How do I know if I have a cervical disc? What is its risk and how to deal with it?
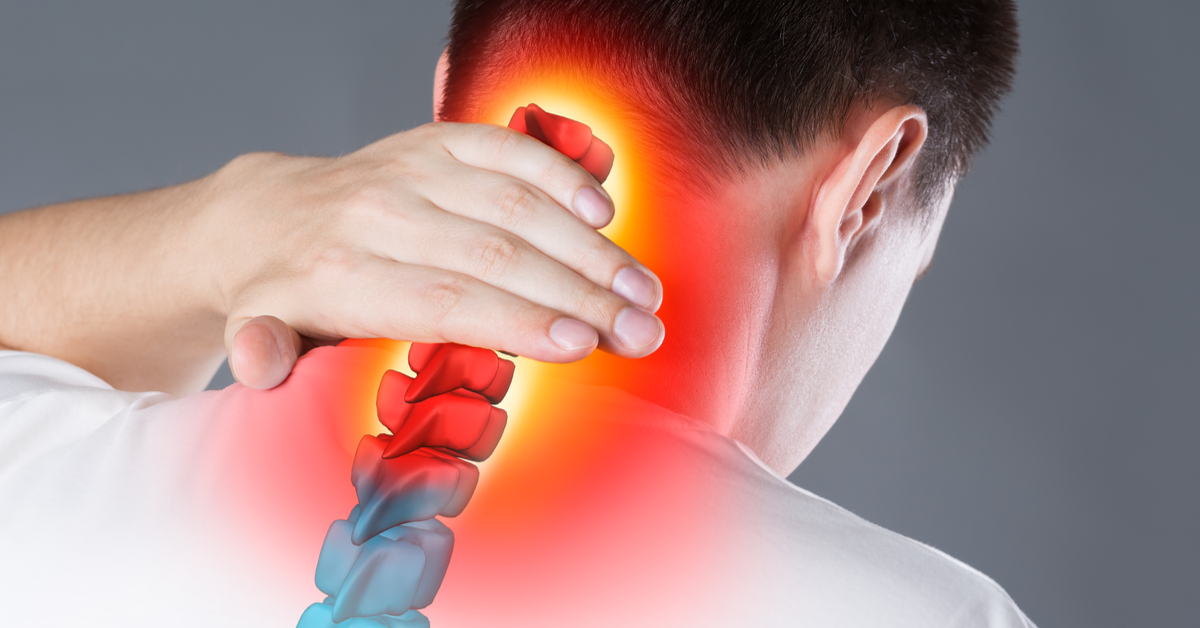
How do I know if I have a cervical disc?
Cervical disc is a common problem that affects many people around the world. Also known as a herniated cervical disc or cervical disc prolapse, it is a condition that occurs when the intervertebral disc, which acts as a cushion for the vertebrae in the cervical spine, is damaged. In this article, I will explain how to recognize the symptoms and signs of a cervical disc, and when to seek medical help.
Symptoms of a cervical disc:
- Pain in the neck and shoulders: Pain in the neck and shoulder area is one of the most common symptoms of a cervical disc. This pain can be sharp or chronic and may increase with movement or stress.
- Pain in the arms and hands: A damaged cervical disc can press on the nerves in the neck, leading to pain or tingling in the arms and hands. This pain may be accompanied by muscle weakness and difficulty controlling the hand.
- Chest pain: In some cases, people with a cervical disc may experience chest pain due to nerve involvement in the area.
- Numbness and tingling in the muscles: Numbness or tingling can occur in the muscles connected to the neck, shoulders, arms, and hands.
- Changes in movement and balance: You may experience difficulty in neck movements and overall balance due to pain and nerve pressure.
When to seek medical help:
If you are experiencing any of the symptoms mentioned above, you should consult a doctor or medical professional for an appropriate assessment and treatment. Treatment may include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy sessions, rehabilitation exercises, and in some cases, surgery.
An accurate diagnosis of the cervical disc problem often requires reliance on radiographic images such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and their impact on the patient’s life.
Prevention and care:
- Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight increases the pressure on the spine and can increase the risk of developing disc problems.
- Regular exercise: Muscle-strengthening exercises and improving the flexibility of the neck and back can help prevent disc problems.
- Maintaining good posture: You should sit and stand with the correct posture to reduce pressure on the spine.
- Avoid heavy lifting: Avoid lifting heavy objects incorrectly, and use correct lifting techniques when necessary.
