Back Pain: What Causes It, and When Is It Serious?
Lower Back Pain
7 Effective Ways to Relieve Lower Back Pain:
- Engage in Light Exercise: Start with stretching and strengthening exercises for the back and abdomen, such as side planks and spinal exercises. Consult a physical rehabilitation specialist for an appropriate exercise program tailored to your condition.
- Avoid Prolonged Sitting: Take short breaks to stand and walk throughout the day, and regularly change your sitting position. Use lumbar support cushions while sitting at your desk.
- Maintain a Healthy Body Weight: Keeping a healthy weight is crucial, as excess weight increases pressure on the spine and may lead to increased back pain.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting: Be sure to evenly distribute weights when lifting and use proper techniques for lifting heavy objects, such as bending your knees and keeping your back straight.
- Use Non-Pharmacological Treatments: Try non-pharmacological treatments such as heat therapy, massage, meditation, and deep breathing exercises to alleviate back pain.
- Reduce Stress and Psychological Pressure: Stress and psychological pressure can contribute to increased back pain. Use meditation and relaxation techniques to relieve mental stress and calm your mind.
- Consult a Physical Therapist: If lower back pain persists or worsens, consult a physical therapist to evaluate your condition and guide you toward the appropriate treatment and rehabilitation techniques.
In conclusion, do not ignore persistent or recurrent back pain, and seek the necessary treatment to mitigate its negative impact on your quality of life. Consult specialized doctors for an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment.
What Causes Lower Back Pain?
Many people suffer from lower back pain, and the causes of this pain can be multifactorial. Lower back pain is a common issue that affects many people worldwide and can have a negative impact on their daily lives.
In this article, we will explore some of the causes of lower back pain and shed light on the factors that may lead to these pains. Remember that this information is not a substitute for consulting a specialist, so if you are experiencing severe or persistent pain, it is advisable to visit a rheumatologist for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Muscle and Ligament Pain: Lower back pain can result from tearing or straining the muscles and spinal ligaments. This can occur due to sudden movements or strenuous actions involving the back, or as a result of repeatedly lifting heavy loads. A person may experience sharp and sudden pain in the back and may notice swelling and redness in the affected area. It is advisable to avoid activities that increase pressure on the back and hinder the healing process of the tears. Pain can be alleviated by using ice and physical therapy.
Weak Back Muscles: Lower back pain may result from the weakness of back muscles, making it easier for pain and muscle tension to occur in this area. Muscle weakness can lead to improper support of the back, increasing the likelihood of straining ligaments and spinal nerves. To alleviate lower back pain resulting from muscle weakness, it is recommended to strengthen these muscles through rehabilitative exercises directed by a physical therapist.
Herniated Disc: Herniated discs can be one of the causes of lower back pain. In cases of a herniated disc, part of the disc material protrudes between the spinal vertebrae, irritating and compressing the surrounding nerves, resulting in back pain. This pain can be alleviated through massage and physical therapy, and in severe cases, surgical treatment may be necessary.
Spinal Stenosis: Spinal stenosis, a condition that leads to the compression of spinal nerves in the lower back area, may occur. Spinal stenosis can be caused by the misalignment of vertebrae, which increases overlaps and narrows the available space for nerve passage. A person may experience severe and sharp pain in the lower back, and this pain can negatively affect movement and flexibility. Treatment for this condition depends on its cause and severity and may include guided physical therapy. In some rare cases, surgery may be required.
Arthritis: Arthritis is considered one of the chronic causes of lower back pain, as spinal arthritis can lead to the narrowing of space around the nerves and pressure on them. Severe cases of spinal arthritis may result in spinal narrowing, muscle weakness, and severe lower back pain. The treatment for arthritis-induced back pain depends on the cause and severity of arthritis. Treatment may involve taking anti-inflammatory medications, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Spinal Fractures: Bones are composed of dense and rigid tissue, but weakness can occur due to conditions such as osteoporosis, increasing the likelihood of fractures in the spinal vertebrae. Lower back pain may be caused by painful fractures in the vertebrae, accompanied by increased pain during movement and breathing. Treatment for spinal fractures may involve the use of braces and spinal immobilization through medical braces or, in some cases, surgical intervention.
