctor may request X-rays or scans to perform a comprehensive evaluation of the bone and surrounding tissue.
Remember that treating bone inflammation takes time and antibiotics, so it’s essential to follow your doctor’s instructions carefully and complete the prescribed treatment. In some cases, doctors may need to remove a portion of the affected bone or perform a biopsy to take a sample and conduct additional tests.
Don’t hesitate to consult your doctor if you have any concerns about bone inflammation. Early diagnosis contributes to a higher chance of complete recovery and prevention of complications.
What Is Muscle Inflammation and Its Symptoms?
Muscle inflammation is a medical condition that affects muscle tissues, leading to pain and sensitivity in the affected area. Muscle inflammation can be characterized by swelling, redness, and muscle tightness, significantly impacting the quality of life of the affected individual.
In this article, we will highlight some of the prominent symptoms of muscle inflammation:
- Muscle Pain: Muscle pain is one of the primary signs of muscle inflammation, with the patient experiencing sharp pain and soreness in the affected muscles. The intensity of this pain may increase with muscle movement or strenuous exercises.
- Swelling and Redness: Individuals with muscle inflammation may notice swelling and redness in a specific area of their body, such as the arm or leg. These signs indicate muscle inflammation and may significantly worsen in the case of a double injury.
- Fatigue and General Weakness: Patients may suffer from general weakness throughout their body, feeling lethargic and fatigued without a known cause. Muscle inflammation affects the person’s ability to carry out daily activities efficiently.
- Difficulty in Movement: Movement may become challenging and restricted for individuals with muscle inflammation, as this condition affects muscle flexibility and strength.
- Respiratory Distress: Patients may experience difficulty breathing or a sensation of tightness in the chest due to chronic muscle inflammation affecting respiratory muscles.
- Sleep Problems: Muscle pain caused by inflammation can disrupt sleep, making it difficult for the patient to relax and sleep well.
- Joint Pain: Pain from muscle inflammation may extend to adjacent joints, increasing the patient’s suffering and affecting their mobility.
These are some of the key symptoms of muscle inflammation, and if you notice any of these symptoms, it may be best to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and the prescription of an appropriate treatment plan.
What Is Myositis Diagnosis?
Muscle inflammations are conditions that can negatively impact individuals’ lives, and they can be challenging to diagnose accurately. Therefore, doctors use a range of tests and examinations to assess the diagnosis of autoimmune-related myositis. In this article, we will explore what myositis diagnosis involves and how it contributes to diagnosing the disease.
Blood Test: One of the most prominent methods of diagnosing autoimmune-related myositis is a blood test. This analysis allows doctors to estimate the levels of muscle enzymes in the patient’s body. Myositis patients typically have increased levels of creatine kinase (CK) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) enzymes in their blood. If the results show elevated levels of these enzymes, it may indicate the presence of muscle inflammation.
Immune Bodies Examination: Immune bodies examination is an important method for diagnosing autoimmune-related myositis. This test is used to detect the presence of antibodies in the patient’s blood, such as antinuclear antibodies (ANA). These antibodies usually appear in most cases of this condition. However, it is essential to note that the results of immune bodies examinations alone are not sufficient to confirm the diagnosis of myositis. It is important to consider all results from various tests.
Muscle Biopsy: If there is doubt about the diagnosis of myositis, the doctor may suggest a muscle biopsy. This test involves taking a sample of the patient’s muscle and examining it under a microscope to confirm the presence of inflammation or other issues. If the diagnosis is confirmed through a skin biopsy, a muscle biopsy may not be necessary. It is important to note that this test is often used after initial analyses.
Diagnosing autoimmune-related myositis relies on a variety of different tests and examinations. Blood analysis is used to measure the levels of muscle enzymes, while immune bodies examination aids in detecting the presence of antibodies. In cases of doubt regarding the diagnosis, a muscle biopsy may be performed to confirm inflammation.