In conclusion, cervical disc disease is a condition that can be treated and managed successfully if dealt with promptly. If you are experiencing any similar symptoms, it is crucial to consult a doctor for appropriate assessment and treatment. Being aware of the symptoms and taking preventive steps can help maintain good overall health for the neck and spine.
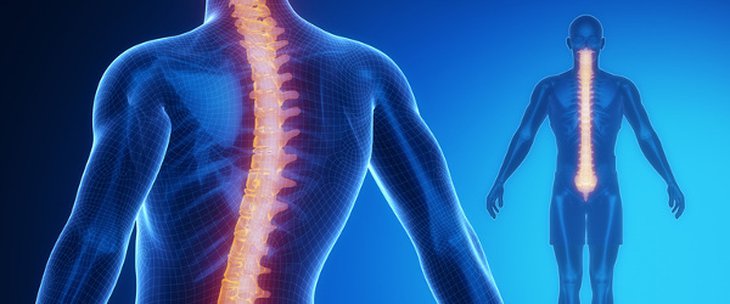
What is the cervical intervertebral disc?
Cervical intervertebral discs: Vital structures in the spine facilitated by the cervical disc.
The cervical intervertebral discs are an important part of the human skeletal structure, playing a vital role in supporting and protecting the spine and ensuring its proper movement. The cervical spine consists of seven vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper part of the back, and each cervical vertebra has its own disc. In this article, we will learn about the components of the cervical intervertebral discs and their vital role in maintaining the health of the spine.
Structure of the cervical intervertebral discs:
- Vertebral discs (cervical disc): These are the main structures in the cervical intervertebral discs. Each cervical disc is characterized by its fibrous middle structure surrounding a gelatinous nucleus in the center. This composition provides the cervical disc with flexibility and strength, which helps in shock absorption and endurance during movement.
- The outer membrane of the disc (annulus fibrosus): Surrounds the gelatinous nucleus in the cervical disc, and consists of layers of crossed fibers. This membrane enhances the structural strength of the disc and prevents the gelatinous nucleus from slipping out.
- Gelatinous nucleus: This is the viscous gel-like substance found in the center of the cervical disc. This nucleus functions to distribute pressures between the vertebrae and reduce friction during spinal movement.
Functions of the cervical intervertebral discs:
- Shock absorption: The cervical intervertebral discs act as a cushion and a conduit for absorbing shocks that the vertebrae may be subjected to during movement and daily activities. This protects the spine and reduces the risk of injuries.
- Facilitating movement: Providing smooth sliding of the vertebrae during movement, which allows the body to bend, stretch, and rotate efficiently.
- Pressure distribution: The intervertebral discs distribute pressures resulting from weight and movement between adjacent vertebrae, contributing to maintaining the spine’s alignment.
Problems with the cervical intervertebral discs:
Cervical intervertebral discs can wear out and become damaged due to factors such as aging, injuries, and spinal diseases. Excessive wear and tear can lead to conditions such as disc herniation, decreased disc height, neck inflammation, and other issues that cause pain and pressure on the nerves.
Risks of Cervical Disc Disease:
- Chronic Pain: One of the most significant risks associated with cervical disc disease is chronic pain. This pain can be localized in the neck or it may extend to the shoulders, arms, and hands. The pain affects the quality of life of individuals and may require long-term treatment.
- Pressure on Nerves and Spinal Cord: Damage to the cervical disc can lead to a herniated disc pressing on nerves and the spinal cord. This can cause acute pain, tingling, numbness in the limbs, and loss of sensory and motor functions.
- Reduced Neck Flexibility: Damage to the cervical disc can lead to reduced neck flexibility and its ability to bend and rotate normally. This affects neck movement and increases the risk of further injuries.
- Sleep and Daily Life Disturbances: Severe pain and nerve pressure can cause sleep disturbances and affect the ability to perform daily activities normally.
Treatment and Prevention:
If you are experiencing neck pain or any symptoms similar to those of cervical disc disease, it is important to consult a specialist. Treatment can include anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy sessions, and rehabilitation exercises. To prevent cervical disc problems, it is important to avoid excessive strain on the neck and to maintain good postures when sitting and sleeping, as well as to practice appropriate exercises to strengthen the neck muscles.
Cervical disc disease is a serious condition that should be taken seriously. If you feel neck pain or suffer from any related symptoms, do not hesitate to consult a doctor for necessary evaluation and treatment. Being aware of risk factors and following preventive measures can help maintain the health of the neck and spine in general.
Can cervical disc disease be cured?