Lower back pain is a common issue that affects many people. The causes of lower back pain can vary, ranging from lack of exercise and weak muscles to arthritis and spinal fractures. It is advisable to consult a rheumatologist to accurately diagnose the back condition and seek their advice on the appropriate treatment plan. Treatment may include muscle rehabilitation exercises, medication, physical therapy, and, in some cases, surgical intervention. The important thing is to take preventive measures to maintain back health and avoid factors that increase the likelihood of lower back pain, such as maintaining good posture while sitting, staying active, and regularly strengthening back muscles.
When Is Lower Back Pain Serious?
When a person experiences lower back pain, they may be concerned about the seriousness of their condition. Sometimes, the pain can be a symptom of a serious issue that requires immediate treatment, while other times, it may result from a minor and non-serious cause. In this article, we will discuss several factors to consider when determining the seriousness of lower back pain.
Severity and Duration of Pain: If the severity of the lower back pain is intense and acute, and if the pain persists for an extended period without improvement after several days or weeks, this may indicate a serious problem that requires consultation with a doctor. One should not wait until the symptoms become extremely severe before seeking medical attention.
Pain Radiating to the Leg: If the pain extends from the back and includes the leg, there may be pressure on the nerves in the spinal column. These symptoms may indicate an issue with a disc or muscle tunnel narrowing, which requires evaluation and treatment by a doctor.
Weakness or Numbness in the Legs: If lower back pain causes weakness in the legs, numbness, or tingling, this could be an indicator of nerve compression or spinal cord pressure. It is essential to consult a doctor promptly for an evaluation and to determine the appropriate treatment.
Changes in Urination or Loss of Bladder Control: If there are changes in urination, such as difficulty urinating or loss of bladder control, this may indicate a problem with the spinal column. Immediate consultation with a doctor is necessary to assess the condition, determine the cause, and initiate treatment.
Date of Injury or Fall: If there is a history of injury or a fall on the back, there may be a risk to the spine and the surrounding nerves. It is advisable to consult a doctor for an evaluation to determine if imaging or treatment is necessary. Continuous or Recurrent Pain Episodes: If you experience recurrent or persistent episodes of lower back pain, this may indicate a structural issue or a spinal disorder. It may be necessary to consult an orthopedic specialist for diagnosis and treatment.
In the end, these considerations and criteria should be taken into account when assessing the seriousness of lower back pain. It is essential to consult a doctor for a proper diagnosis and to determine the appropriate treatment. Do not hesitate to seek medical care when experiencing unusual or unfamiliar symptoms.
What Is the Treatment for Lower Back Pain?
Lower back pain is a common type of pain that many people experience. Treating this type of pain may require medical consultation and professional interventions. However, there are some steps that can be taken at home to alleviate lower back pain and expedite the healing process.
Walking Exercises: Research has shown that low-intensity aerobic exercises, such as walking, can help alleviate back pain. Walking is simple and easy to incorporate into daily routines. You can walk for a short duration as part of your daily activities, such as shopping or strolling. Walking promotes back muscle strength and maintains spinal stability.
Heat and Cold Therapy: Heat and cold can be used to alleviate back pain. A heating pad or a hot pack can be used once to warm the painful area. As for cold therapy, you can use a bag of frozen vegetables or pre-made ice and place it on the painful area. Heat therapy dilates blood vessels and improves blood flow, while cold therapy is believed to reduce swelling and inflammation.
Pain Relievers: Over-the-counter pain relievers can be used to alleviate lower back pain. These include over-the-counter pain relievers like paracetamol and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen. Topical creams and gels containing active ingredients like capsaicin, salicylic acid, and camphor can also be used for localized pain relief.
Stretching Exercises: Stretching exercises are simple and easy to do at home, and they help alleviate back pain and improve muscle flexibility. You can try simple stretching exercises like bringing your knees toward your chest or placing your hands behind your knees and pulling them towards your chest. Stretching should be done slowly and comfortably without ignoring excessive pain.
