What is the effect of cervical spine compression on nerves? Learn about treatment methods
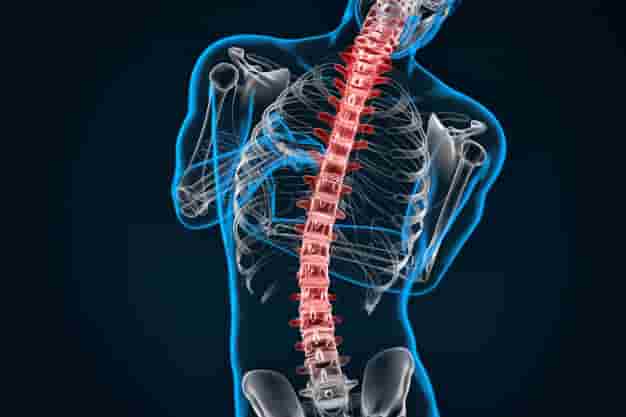
The Effect of Cervical Spine Compression on Nerves
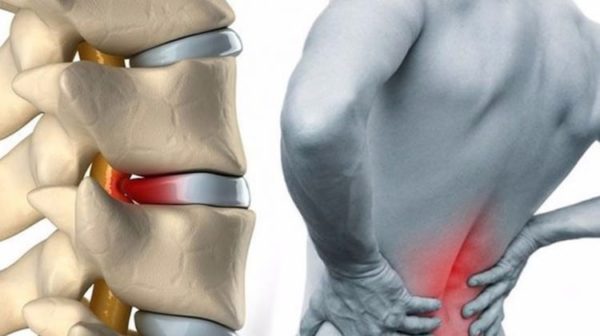
Cervical spine compression can lead to several health problems and troublesome symptoms. If there is continuous pressure and an increase in the compression on the nerves in this area, it may result in nerve compression and irritation around the cervical vertebrae. Individuals experiencing cervical spine compression may feel pain, weakness, and numbness in areas affected by the nerve.
In this article, we will explore the effect of cervical spine compression on nerves in detail, along with potential causes, symptoms, diagnostic methods, and treatment options.
Causes of Cervical Spine Compression on Nerves
There are several potential causes of cervical spine compression on nerves, including:
- Disc Herniation: Disc herniation occurs when the cervical disc moves between the vertebrae and compresses the roots of the surrounding nerves. This can result from inflammation or tearing of the disc and the leakage of a portion of it outward.
- Bone Spur: Bone spur development in cervical joints, due to aging or arthritis, can lead to narrowing of the space between the vertebrae and an increase in nerve compression.
- Inflammation and Swelling: Swelling and inflammation in the cervical vertebrae area, resulting from injury or arthritis, can increase the pressure on the nerves.
- Injuries: Severe injuries or fractures in the cervical vertebrae can cause an increase in nerve compression and pressure.
Diagnosis of Cervical Spine Compression on Nerves
To diagnose cervical spine compression on nerves, a doctor may perform a series of examinations and tests, including:
- Physical Examination: The doctor may conduct a physical examination and review your medical history to assess your symptoms and evaluate your overall condition.
- Computed Tomography (CT) or Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Scans: The doctor may request imaging of the affected vertebrae to reveal any structural changes or disc herniation.
- Nerve Function Tests: Nerve function tests may be ordered to determine the extent of the impact of cervical spine compression on nerve functions and their connections.
Treatment for Cervical Spine Compression on Nerves
The treatment options for cervical spine compression on nerves depend on the severity of symptoms and their cause. The doctor may recommend the following treatments:
- Non-Surgical Treatment: This type of treatment may include rest, avoiding painful activities, applying ice or heat to relieve pain, and taking over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles around the spine, improve posture, and increase flexibility. Physical therapy methods may include rehabilitation exercises, massage, and thermal or cold therapy.
- Improving Movement Guidance and Relaxation Techniques: Learning movement guidance, meditation, and relaxation techniques can be beneficial for pain control and improving comfort.
- Medications: The doctor may prescribe some anti-inflammatory drugs, pain relievers, or muscle relaxants to alleviate symptoms.
- Surgical Treatment: In cases where non-surgical treatments do not provide relief, surgery may be necessary. The type of surgery depends on the cause of spinal nerve compression and the severity of symptoms.