Cervical disc disease is a medical condition that affects the cartilaginous disc between the vertebrae in the neck region of the spine. This cartilaginous disc is an important part of the spine that plays a vital role in supporting the spine and ensuring its proper movement. This disc can become damaged or deteriorate due to various factors, raising a common question about the possibility of recovering from cervical disc disease.
Diagnosis and Causes:
To determine the possibility of recovery from cervical disc disease, it is first necessary to differentiate between various types of cervical disc problems and to know whether the issue requires medical intervention or can heal naturally. Common causes of cervical disc issues include:
- Aging: Over time, the composition of the disc can change and become less flexible.
- Injuries: Accidents and injuries such as car crashes or severe falls can cause damage to the disc.
- Arthritis: Diseases like cervical spondylosis can lead to disc deterioration.
- Stress and Psychological Tension: Stress and tension can increase pressure on the spine.
Possibility of Recovery:
The possibility of recovery from cervical disc disease depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s condition and the severity of the problem. In mild cases, healing may be possible without the need for special medical treatment. In other cases, the patient may need to undergo treatment to alleviate pain and improve function.
Treatment and Management of Cervical Disc Disease:
- Rest and Activity Reduction: In acute cases, it may be necessary to reduce activity and give the neck time to heal.
- Medication: Anti-inflammatory drugs and pain relievers may be part of the treatment.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy sessions can help strengthen the neck muscles and improve flexibility. Rehabilitative Exercises: There are specific exercises that can help improve the neck’s posture and strength.
- Surgical Intervention: In severe cases that do not respond to other treatments, surgery may be necessary to remove the damaged disc or stabilize the vertebrae.
- Prevention: Regular Exercise: Strengthening the muscles of the neck and spine can help prevent cervical disc problems.
- Maintaining Good Posture: Avoid sitting for long periods and ensure proper posture while sitting and sleeping.
- Stress Management: Effectively managing stress and tension can reduce the risk of exacerbating cervical disc problems.
The possibility of recovery from cervical disc disease depends on multiple factors such as the type of damage, the severity of the problem, and the treatment pursued. In many cases, symptoms can be improved and comfort increased thanks to proper treatments and management. If you are suffering from neck pain or suspect a problem with a cervical disc, you should consult a specialist for an evaluation and appropriate treatment.
How does a patient with cervical disc disease sleep?
How can a patient with cervical disc disease sleep comfortably and healthily?
Patients with cervical disc disease often suffer from pain and tension in the neck area, which can make sleeping difficult and uncomfortable. However, there are measures and techniques that can help these patients improve the quality of their sleep and reduce pain during sleep. In this article, we will look at how a patient with cervical disc disease can sleep comfortably and healthily.
Optimal sleeping position for a patient with cervical disc disease:
- Lying on the back position: It is preferable for a patient with cervical disc disease to sleep on their back with a supportive pillow under their head and neck. This position helps maintain the spine’s axis straight and relieves pressure on the neck.
- Lying on the side position: If sleeping on the back is uncomfortable, the patient can sleep on their side by placing a supportive pillow under the head and under the upper side of the body. Sleeping on the stomach should be avoided as it can increase neck tension.
- Using an appropriate pillow: It is preferred to use a neck-support pillow that provides support to the neck area. Pillows specially designed for cervical disc disease patients with a neck cutout can be very helpful.
Tips for comfortable sleep:
- Avoid excess weight: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce pressure on the spine and improve sleep quality.
- Avoid excessive activity before bedtime: Physical activities that are intense or increase neck tension should be avoided before going to bed.
- Relaxation and stress relief: Relaxation techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help calm the mind and body before sleep.
- Benefiting from massage: Targeted massage sessions for the neck and shoulders can relieve tension and pain.
- Consult a doctor: If neck pain and tension persist during sleep, it is advisable to consult a specialist for an accurate assessment and specific guidance.
Treatment and care for cervical disc disease:
- Medical treatment: In some cases, it may be necessary to use medication to alleviate pain and swelling.
- Physical therapy: Physical therapy sessions help strengthen neck muscles and improve their flexibility.
- Rehabilitation exercises: Exercises prescribed by a physical therapist can help strengthen the muscles and increase stability in the neck area.
Sleeping comfortably and healthily for a patient with cervical disc disease depends on the correct position and support, and on avoiding factors that increase pain and tension in the neck. It is always necessary to consult a specialist for an assessment and guidance and to ensure appropriate health care for a patient with cervical disc disease.
Can Neck Cartilage Cause Paralysis?
