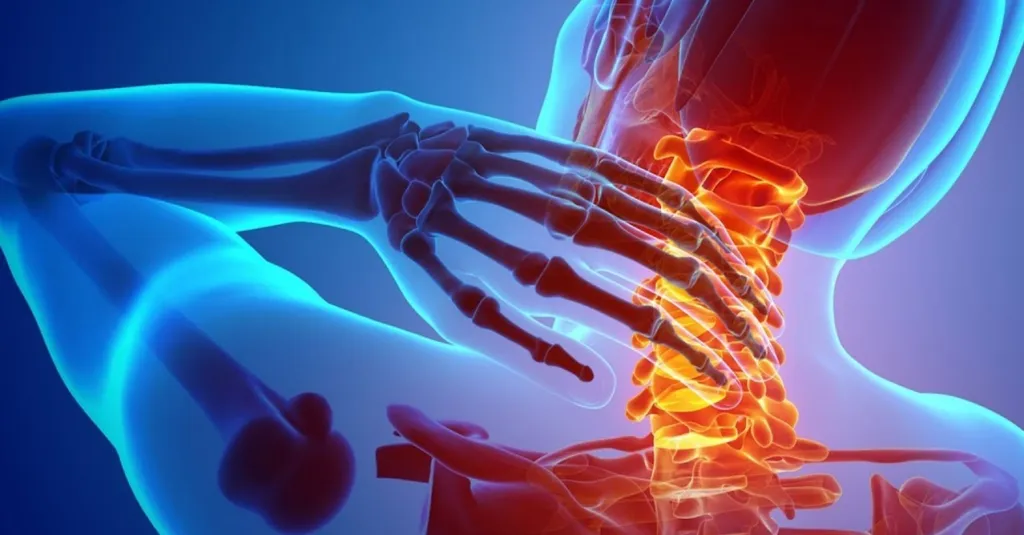
Learn More About Spinal Protrusion and Is Spinal Protrusion Normal?
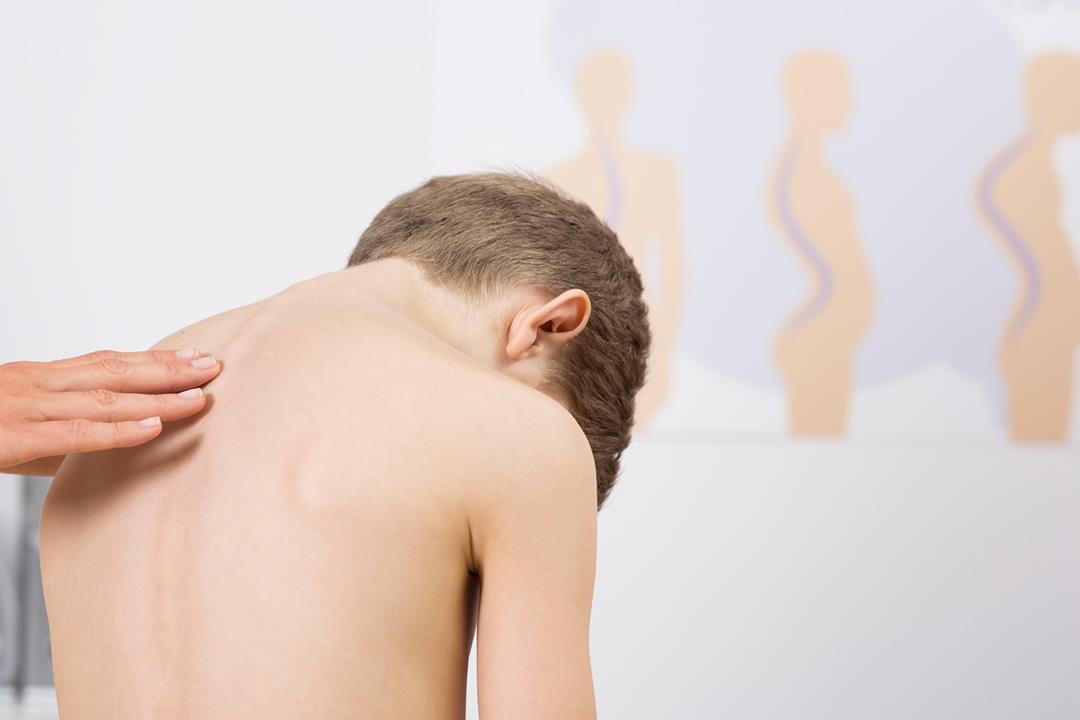
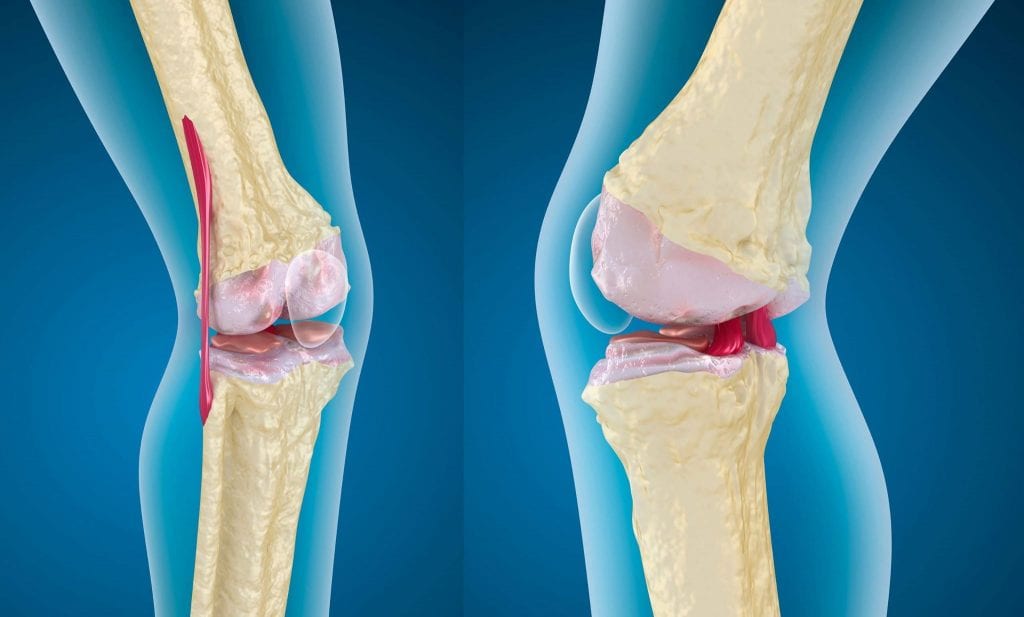
Spinal Vertebrae Protrusion
The protrusion of the vertebrae in the back is a condition that occurs due to a lack of gelatinous substance inside the spinal discs, and it may be a result of aging or a spinal injury. Here is what you need to know about disc protrusion in the back:
- Structure of the Spine: The spine consists of a series of interlocking bones called vertebrae, which provide support for the back and allow it to move and bend. Between each vertebra, there is a cartilaginous tissue called the spinal disc.
- Protrusion of the Spinal Discs: Protrusion of the spinal discs occurs as a result of damage to the gelatinous substance within them, which deteriorates over time. Disc protrusion can be due to aging, where the disc gradually changes from its normal shape to a bulging form.
- Causes of Disc Protrusion: The cause of disc protrusion can be a spinal injury, such as car accidents or severe falls. Disc protrusion can also occur due to changes in the structure of the spine or curvature of the back.
- Symptoms Associated with Disc Protrusion: Symptoms caused by disc protrusion can include pain in the back and neck area, and a feeling of numbness or weakness in the limbs connected to the affected spinal column.