Cervical spine nerve compression does not typically pose a serious condition; however, if you experience bothersome symptoms that negatively impact your quality of life, it is advisable to consult a specialist. A doctor can provide a precise diagnosis and recommend an appropriate treatment plan to alleviate symptoms and improve your overall condition.
What Are the Symptoms of Spinal Nerve Compression?
Spinal nerve compression can lead to painful and bothersome symptoms that affect the individual’s life. Nerve compression occurs when nerves are compressed due to repeated pressure or spinal disc herniation, resulting in inflammation and irritation of the nerves surrounding the spinal cord.
Symptoms of spinal nerve compression vary depending on the location and severity of the compression. Here are some common symptoms of spinal nerve compression:
- Pain at the Compression Site: The affected person may experience sharp pain at the site of compression, such as the neck or back. The pain may be continuous or intermittent and can worsen with certain movements or activities.
- Numbness and Tingling: Spinal nerve compression can lead to numbness and tingling in areas affected by the compressed nerves. The individual may feel numbness in the extremities, such as the hands and feet, often accompanied by tingling or loss of sensation.
- Muscle Weakness: Spinal nerve compression may result in weakness in the muscles surrounding the affected area. The individual may find it difficult to move the affected area easily or correctly.
- Radiating Pain: The affected person may experience pain radiating from the compression site to other parts of the body. For example, if there is pressure on a spinal nerve, the person may feel pain spreading from the back to the legs.
- Sensory Changes: Individuals with spinal nerve compression may experience sensory changes, such as heightened sensitivity to heat and cold.
- Bowel and Bladder Dysfunction: Spinal nerve compression can affect the functioning of the bowels and bladder, leading to difficulty in urination or defecation.
- Difficulty in Movement: People with spinal nerve compression may find it challenging to perform certain movements or walk easily. They may experience overall weakness in the compression area.
- Severe Pain: In severe cases of spinal nerve compression, the individual may suffer from intense pain, especially when sitting or standing for extended periods.
These are some common symptoms of spinal nerve compression. Individuals experiencing similar symptoms should seek medical attention for a precise diagnosis and appropriate treatment. These symptoms should not be ignored as they may indicate a more serious problem that requires immediate medical care.
What Happens When the Spine Presses on a Nerve?
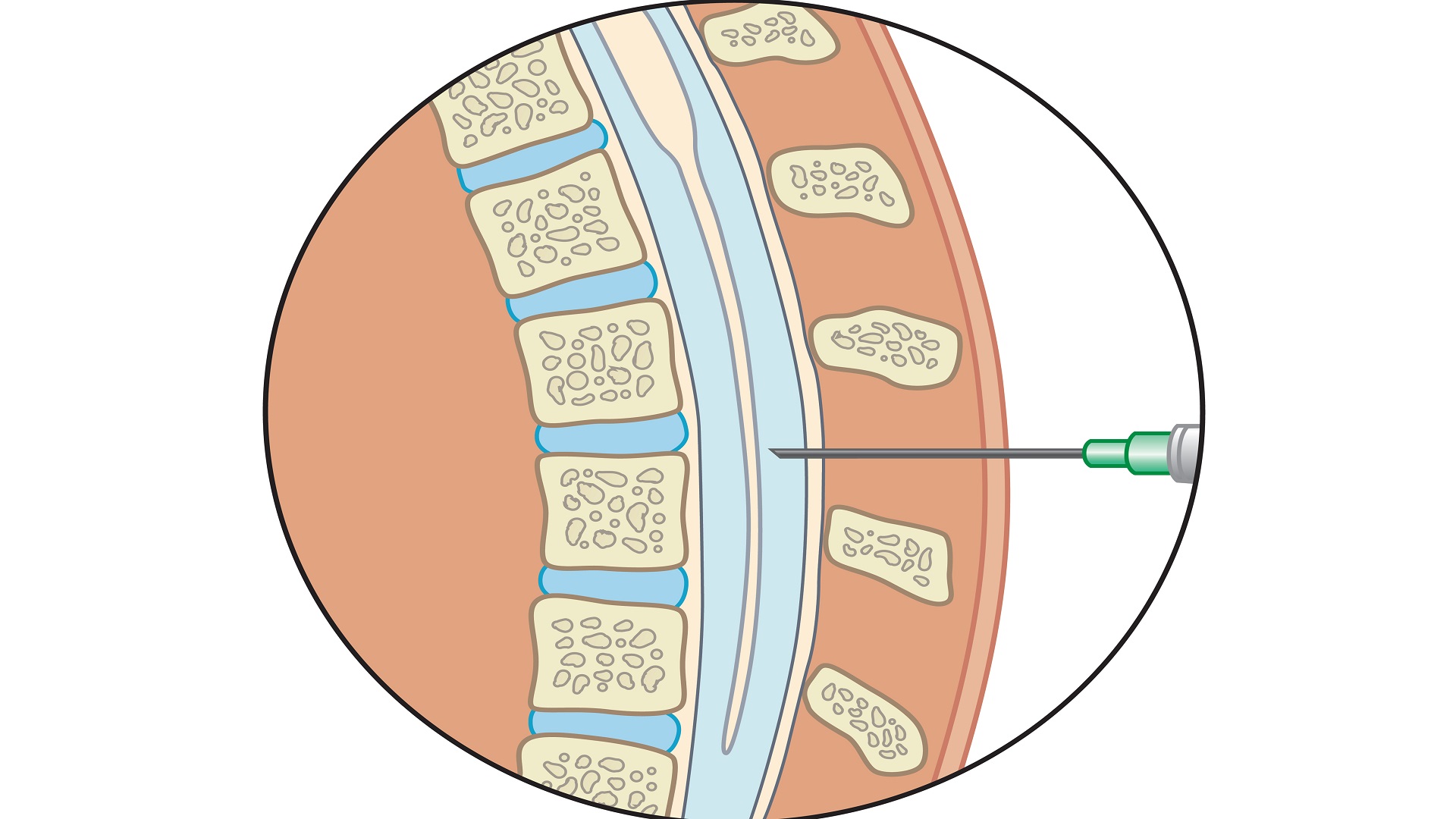
