Learn about the causes of disc compression on the nerve, its symptoms, and treatment options.
Disc Compression on Nerve: Important Information
- Definition of Disc Compression on Nerve:
Disc compression on the nerve occurs when the vertebral disc shifts from its position and compresses the nerve roots in the spinal column. This compression causes severe pain that radiates from the affected area to other parts of the patient’s body, such as the neck, back, arms, and legs.
- Causes of Spinal Disc Compression on Nerve:
Disc herniation is one of the causes of spinal disc compression on the nerve. Injuries to the spinal area, whether due to accidents or prolonged sitting in improper postures. Tearing of tissues around a specific vertebra due to injury or aging.
- Symptoms of Disc Compression on Nerve:
Common symptoms include continuous and radiating pain from the site of compression to other parts of the body. The pain may be accompanied by a sensation of numbness and tingling in the affected areas.
- Treatment Options for Spinal Disc Compression on Nerve:
Using medications such as pain relievers and anti-inflammatories to alleviate symptoms. Referring the patient to physical therapy sessions to strengthen and relieve tension in the back muscles.
- Preventive Measures:
Avoid heavy lifting and maintain proper posture while sitting and standing. Engage in regular exercise to strengthen the back muscles and the ligaments surrounding the spinal column.
It is advisable to consult a specialist physician to diagnose cases of disc compression on the nerve and determine appropriate treatment based on each individual case.
What Is the Treatment for Disc Compression on Nerve?
Disc compression on the nerve is a common injury that can cause severe pain and numbness in the extremities. This condition occurs when a spinal disc, known as the disc, compresses the nerve roots, leading to uncomfortable symptoms. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, there are several treatment options for disc compression on the nerve, including:
- Rest and Activity Reduction: The doctor may recommend reducing activity and rest to minimize irritation and decrease pressure on the affected nerve.
- Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may help alleviate pain and inflammation. Pain-relieving medications may also be prescribed if the pain is severe.
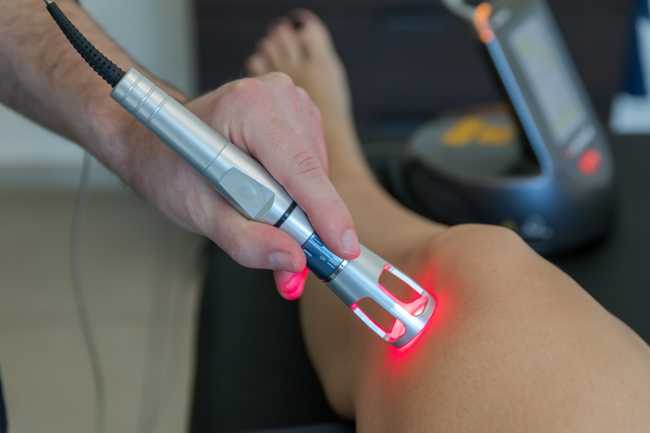
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy sessions can assist in strengthening the muscles around the affected area and improving spinal column flexibility.
- Targeted Injections: Some doctors use targeted injections to relieve pain and inflammation around the compressed nerve.