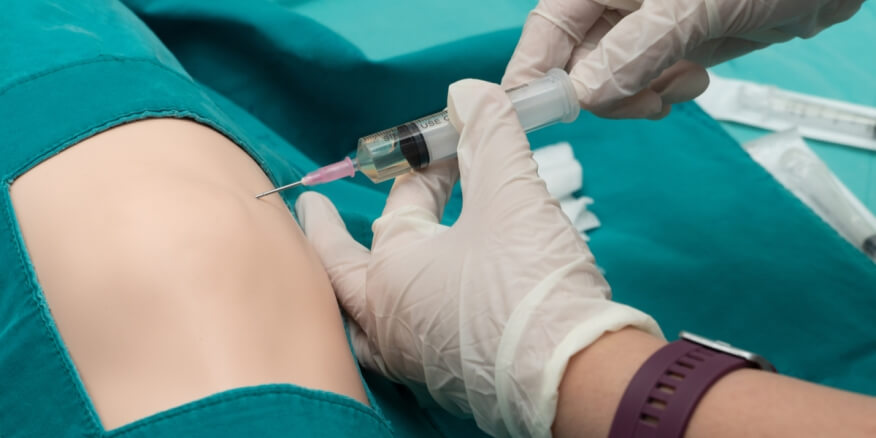
- Diagnosis and Treatment: To diagnose disc protrusion, X-rays or MRI imaging may be used to monitor changes in the structure of the spine. Treatment depends on the severity of the symptoms and may include physical therapy, instructions for maintaining proper back posture, and reducing pressure on the affected spinal discs. In severe cases, surgery may be suggested.
- Precautions and Tips: To prevent disc protrusion or the worsening of the condition, it is advised to follow some important tips. Maintain a good body posture while sitting and standing, and avoid lifting heavy loads incorrectly. It is also important to perform appropriate exercises to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles.
Back disc protrusion is a medical condition that requires a professional evaluation to determine the problem’s diagnosis and develop an appropriate treatment plan. It is important to consult a specialist for an assessment and to receive appropriate advice and treatment.
What Causes Back Vertebrae Protrusion?
Back vertebrae protrusion or spinal protrusion is a common condition that many people may suffer from. This protrusion can have a negative impact on an individual’s daily movement and comfort. But what are the causes of this condition, and what factors may contribute to its occurrence? In this article, we will explore some common causes of back vertebrae protrusion.
Aging: As time progresses, the spinal disc begins to deteriorate and suffer from a loss of gel-like substance within it. This deterioration, a result of aging, can contribute to the protrusion of spinal vertebrae.
Injuries and Accidents: Spinal protrusion may result from traumatic injuries to the spine, such as car accidents or severe falls. These injuries can lead to damage of the spinal disc and a decrease in spinal flexibility, resulting in vertebrae protrusion.
Physically Demanding Activities: Back vertebrae protrusion can occur from engaging in physically strenuous activities and excessive effort, such as lifting heavy weights or performing intense exercises unsafely. This intense pressure on the spinal disc can cause damage and lead to vertebrae protrusion.
Spinal Structural Deformities: Spinal deformities such as kyphosis, scoliosis, spinal misalignment, or incorrect vertebral recording can lead to their protrusion. These deformities may be hereditary or acquired over time.
Prolonged Sitting in Daily Activity: Sitting for long periods without changing body posture can lead to weakening of the muscles in the back area, accumulation of pressure on the spinal disc, and vertebrae protrusion.
In conclusion, individuals suffering from back vertebrae protrusion should adhere to the advice of a qualified medical consultant, managing the condition according to their guidance. Consulting a doctor and undergoing necessary examinations may help in identifying the precise causes of vertebrae protrusion and implementing appropriate treatment.
Is Spinal Protrusion Normal?
Here is a list containing some important information regarding spinal protrusion and whether it is considered normal or not:
Spinal protrusion may be a symptom of a problem in the spinal bones, where there is a deviation in the shape of the vertebrae and a change in their normal distribution. Spinal protrusion typically results from a weakness in the spinal bones, which causes their compression or fracture, and is common among the elderly. Spinal protrusion can also occur in children, typically beginning during the growth spurt before puberty. Humpback in children can be accompanied by some other medical issues.