Please note that the diagnosis of autoimmune-related myositis requires reliance on a variety of tests and examinations, and therefore, the diagnosis should always be finalized after a comprehensive review of all results and accompanying symptoms. Therefore, it is always recommended to consult with a specialized doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan.
How to Distinguish Between Bone and Muscle Pain?
Bone and muscle pain is a common issue faced by many individuals. Distinguishing between these two types of pain can be challenging, but there are several factors that can help differentiate them. In this article, we will explore some ways to identify the source of the pain.
Direct Source of Pain:
- Muscle Pain: Muscle pain may occur due to muscle strain or overexertion. This pain is often described as sharp and short-lived, typically fading after a period of rest.
- Bone Pain: Bone pain can result from direct injuries or the deterioration of bone health. Individuals experiencing bone pain may feel severe and steady pain in the affected area.
Location of Pain:
- Muscle Pain: Muscle pain tends to be localized in specific areas of the body, such as the shoulders or neck. The pain may worsen with the movement or strain of the affected muscles.
- Bone Pain: Bone pain can affect larger areas of the body, such as joints or broad bone regions. This pain may be constant or intensify with joint movement.
Impact on Joint Mobility:
- Muscle Pain: Muscle pain usually does not significantly affect joint mobility. In most cases, this is referred to as one of the treatments for muscle pain.
- Bone Pain: Bone pain is noted to significantly impact joint mobility. This can be associated with restricted movement or other symptoms like joint swelling.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Muscle Pain: People experiencing muscle pain may need rest and specific measures to soothe the muscles, such as applying heat packs or performing muscle-relaxing exercises.
- Bone Pain: The treatment for bone pain involves consulting a medical professional and undergoing tests to determine the cause of the pain. Supportive treatments such as taking pain relievers or undergoing physical therapy may be recommended.
If you have any complaints of bone or muscle pain, it is advisable to consult with a specialized physician for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate guidance and treatment. You may also need additional tests to determine the underlying cause of the pain.
Does Bone Inflammation Show Up in Blood Tests?
Yes, bone inflammation can appear in blood tests. Blood tests can reveal changes in certain levels of blood cells and proteins that indicate inflammation. For example, an elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and elevated serum creatinine levels can be signs of bone inflammation. However, the diagnosis of bone inflammation cannot be accurately determined through blood tests alone, and additional examinations such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) are typically necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
It is always important to consult with a physician for clinical assessment and the necessary tests to determine and treat any potential cases of bone inflammation.
What Is the Strongest Treatment for Bone Inflammation?
Bone inflammation is a painful condition that affects the quality of life of those affected by it. Therefore, many people seek the best and strongest treatment to relieve pain and alleviate symptoms in this condition. Here is a list of the strongest treatments for bone inflammation:
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): This group of medications includes elements such as ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen and is effective in reducing swelling and pain associated with bone inflammation. However, their use should be supervised by a physician, as some NSAIDs may cause stomach disturbances and bleeding, so it is important to consult a doctor before using them.
Antibiotics: In the case of infection accompanying bone inflammation, antibiotics may be necessary to eliminate the bacteria causing the infection. Consultation with a doctor is necessary to determine the appropriate dosage and treatment period.
Pain Relievers: These medications are used to alleviate the severity of pain associated with bone inflammation. This includes pain relievers such as paracetamol and ibuprofen.
Corrective Treatment: In some cases, there may be a need for surgical treatment to correct any bone deformities or changes. This may include removing damaged parts of bones, excising tumors, or using fixation with screws.
Rehabilitation Treatment: This treatment is used after hospital discharge and includes physical rehabilitation exercises and physical therapy. The goal of this treatment is to regain strength and movement in the affected joint.
It is essential to consult a doctor before determining the strongest treatment for bone inflammation and to determine the appropriate plan for each case individually. Remember that this information does not replace consultation with a specialized physician.
How Long Does Bone Inflammation Treatment Take?
Bone and joint inflammation is a serious health condition that requires proper treatment. Many people wonder about the duration of treatment for this inflammation, and in this article, we will shed light on that.