Neck cartilage is a condition that affects the cartilaginous disc between the vertebrae of the spinal column in the neck area. This disc is characterized by its vital role in supporting the spine, facilitating movement, and absorbing shocks. Many people experience issues with their neck cartilage at various stages of their lives, but can these issues lead to paralysis? In this article, we will explore the relationship between neck cartilage and paralysis and understand how to deal with this condition.
Neck Cartilage and Paralysis:
Neck cartilage itself does not directly cause paralysis. However, it can lead to pressure or irritation of the nerves in the neck area, which can result in symptoms such as pain, tingling, and numbness in the arms and hands. In severe cases, this nerve pressure can cause muscle weakness in the arms and hands, which may resemble some symptoms of paralysis. However, this is not complete paralysis, which means a total loss of movement.
Symptoms Associated with Neck Cartilage: Neck Pain: Pain is one of the common symptoms of neck cartilage issues. The pain can be acute or chronic and may increase or decrease with changes in the neck’s position. Tingling and Numbness: The pressure of the cartilaginous disc on the nerves can cause tingling and numbness in the arms and hands. Muscle Weakness: In severe cases, the pressure of the cartilaginous disc on the nerves can lead to muscle weakness in the arms and hands.
Risk Factors:
Some factors can increase the risk of serious effects on the spine due to problems with neck cartilage. These factors include:
- Delayed diagnosis and treatment: Not addressing neck cartilage problems in time can increase the risk of worsening symptoms and further affecting the nerves and muscles.
- Previous injury: If there is a history of previous injuries in the neck, this may be a factor that increases the risk of developing issues with neck cartilage.
- Aging: With age, the organs and tissues in the body become less capable of recovering from damage, which increases the risk of exacerbating problems.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Medical Consultation: If you are experiencing symptoms of neck cartilage problems such as pain, tingling, and numbness, you should consult a specialist doctor for necessary assessment and treatment.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy sessions can help strengthen the neck muscles and improve their flexibility.
- Medication: In some cases, anti-inflammatory medications and pain relievers may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms.
- Surgery: In severe cases that do not respond to other treatments, surgery may be necessary to repair the problem.
Although neck cartilage does not directly cause paralysis, it can result in symptoms resembling paralysis in severe cases. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek the necessary medical care and adhere to the treatments and guidance provided by health specialists to prevent the problem from worsening and to improve your quality of life.
Does neck cartilage cause headaches?
Headaches are a common condition that affects many people around the world, and there are several factors that can cause headaches. Among these factors, neck cartilage is one that can lead to the development of headaches. In this article, we will explore the relationship between neck cartilage and headaches and how this matter can be dealt with.
Neck Cartilage and Nerve Pain:
Neck cartilage is a condition that affects the cartilaginous disc located between the vertebrae of the spine in the neck area. This cartilaginous disc functions to provide balance and support to the spine and contributes to guiding movement and absorbing shocks. When this disc is damaged or slips, it can cause pressure on the nerves in the neck area.
This pressure on the nerves can lead to a range of symptoms that include pain, numbness, and tingling in the neck, shoulders, arms, and hands. If this nerve pressure is present in the head or neck area, it may lead to the onset of headaches.
Types of Headaches Associated with Neck Cartilage:
- Tension Headache: Pain in the head and neck area can be a result of the tension of the muscles surrounding the neck. Damaged neck cartilage can lead to increased muscle tension and thus the appearance of tension headaches.
- Migraine: Migraine is a common type of headache and may be related to the pressure of the cartilaginous disc on the nerves in the neck.
- Cervicogenic Headache: In some cases, pressure from neck cartilage on nerves and blood vessels in the head can cause cervicogenic headaches.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
If you suffer from headaches associated with neck cartilage, you should consult a specialist doctor for assessment and necessary treatment. Treatment can include:
- Medication: Doctors may recommend anti-inflammatory medications and pain relievers to alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy sessions can help strengthen the neck muscles and improve their flexibility.
- Rehabilitative Exercises: Specific rehabilitative exercises can help improve the posture of the neck and increase its strength.
- Relaxation and Stress Relief: Relaxation techniques such as meditation and deep breathing can help calm the mind and body and reduce stress.
- Consulting a Specialist: If the headache persists or the symptoms worsen, the doctor may need to consider advanced treatment options such as surgery.
Neck cartilage can lead to the onset of headaches by putting pressure on nerves or by increasing muscle tension in the neck. It is essential to seek necessary medical care if you suffer from headaches associated with neck cartilage to get the right assessment and treatment and to improve your quality of life.