- Spinal protrusion is generally not normal and can cause health problems such as back pain and reduced mobility.
- Spinal protrusion can occur for several reasons, including fractures or breaks in the vertebrae and deformities in the shape of the spine.
- Spinal protrusion is not normal if the curvature is beyond natural limits and causes pain and reduced mobility.
- A doctor should be consulted if you notice an increase in the curvature of the upper part of your back or in your child’s spine, as a medical examination can determine the cause of the deviation and treat it appropriately.
- The doctor may recommend additional examinations and tests, such as X-rays or MRI, to assess the position of the spine and detect any health problems that may be causing the protrusion.
Note: Spinal protrusion should not be ignored, and a doctor should be visited to assess the condition and direct appropriate treatment if necessary.
What are the most outwardly protruding vertebrae?
The bony vertebrae are among the most important and significant parts of the human body. Each vertebra has a specific role in supporting and protecting the spine. Although vertebrae are known for their function as components of the spine, some are more noticeably protruding than others. In this article, we will look at the most outwardly protruding vertebrae.
C7 Vertebra: The seventh cervical vertebra (C7) is the most outwardly protruding in the spine. It is located in the upper part of the spine, extending from the neck to below the shoulders. The prominence of this vertebra is clearly noticeable in the back of the neck and is easily observed by people when turning their heads.
L5 Vertebra: The fifth lumbar vertebra (L5) is second in terms of severe outward protrusion. Although most people’s spines have five lumbar vertebrae, the fifth vertebra is the most prominently protruding. It is located in the lower part of the spine and is connected to the pubis and pelvis.
C5 Vertebra: The fifth cervical vertebra (C5) is also one of the vertebrae that protrudes noticeably in the spine. It is located below the fourth cervical vertebra, extending to the upper part of the lower neck. People can notice the protrusion of this vertebra when they bend their head down or look up.
L2 Vertebra: If you suffer from a noticeable protrusion in the spine in the middle of the back, it may be due to the second lumbar vertebra (L2). This vertebra is situated between the first and third lumbar vertebrae and is one of the most stable and pressure-bearing vertebrae.
L4 Vertebra: The fourth lumbar vertebra (L4) comes in our list as one of the vertebrae that might protrude noticeably. It is located in the middle of the back and is an important part of the spine.
The most outwardly protruding vertebrae can reflect potential problems in the spine, so it is important to consult a doctor if there is any noticeable change in the protrusion of the vertebrae. Orthopedic doctors and spine surgeons undertake the examination of the vertebrae and direct appropriate treatment, whether by traditional methods or through surgical operations.
What is Lumbar Spinal Bulging?
Here’s a brief list explaining what lumbar spinal bulging is, what can cause it, and how to treat it:
Definition of Lumbar Spinal Bulging:
- Lumbar spinal bulging refers to the drying or damage of the spongy material found between the vertebrae in the spine.
- A lumbar disc is present between each pair of vertebrae, serving as a flexible cushion that absorbs shocks.
Causes of Lumbar Spinal Bulging:
- Unhealthy lifestyle: Such as smoking, lack of exercise, poor nutrition, which can cause problems in the lumbar vertebrae.
- Aging: Due to natural changes in the body, the lumbar disc becomes dry and damaged.
Symptoms of Lumbar Spinal Bulging:
- Pain in the back and buttocks: The person may experience moderate pain in the back and buttock area.
- Numbness and tingling: There may be numbness and tingling in specific areas of the body.
- Muscle weakness: The person may notice general muscle weakness.
How to Treat Lumbar Spinal Bulging:
- Physical therapy: Can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the vertebrae and reduce pain.
- Rehabilitation exercises: Targeted rehabilitation exercises can improve muscle strength and vertebral movement.