Adaptation Period: After starting treatment for bone and joint inflammation, patients may need several weeks for their bodies to adapt to the new level of activity. During this period, joints may experience some discomfort, but it is essential to continue with exercises and maintain mild activity to help the joints adapt and alleviate the pain.
Treatment Duration: The duration of treatment can vary depending on the severity of each person’s condition. Generally, treating bone and joint inflammation may take from six to eight weeks. However, this depends on factors such as the severity of inflammation and the effects of the treatment used.
Response to Treatment: Patients undergo regular follow-ups with treating physicians to assess their response to treatment. In the case of a good response, they may feel improvement in their condition after just a few weeks. In such cases, treatment may continue for several additional months to ensure the stability of their condition.
Side Effects: Some side effects may appear during the treatment period, and it is essential to discuss these side effects with the specialized doctor and how to deal with them. Side effects may include issues like nausea, headaches, sleep disturbances, or mood changes.
Managing Other Health Conditions: Patients may have other health conditions that pose challenges during treatment. In such cases, it is crucial for the patient to seek advice from the treating doctor on how to manage these conditions while undergoing treatment.
Alternatives: Sometimes, there may be an alternative medication of the same type used for treating bone and joint inflammation. It is essential to discuss this with the doctor and inquire about the possibility of using an alternative medication in case the patient’s condition does not improve.
This article emphasizes the importance of consulting with a specialized physician before starting or changing any treatment and that the duration for improvement in bone and joint inflammation may vary from person to person.
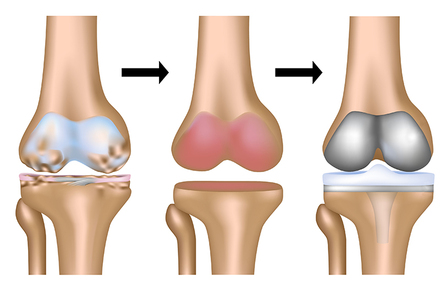
What’s the Difference Between Bone Inflammation and Joint Inflammation?
Bone and joint inflammations are common conditions among people, but you may have some confusion about whether bone inflammation is the same as joint inflammation or not. In this article, we will highlight the significant differences between these two conditions:
- Different Affected Areas:
Bone Inflammation (Osteoarthritis) affects the joint cartilage and occurs due to excessive joint use over time. It results in cartilage degeneration, leading to joint pain and impairment of joint movement.
Joint Inflammation (Rheumatoid Arthritis) is an autoimmune disorder that primarily affects the joint membranes (synovial membrane). It causes inflammation and swelling in the joints and can lead to cartilage and bone damage near the joint in advanced stages.
- Causes:
Bone Inflammation primarily occurs due to the deterioration of joint cartilage over time, as a result of excessive joint use.
Joint Inflammation is caused by an immune system disorder where the immune system attacks the joint membranes (synovial membrane), resulting in inflammation and pain.
- Impact on the Body:
Bone Inflammation affects specific joints that are frequently used, such as the knee joint or only a specific point on the range of motion.
Joint Inflammation may affect all joints in the body, especially in severe cases.
- Care and Treatment:
For Bone Inflammation, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are typically used, and efforts are made to avoid excessive joint use to reduce additional wear and tear on joint cartilage.
For Joint Inflammation, treatment usually involves the use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) and biologic inhibitors targeting joint inflammation.
- Targeted Individuals:
Bone inflammation is generally common in older adults and becomes more severe with aging. Joint inflammation is a type of immune system disorder that can affect people of all ages and genders.
- Genetic Susceptibility:
Some forms of joint inflammation have a genetic impact, meaning that someone is more likely to develop joint inflammation if one of their parents or relatives has the condition. Genetic factors do not have a major impact on the development of bone inflammations.
In summary, bone inflammation is a result of joint cartilage deterioration due to excessive stress, while joint inflammation occurs due to an immune system dysfunction. Each condition requires a different and specialized approach to treatment, but these are the key differences between bone and joint inflammations.
Is Bone Inflammation a Chronic Disease?