When there is pressure on the vertebrae in the back, it can lead to a condition known as spinal nerve compression (or nerve root compression). This pressure can result from several causes, such as spinal disc herniation, spinal stenosis, inflammation, or other factors.
When a nerve is compressed, it can manifest symptoms like sharp or chronic pain in the back or the affected lower part of the body, tingling, pins and needles, muscle weakness, and numbness. The treatment for nerve compression depends on its cause and severity and may include pain-relieving medications, physical therapy sessions, muscle-strengthening exercises, and, in some cases, surgical intervention to alleviate pressure on the affected nerve.
It is crucial to consult a specialist for a thorough assessment, accurate diagnosis, and the appropriate treatment if you are experiencing symptoms of nerve compression in the back.
What Is a Disc Herniation?
An intervertebral disc, commonly known as a spinal disc, is an essential structure in the spinal column that acts as a cushion between vertebrae, absorbing shock and aiding joint movement. The spinal disc consists of a tough outer shell surrounding a gel-like inner core called the nucleus pulposus. When a spinal disc deteriorates or becomes damaged, it can lead to compression of the surrounding nerves.
Levels of Damage in Disc Herniation
Symptoms of spinal nerve compression vary depending on the level of damage and the extent of the herniation. The levels of damage can be classified as follows:
- Early Stage: This stage occurs when the spinal disc begins to deteriorate, causing sporadic and varying degrees of pain in the back or neck. These symptoms can be temporary and may lead to chronic pain in some cases.
- Intermediate Stage: In this stage, the spinal disc starts to slip or move out of place, resulting in pressure on the nerve. This can lead to pain radiating from the neck to the arm or from the back to the leg. Tingling may also occur in the affected limbs.
- Advanced Stage: When the pressure on the nerve increases significantly, the pain becomes severe and intolerable. Numbness may become more pronounced, and it can lead to muscle weakness in the affected areas. In some cases, this can even result in disabilities.
Do Vertebrae Affect Nerves?
Yes, vertebrae can significantly affect nerves. Nerves extend from the spinal cord through the vertebrae in the human body, and when problems occur in the vertebrae, such as herniated discs or spinal canal narrowing, pressure can be exerted on the nerves that pass through them.
This can lead to severe pain, numbness, and weakness in the areas supplied by the compressed nerves. Examples of this include back and neck pain, radiating pain to the limbs, muscle weakness, and loss of sensation in specific parts of the body.
What Is the Treatment for Cervical Spinal Compression?