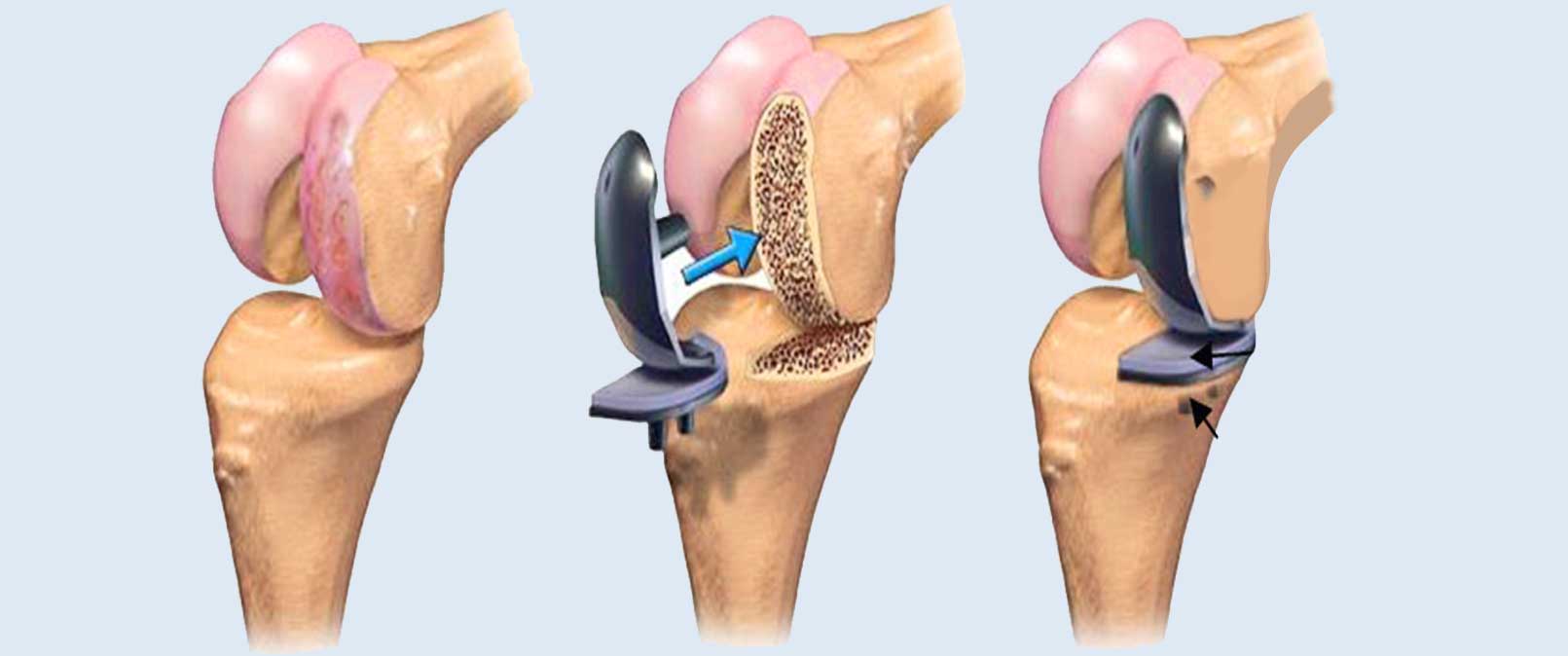
- Surgery: In severe cases and when other treatments are ineffective, surgery may be the last resort. The choice of surgery depends on the patient’s condition and the extent of nerve involvement.
It is crucial to work collaboratively with your doctor to provide the necessary assessment and select the most suitable treatment for your specific condition.
Does Spinal Compression Affect Nerves?
Medical sources indicate that spinal compression on nerves is a health issue that can cause continuous pain and nerve irritation. This problem may result from disc herniation, ring tears, or increased pressure on the nerves surrounding the spinal structures.
In this article, we will briefly outline three primary ways to treat spinal disc compression on nerves.
Non-Surgical Interventions:
- Physical Therapy: This includes rehabilitation exercises and massage to relieve muscle tension and increase the strength and flexibility of the back area.
- Heat Therapy: Using localized heat with hot water or a heating pad helps alleviate pain and improves blood flow to the affected area.
- Pain Relievers: Pain relievers can be taken to temporarily alleviate pain and relax muscles.
Surgery: If a person does not respond to non-surgical treatments and experiences deterioration or nerve compression that threatens their health, surgery may become an option. This may involve removing a portion of the affected disc or replacing it with an artificial disc.
Medication Treatment: Some medications like muscle relaxants, pain relievers, and anti-inflammatory drugs can be used to reduce swelling and pain. The doctor may also prescribe some medications belonging to the serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI) class, which enhance pain signals to the nervous system.
However, it is always advisable to consult with a doctor before taking any steps in the treatment of spinal disc compression on nerves, as a proper diagnosis should be provided, along with personalized advice and an appropriate treatment plan based on the patient’s condition.
It is worth mentioning that the treatment of spinal disc compression on nerves depends on accurate diagnosis and various factors, and there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Therefore, it is important to communicate with a specialized medical team to determine the best approach for each case.