Bone and joint inflammation is a serious health condition that affects the bones and can have a significant impact on the lives of affected individuals. It is important to know whether this disease is chronic or not, so we will provide some information about it in this list.
- Chronic Health Conditions may become chronic: People with chronic health conditions such as diabetes or kidney failure are more susceptible to developing bone inflammation. Weak immune systems can lead to the deterioration of their condition, and bone and joint inflammation may develop into a chronic condition.
- Disease Progression: In many cases, bone and joint inflammation is acute and short-term, developing rapidly and can be easily treated with appropriate antibiotics and treatments. However, in some cases, the disease may progress to become chronic, lasting for months or even years.
- Symptoms of Chronic Bone and Joint Inflammation: Chronic bone and joint inflammation may cause bone pain and recurrent soft tissue infections. This inflammation may be accompanied by continuous or intermittent pus drainage through the skin.
- Diagnosing Chronic Bone and Joint Inflammation: It is customary to take bone tissue samples by needle or during surgery to diagnose this disease. Through analyzing these samples, doctors confirm the diagnosis of bone and joint inflammation and determine its type.
- Early Treatment is Key: Typically, bone and joint inflammation can be successfully treated with antibiotics, provided it is diagnosed in its early stages. Surgery may also play a role in specific cases. If bone and joint inflammation is not treated properly, it may develop into a chronic condition and be associated with other health problems.
- Chronic Bone Inflammation May Recur: Although chronic bone inflammation is rare, new abscesses may appear after the patient has recovered, leading to a recurrence of health problems.
In conclusion, community members should be aware of the risks of bone and joint inflammation and take necessary precautions to prevent it. In cases of suspected bone and joint inflammation, it is essential to consult a doctor to determine the proper diagnosis and treatment.
What Vitamin Is Responsible for Joint Pain?
Many people suffer from joint pain, and a deficiency in certain vitamins may be responsible for this pain. In this article, we will discuss the most important vitamins that play a role in relieving joint pain and provide some sources where you can obtain these vitamins.
- Vitamin D: One of the most important vitamins for maintaining joint health and reducing inflammation is vitamin D. Your body needs vitamin D for the strength and robustness of joints. Vitamin D promotes the growth of cartilage and bones and plays an effective role in preventing hammer disorders.
- Natural Sources of Vitamin D:
Source Amount Egg Yolk 400 International Units (IU) per egg yolk Fatty Fish (such as salmon, tuna, and sardines) 1000-2000 IU per serving Vitamin D-fortified Milk 100-130 IU per cup
It is recommended to consume these natural sources of vitamin D daily to promote joint health.
- Vitamin E: Another vitamin that contributes to relieving joint pain is vitamin E. Vitamin E is a potent anti-inflammatory, and some studies have shown its positive impact on reducing joint pain. Additionally, vitamin E may help strengthen cartilage and tendons, improving joint mobility.
- Natural Sources to Get Vitamin E:
Source Amount Wheat Germ Oil 15 International Units (IU) per teaspoon Hazelnut Oil 20.3 International Units (IU) per teaspoon Sunflower Oil 7.4 International Units (IU) per teaspoon Almond Oil 41.6 International Units (IU) per teaspoon
Consuming these vitamin E-rich sources daily can contribute to reducing or avoiding joint pain.
- Vitamin K: Another vitamin that helps alleviate joint pain is vitamin K. Vitamin K is considered an anti-depressant vitamin and has prominent anti-inflammatory properties. It may reduce water retention and swelling associated with joint inflammation.
- Natural Sources to Get Vitamin K:
Source Amount Spinach 145 milligrams per 100 grams Kale 81 milligrams per 100 grams Broccoli 110 milligrams per 100 grams Radish 25 milligrams per 100 grams
These natural sources of fruits and vegetables can provide your body with vitamin K and help alleviate joint pain.
The mentioned vitamins, including vitamins D, E, and K, are among the most important vitamins that contribute to relieving joint pain. By consuming the mentioned natural sources, your body can obtain these vitamins properly to support joint health and reduce pain.