Maintaining Regular Physical Activity: Maintaining regular physical activity is an essential part of keeping your back healthy. Avoid sitting for extended periods and move regularly throughout the day. You can consult a doctor or a physical therapist for guidance on appropriate exercises to strengthen the back muscles.
Cases of lower back pain may require additional medical interventions such as physical therapy or medication. If the pain persists or symptoms worsen, it is advisable to consult a doctor for an evaluation and appropriate treatment.
In the end, it’s important to remember that any type of treatment for lower back pain requires patience and commitment to following instructions and exercises regularly. Avoiding practices that may exacerbate pain and prioritizing rest and self-care are crucial during the recovery period.
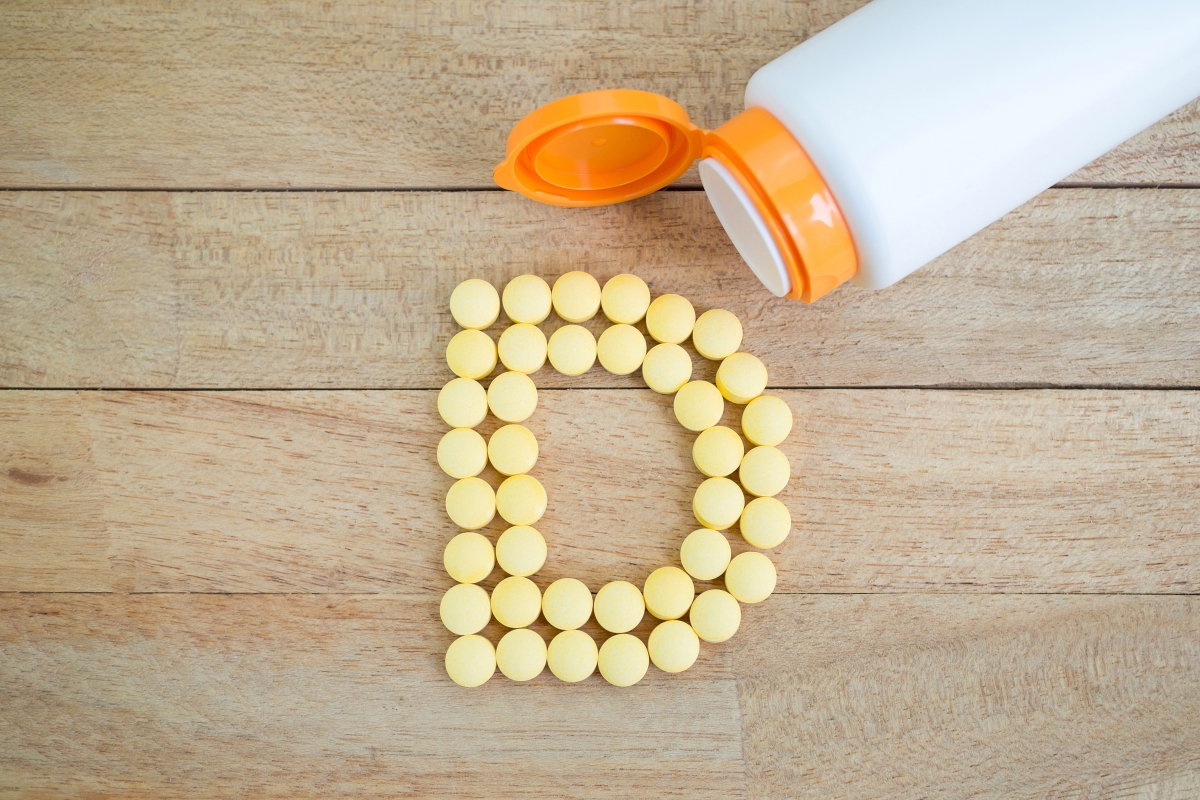
Does Vitamin D Deficiency Cause Lower Back Pain?