What Are the Symptoms of Spinal Nerve Compression?
Symptoms of cervical spine nerve compression occur due to repeated pressure on the nerves in the neck area. This pressure can have a negative impact on nerve functions and surrounding tissues, leading to bothersome and painful symptoms. Here is a list of the most prominent symptoms of cervical spine nerve compression:
- Pain: Patients may experience localized pain in the neck area, which can radiate to the shoulders, arms, or upper back.
- Tingling and Numbness: Some individuals may feel tingling sensations or numbness in the affected areas.
- Weakness: Muscle weakness in the arms or hands is a common symptom of nerve compression.
- Decreased Reflexes: Reflexes in the affected areas may become less responsive.
- Changes in Coordination: Patients may notice a decline in coordination and fine motor skills.
- Difficulty in Gripping: Handling objects or gripping may become challenging.
- Headaches: Nerve compression in the neck can sometimes lead to headaches.
These symptoms can vary in intensity and may require prompt medical attention for diagnosis and treatment.
Neck and Back Pain: You may experience severe pain in the neck and back area due to pressure exerted on the cervical spine.
Numbness and Tingling: Numbness and tingling can occur in various parts of your body, such as the arms, hands, and legs.
General Weakness: You may feel weakness in the muscles of the arms and legs, affecting your ability to perform daily activities normally.
Headache: Pressure on the cervical spine nerves can cause pain in the head region, which may be continuous or intermittent.
Difficulty Controlling Movement: You may have difficulty controlling movement and overall sensation in your body, especially in areas affected by compressed nerves.
Digestive System Function Changes: Pressure on the cervical spine nerves can lead to changes in your digestive system functions, such as difficulty in bowel movements or impaired control over elimination.
Balance and Coordination Problems: Cervical spine nerve compression can affect balance and coordination, making walking and movement stability challenging.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek immediate medical care for proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
What Are the Symptoms of Spinal Cord Compression?
The spinal cord can be subjected to pressure due to various reasons, such as the presence of tumors, vertebral friction, infections, abscesses, or nerve compression. This pressure can lead to several symptoms. In this article, we will take a look at some of these symptoms:
- Weakness: Weakness or numbness in the arms or legs is a common symptom of spinal cord compression.
- Pain: Patients may experience localized or radiating pain in the back or neck region.
- Loss of Sensation: A decrease in sensation or loss of feeling in specific areas of the body can occur.
- Difficulty Walking: Some individuals may find it challenging to walk or experience balance issues.
- Changes in Bowel or Bladder Control: Spinal cord compression can lead to problems with controlling bowel or bladder functions.
- Spasticity: Muscle stiffness or spasms may occur.
- Changes in Reflexes: Reflexes may become exaggerated or diminished in response to spinal cord compression.
These symptoms can vary in severity, and early medical evaluation and intervention are crucial for proper management.
Sharp Pain: The affected person may experience severe, burning pain in the arms, buttocks, or lower legs. This pain may worsen with body movement or staying in a specific position for an extended period.
Numbness and Tingling: The affected person may feel numbness in a specific area of their body, such as the hands or feet, accompanied by a tingling sensation.
Disruption of Bladder and Bowel Function: Individuals with spinal cord compression may experience difficulty controlling urination or bowel movements, leading to a loss of control over these functions.
Muscle Weakness: Spinal cord compression can affect the nerves responsible for controlling muscle movement, resulting in overall weakness in the body and difficulty moving certain body parts.
Neck and Back Pain and Stiffness: The affected person may experience pain and stiffness in the neck or back area, which may worsen as the condition progresses.
Neurological Abnormalities: Some individuals may notice differences in nerve activity, such as decreased coordination between different body parts or partial loss of sensation in certain areas.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is essential to consult a physician for a proper diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Do not hesitate to ask any questions to understand your condition and the potential diagnostic and treatment steps that doctors may provide.
Is Compressed Nerve Serious?
Compressed nerves are a common condition in the body, often resulting from repetitive activities or prolonged positioning. This condition is characterized by increased pressure on the nerves in the areas between bones, ligaments, and tendons, which can lead to painful symptoms.