Cervical spinal compression is a common condition that affects the spinal column and the nerves that pass through it. Cervical spinal compression occurs when one of the base discs between the vertebrae is compressed, leading to irritation and inflammation of the nerves extending from these discs. It can cause troublesome symptoms like pain, tingling, and weakness in the areas served by these nerves.
Fortunately, there are several effective ways to treat cervical spinal compression and alleviate its accompanying symptoms. In this article, we will explore the top 3 methods for treating cervical spinal compression on nerves.
Conservative Treatment
Conservative treatment is one of the first options in the management of cervical spinal compression. This treatment includes measures that patients can follow on their own before resorting to more invasive therapies. It involves:
- Rest: Patients with cervical spinal compression are advised to rest and stay in a comfortable position to reduce pressure on the nerves. Taking breaks and avoiding prolonged periods of standing or sitting is recommended.
- Application of Compresses: Warm or cold compresses can be used on the affected area to alleviate pain and provide relief. Applying suitable compresses for 20 minutes several times a day is recommended.
- Gentle Exercises: Stretching and muscle-strengthening exercises can help strengthen the muscles around the vertebrae and alleviate nerve pressure. It’s advisable to consult a doctor or a healthcare professional to determine appropriate exercises and receive guidance on how to perform them correctly.
Medical Treatment and Medications
When conservative treatment is not sufficient to alleviate pain and symptoms, medical treatment and medications may be required. Here are some available options:
- Taking Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can be used to relieve pain.
- Topical Medications: Topical creams or ointments containing pain-relieving compounds can be used to alleviate localized back pain.
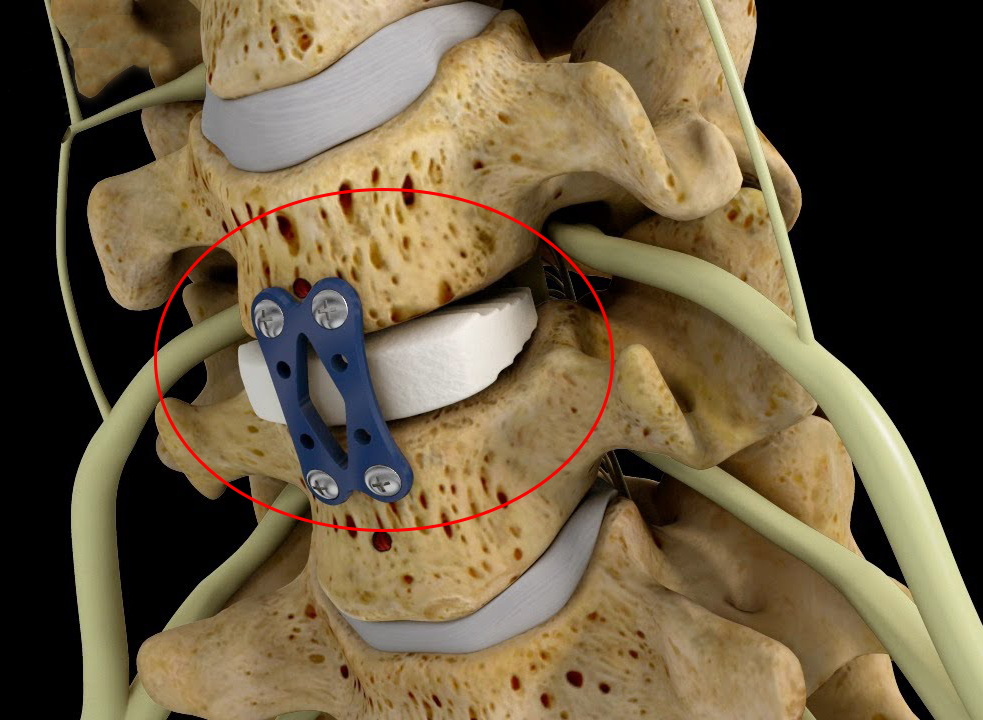
Surgical Treatment
In severe cases and when the patient does not respond to conservative treatments and medications, the doctor may resort to surgical treatment as a last resort. Surgery is usually performed to remove pressure from the affected nerve or repair a herniated disc. It is important to consult with a specialist and a healthcare provider before making the decision to undergo surgery.
Before applying any treatment for cervical spinal compression, it is advisable to consult with an experienced physician, discuss the available options, and properly assess the condition.
In conclusion, it is emphasized the importance of following the doctor’s guidance, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and regularly engaging in exercises to maintain back health and prevent future problems.