- Medications: The doctor may prescribe medications to help relieve pain and swelling.
- Surgery: In advanced cases, the doctor may resort to surgery to replace the lost disc or stabilize the damaged vertebrae.
Prevention of Lumbar Spinal Bulging:
- Daily exercise: Strength, flexibility, and balance exercises should be done to strengthen muscles and support the vertebrae.
- Maintaining a correct posture while sitting, standing, and sleeping: It is important to use suitable pillows and furniture to maintain a correct back posture.
- Attention to healthy nutrition: Foods rich in calcium and vitamin D should be consumed to strengthen bones.
- Avoid factors that can lead to drying and damage of the lumbar vertebrae such as smoking and unhealthy nutrition.
Lumbar spinal bulging is a condition that requires those affected to seek appropriate medical advice. It is advised to continue following treatment and practice prevention to maintain spinal health.
What are the Most Dangerous Vertebrae in the Spine?
The C1 and C2 vertebrae are considered the most dangerous vertebrae in the spine. They are located in the neck area and play a crucial role in connecting the spine to the head. The C1 vertebra, also known as “Atlas,” and the C2 vertebra, known as “Axis,” are the first two vertebrae in the neck.
The spine consists of 33 or 34 vertebrae, depending on whether all the coccygeal vertebrae are fused or not. The spine is divided into five regions, with the cervical vertebrae being among the most dangerous due to their sensitive location.
The impact of injury to the most dangerous vertebrae in the spine includes loss of control over the neck and surrounding area, leading to complete paralysis in that region. Injuries in these vertebrae range from fractures and tears to spinal cord inflammations and nerve compression.
Here are some types of injuries to the most dangerous vertebrae of the spine:
- Cervical Vertebrae Injuries: These include neck fractures, ligament tears, and nerve damage. Such injuries typically require crucial surgeries to stabilize the vertebrae and restore the spine’s natural alignment.
- Thoracic Vertebrae Injuries: These injuries usually occur due to car accidents or severe falls. They can cause spinal cord damage, paralysis, and loss of movement and sensation.
- Lumbar and Sacral Vertebrae Injuries: Located at the lower part of the spine, these contain several fused coccygeal vertebrae. Injuries can cause pressure on the lumbar and sacral nerve roots, leading to back pain and numbness.
- Coccygeal Vertebrae Injuries: These usually occur due to falls onto the buttocks or extreme sports accidents. They cause pain in the sacrum and coccyx, making sitting and movement difficult.
Injuries to the most dangerous vertebrae of the spine have negative effects on multiple parts of the body. They can lead to loss of movement control, loss of sensation in the limbs, malfunctioning of the stomach and intestines, and an increased risk of infectious diseases like blood clots and pressure ulcers.
To maintain spinal health and avoid injuries, it is recommended to regularly exercise to strengthen the back and neck muscles, follow proper lifting and bending methods, and adjust sitting and sleeping postures.
**Always consult a specialist for the diagnosis and treatment of any spinal issues.
Is There a Treatment for Protruding Back Vertebrae?
It’s known that a natural protrusion is common in the cervical vertebrae among people and is expected. However, some individuals may experience issues with protruding vertebrae in the back and may wonder if there is a solution or treatment.
Here is a list of some treatments and procedures that can be taken to deal with protruding back vertebrae:
- Physical Therapy: Doctors may recommend visiting a physical medicine and rehabilitation specialist to develop an appropriate treatment program. Physical therapy teams can provide massages and specific exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility in the back and neck. Physical therapy may require regular sessions for the best results.
- Medications: The doctor may prescribe certain pain relievers to alleviate pain and possible inflammation in the back. It’s important to consult with a doctor about the appropriate dosage and potential side effects.
- Exercises and Self-Care: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and performing suitable exercises can be important in strengthening the muscles that support the back. The specialist may recommend a specific set of exercises and daily practices that can help maintain the spine’s alignment.