In this article, we will explore the seriousness of this condition and whether it should be taken seriously:
Impact on Body Movement: When the space around nerves is narrowed, a person may have difficulty controlling their body movements. This can affect their ability to move and perform various tasks in their daily life.
Increased Pressure in Surrounding Areas: If compressed nerves are not addressed promptly, the pressure in the surrounding areas may gradually increase. This can lead to swelling and inflammation in the affected area, making it more challenging to control.
Exacerbation of Symptoms: The person with a compressed nerve may notice the worsening of symptoms when moving the affected area. These symptoms may include a feeling of pins and needles in the region, weakness, and loss of sensation, along with increasing pain.
Impact on Quality of Life: Increasing the severity of compressed nerve pain can lead to a decrease in the affected person’s quality of life. It may become challenging for them to perform routine activities with ease, such as lifting heavy objects or even executing simple movements.
However, compressed nerves may not be serious in all cases. Some patients experience gradual improvement without the need for treatment, as the pain gradually subsides over time with the disappearance of the underlying cause and the reduction of nerve pressure. This may take anywhere from days to weeks, or possibly even longer.
If the pain persists after a prolonged period or if you notice a continuous worsening of symptoms, the affected individual should consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and the determination of an appropriate treatment plan. It is important not to ignore those cases that negatively impact an individual’s life and their ability to perform routine activities.
While compressed nerves may not be serious in all cases, it is important to take this condition seriously and promptly to avoid worsening symptoms and negatively affecting the individual’s life. Each case should be evaluated individually, and necessary steps should be taken to alleviate pain and promote the healing of the compressed nerve.
How Do I Self-Treat Disc Herniation?
- Maintaining Proper Sleeping Position: Try different sleeping positions to find out which one helps reduce pain and tension. Use suitable pillows to support your spine and reduce pressure on the herniated discs. Avoid sleeping on your stomach as it can lead to tension in the lower back area.
- Following a Healthy Diet: Avoid consuming foods that can cause inflammation, such as stimulants and saturated fats. Encourage the consumption of anti-inflammatory foods, such as vegetables, fruits, and fish.
- Engaging in Rehabilitation Exercises: Look for rehabilitation programs specifically designed for treating lower back disc herniation and follow them regularly. It is recommended to perform exercises that strengthen the muscles of the back and abdomen to support your spine and strengthen the painful area.
Avoiding Bad Situations and Lifting Weights: Avoid lifting heavy objects and try to avoid positions that strain your back. When carrying heavy objects, use proper lifting technique and bring the object close to your body to reduce pressure on your back. Consult a Healthcare Specialist: If the pain persists or worsens, it is recommended to visit a specialist in joint disorders or physical therapy. The specialist will guide you towards a comprehensive treatment plan that may include physical therapy sessions, medication, or even surgery if necessary.
Individuals suffering from herniated discs in the lower spine should be cautious and follow the treatment and prevention guidelines mentioned above. Always remember that in case of worsening or persistent pain, it is important to consult a healthcare specialist for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Can Herniated Discs Be Treated with Physical Therapy?
Yes, physical therapy can be used as a part of herniated disc treatment. Physical therapy can help alleviate pain, increase mobility, and improve the strength of the muscles surrounding the affected joint. Physical therapy includes muscle-strengthening exercises, flexibility exercises, massage techniques, and balance and stability exercises.
However, the condition of the herniated disc and the severity of the problem should be assessed by healthcare professionals. In some severe cases, physical therapy may not be sufficient, and surgery may be necessary to repair the damaged disc.
It is crucial to always consult your doctor or specialist when dealing with disc herniation or any other health issue for an accurate evaluation and an appropriate treatment plan.
Can Herniated Discs Be Completely Cured?
Herniated discs are a common ailment affecting many people worldwide. While there is no definitive cure for herniated discs as of now, significant improvement in patients’ condition can be achieved through interventions carried out by specialized medical teams.
If you are experiencing symptoms and effects of a herniated disc, you may have an important question: “Can this condition be completely cured?” In this article, we will address this question.