Vitamin D deficiency is a common condition in today’s world, and one of the potential symptoms of deficiency is experiencing lower back pain. In this article, we will explore the relationship between vitamin D deficiency and lower back pain and the possibility of its occurrence.
Introduction to Vitamin D Deficiency: Vitamin D is considered one of the essential vitamins for the human body, playing a crucial role in bone and dental health. The body receives vitamin D through exposure to sunlight, as well as from the consumption of certain nutritious foods such as fatty fish and egg yolks.
The Relationship Between Vitamin D Deficiency and Back Pain:
There is some research indicating a relationship between vitamin D deficiency and back pain, including lower back pain, which is one of the most common types of pain worldwide. Certain symptoms may suggest a deficiency of vitamin D in the back, given its impact on bone and muscle health.
A study conducted in 2015 aimed to investigate the connection between vitamin D deficiency and chronic back pain. This study found that 98 individuals suffering from chronic lower back pain had a deficiency in vitamin D. It also found a higher proportion of increased pain severity with lower levels of vitamin D in the body.
Furthermore, other studies have linked vitamin D deficiency to bone and joint pain, arthritis, muscle tension, depression, and bone fatigue. It is believed that vitamin D deficiency affects the absorption of calcium in the body, leading to weakened bones and an increased likelihood of back and bone pain.
How to Avoid Vitamin D Deficiency and Back Pain:
There are several ways to prevent vitamin D deficiency and reduce the potential back pain associated with it. These methods include:
- Sun Exposure: Spend time outdoors and expose yourself to sunlight for 10-15 minutes daily, making sure that parts of your body, such as the face and arms, are exposed to the sun.
- Nutrient-Rich Foods: Consume vitamin D-rich foods, such as egg yolks, fatty fish like salmon and sardines, and vitamin D-fortified dairy products.
- Supplements: You may need to take vitamin D supplements if you have a severe deficiency. Consult a doctor before taking any supplements to determine the appropriate dosage.
- Medical Consultation: If you experience ongoing or chronic back pain, it is advisable to visit a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.
In conclusion, vitamin D deficiency may have an impact on bone and muscle health and can potentially cause lower back pain in some individuals. Therefore, it is important to ensure an adequate level of vitamin D in the body through sun exposure and the consumption of nutrient-rich foods containing this vitamin.
When Should You Visit a Doctor for Lower Back Pain?
When a person experiences pain in the back area, they may wonder when it’s necessary to visit a doctor. Back pain is quite common and often results from simple causes such as muscle tension or ligament strain. In many cases, back pain can gradually subside without the need for a doctor’s visit. However, in some instances, back pain may be a sign of a more serious health issue. In this article, we’ll take a look at when you should visit a doctor when experiencing lower back pain.
- Sudden Change in Pain Severity: If the pain’s intensity suddenly increases and becomes severe, there may be a more serious problem. This could indicate issues such as a slipped disc or nerve compression. In this case, it is essential to visit a doctor immediately for evaluation and diagnosis.
- Persistent Pain: If the back pain persists for more than two weeks without improvement, there may be a more complex and serious underlying cause. Conditions like joint inflammation or ligament tears should be assessed and treated by a doctor.
- Presence of Other Warning Signs: Some signs may point to a serious health problem when experiencing back pain. These signs include weakness in the legs, severe abdominal pain, difficulty controlling urine or stool, movement or sensation disturbances. If you notice these symptoms, you should visit a doctor immediately.
- Presence of Risk Factors Such as Injury or Stress: In some cases, certain factors may increase the risk of back problems. For example, if you’ve had an accident or a fall, or if you work in a job that causes increased stress on the back, you should visit a doctor if you experience back pain.
- When Pain Is Accompanied by Other Symptoms: Sometimes, back pain can be a sign of an issue in another part of the body. If you experience other symptoms such as shortness of breath, chest pain, or difficulty controlling urination or bowel movements along with back pain, you should see a doctor to determine the underlying cause.
In conclusion, it’s important to remember that this information is for educational purposes only and should not be used as a substitute for medical advice. If you’re experiencing back pain, you should consult a doctor for proper diagnosis and treatment.