- Surgical Treatment: In severe cases and when other treatments do not respond, the doctor may consider surgery. The surgical method depends on the cause of the vertebral protrusion and its impact on the individual’s health and daily life. This step should be taken cautiously and after consultation with a specialized medical team.
Please note that this information is provided based on online data, and for a specific diagnosis and personalized treatment, individuals should consult a specialist doctor.
In conclusion, individuals suffering from back vertebrae protrusion should consult specialized doctors and refer to reliable medical pamphlets and scientific documents for accurate guidance and personal diagnosis.
Does Excess Weight Affect Back Vertebrae?
Excess weight can be a contributing factor to back pain. Overweight and obesity can increase pressure on the spine and joints, leading to tissue deterioration and damage, thereby causing back pain. In this article, we will review some of the harmful effects of obesity on back pain, as well as some measures that can be taken to alleviate these pains.
Additional Pressure on Joints: Excess weight is an additional strain on the joints, leading to damage to the surrounding tissues and consequently causing back pain. The spine is subjected to significant pressure due to excess weight, affecting the health of the vertebrae and the discs between them.
Increased Risk of Disc Relapse: Disc relapse is a condition where the disc between vertebrae moves, causing chronic lower back pain. Excess weight increases the risk of this condition as it puts more pressure on the intervertebral discs. Consequently, losing excess weight can reduce the likelihood of this problem and alleviate associated pain.
Weakness of Back Muscles: Back muscles support and strengthen the spine, but excess weight can lead to muscle weakness. When back muscles are weak, the spine is unstable and lacks adequate support, increasing the likelihood of back pain.
Balance Problems: Excess weight can affect the body’s balance and center of gravity, weakening the stability of the spine. When balance is unstable, there is additional pressure on the vertebrae, which can lead to back pain.
To minimize the impact of obesity on back pain, the following measures can be taken:
Reduce Excess Weight: This can be achieved by following a healthy and balanced diet, and regularly engaging in physical activity. Exercise: Strength and aerobic exercises can help strengthen back muscles and support the spine. Improve Posture: Sitting and standing with correct posture can reduce pressure on the spine and alleviate back pain. Relaxation and Stress Reduction: Relaxation and practicing meditation techniques can help reduce stress and alleviate back pain.
In summary, excess weight can affect the back vertebrae and increase the likelihood of back pain. Maintaining a healthy weight and adopting a healthy lifestyle are important to prevent back pain associated with obesity.
Does a Back Brace Treat Kyphosis?
Degenerative disc disease and herniated discs are two common conditions that many suffer from, and many look for ways to alleviate their back pain and problems. Some turn to back braces in an attempt to treat kyphosis. But does a back brace really treat this condition? Let’s find out the truth.
Back Brace: A Supportive Treatment Element A back brace is a supportive element in treatment and is not a substitute for prescribed medication. If you suffer from kyphosis, a doctor may recommend wearing a back brace as part of the treatment, along with other practices.
Role of the Back Brace in Kyphosis The back brace aims to strengthen back muscles and straighten your spine. By providing stabilization, it helps relieve pressure on the spine and reduce pain.
Total Reliance on Back Brace is Not Beneficial Relying solely on a back brace as the primary means to correct kyphosis is not advisable. Consult with your treating physician about the appropriate brace and correct usage instructions.
Consult a Doctor Before Using Before using any type of back brace, it is important to consult with your treating physician to determine if it is suitable for your specific condition. You may be directed to a particular type or advised to practice other methods to alleviate kyphosis pain.
Moderate Use of Back Brace The back brace should be used moderately and under a doctor’s supervision. Avoiding reliance on the back brace for long periods and not wearing it at all times can help maintain the strength of the back muscles and improve their endurance.
In conclusion, a back brace is a helpful element in treating kyphosis. However, it is essential to consult a doctor before using it and not to rely on it entirely as the sole treatment method. Always remember that adhering to the instructions of your treating physician and taking care of your back health are key to improving your condition.