- Healing Potential: The answer to the question of whether herniated discs can be completely cured depends on each individual’s condition. Some patients experience significant improvement and symptom relief after appropriate treatment, while others may find it challenging to recover fully.
- Medical Measures: Several measures are employed to minimize the harmful effects of herniated discs and provide comfort to the patient. Treatment may include physical therapy exercises, pain-relieving medications, and avoiding activities that exacerbate the pressure on the affected disc.
- Surgical Intervention: In some cases, there may be a need for surgical intervention to treat a herniated disc if the patient’s condition is very acute, chronic, and unresponsive to conventional treatments. The intervention aims to remove or replace the damaged disc with an artificial one.
- Complete Recovery: Despite the significant improvement that can be achieved through implemented measures, the physiological composition of the disc does not fully return to its original state. Some scarring or wrinkles may remain in the affected area, which can cause varying degrees of discomfort.
- Pain Management and Relief: If surgical intervention is not required, additional methods can be used to alleviate the pain of a herniated disc. Techniques such as ice therapy, appropriate exercises, and pain-relieving medications can be employed for an extended period.
While there is no “complete” cure for herniated discs, with the necessary medical procedures, patients can significantly alleviate their pain and improve their quality of life. It is advisable to consult a specialist to assess the patient’s condition and develop an effective treatment plan as needed.
Is Herniated Disc a Serious Condition?
Herniated discs are a common issue that affects people of various ages, and it raises an important question: Is herniated disc a serious condition? In this article, we will explore this matter and clarify whether it should be treated as a serious ailment.
- Safety Implications: The symptoms of herniated discs may appear significant due to their impact on mobility and severe pain, but they are usually not considered serious in terms of long-term effects on a person’s health. However, it should be taken seriously to prevent worsening or the emergence of other problems.
- Responsiveness to Treatment: Individuals with a herniated disc should regularly consult with their doctor to determine the nature and severity of their condition. Treatment may require non-surgical approaches such as physical therapy and supportive therapy. It may also be beneficial to maintain a healthy diet and apply local anesthesia techniques.
- Specialist Consultation: It is undoubtedly important to consult with a specialist doctor when dealing with a herniated disc, as they can provide necessary advice and guidance. Symptoms should not be ignored, and experienced healthcare professionals should be consulted.
While herniated discs can be challenging, they are not necessarily extremely serious. However, proper management is essential to control potential future effects. In any case, seeking medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment is always encouraged.
What Is the Difference Between a Herniated Disc and Spinal Compression?
Many people suffer from spinal problems, and among these issues, herniated discs or spinal compression can occur. These two problems may seem similar in symptoms, but they are entirely different in terms of causes and potential reasons.
Herniated Disc vs. Spinal Compression:
Herniated Disc:
- Typically occurs when a spinal disc protrudes out of its place due to bulges present in or on the side of the disc.
- Can cause sharp pain in the back or nearby regions, with pain radiating into the arms or legs.
- Symptoms may include numbness and temporary paralysis in the affected area.
- Symptoms may worsen during movement and physical activities.
Spinal Compression:
- Arises due to excessive pressure on a vertebra or spinal region.
- May result from common issues such as arthritis, herniated discs, or abnormal cartilage accumulation in a specific area.
- Can lead to narrowing of the spinal canal and the blood vessels surrounding nerves.
- Typically causes severe and intense pain in the affected area, with the possibility of numbness and weakness in the affected regions.
Here is a table highlighting the differences between these two conditions:
| Herniated Disc | Spinal Compression | |
|---|---|---|
| Common Causes | Decreased disc density, aging effects | Arthritis, abnormal cartilage accumulation, tumors |
| Symptoms | Back and leg pain, reduced endurance | Severe pain in the affected area, numbness and weakness in limbs |
| Diagnosis | Clinical history, CT scans | Radiological examinations such as X-rays and MRI |
| Treatment Plan | Pain relief, conservative management, physical therapy | Pain management, arthritis treatment, safe activity management |
Remember that this article is based on available online information, and if you have symptoms or concerns about your condition, it is advisable to visit your doctor for an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan.