What are the signs of recovery from lumbar disc herniation? Does standing affect the patient?
Signs of Recovery from Lumbar Disc Herniation
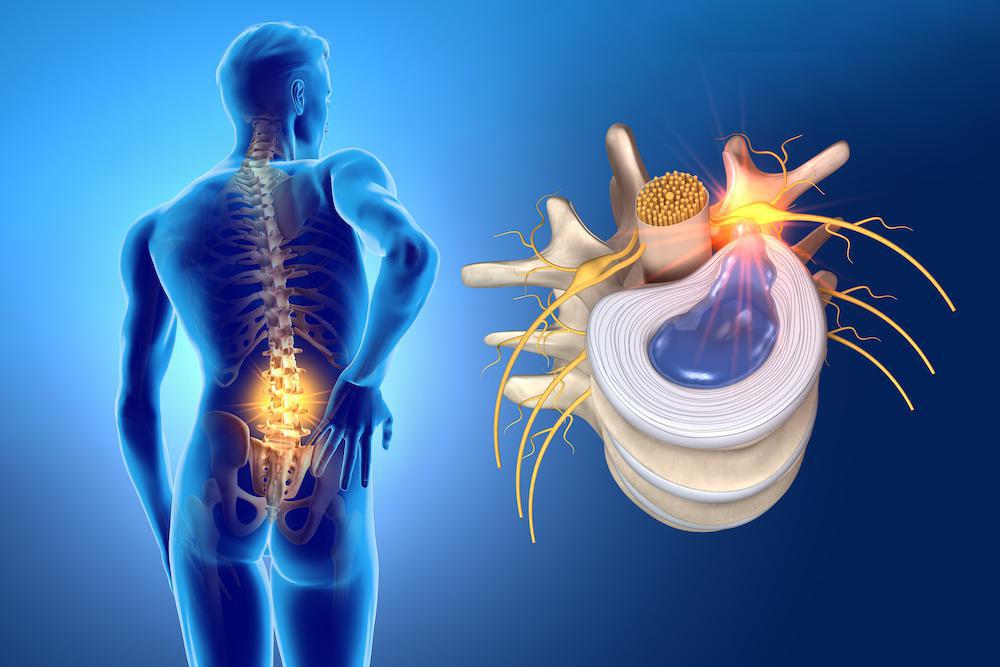
Lumbar disc herniation is a condition that affects the intervertebral discs in the lumbar spine (lower back). This condition can be painful and significantly impact the quality of life for affected individuals. However, many patients may experience signs and symptoms of recovery over time with proper treatment. Here are some signs that may indicate recovery from lumbar disc herniation:
- Pain Improvement: As healing begins, patients may experience a gradual improvement in pain. The pain may start to decrease in intensity, becoming less severe. Pain may become less bothersome during the day and may significantly diminish at night.
- Regained Mobility: Posture and overall body movement are crucial in the recovery process. With the progression of treatment and proper care, patients can regain the ability to perform daily activities more effectively and with greater ease. This movement may include lifting light and heavy objects and engaging in physical exercises without experiencing significant pain.
- Improved Nerve Function: If lumbar disc herniation compresses nearby nerves, it can lead to neurological symptoms like numbness and weakness in the limbs. As the recovery process advances, patients may notice an improvement in nerve function, including the return of sensation and strength in affected limbs.
- Enhanced Psychological Well-being: Lumbar disc herniation pain can have a significant impact on a person’s psychological well-being. As symptoms improve and recovery progresses, patients may experience an uplift in their mental state and an increased satisfaction with life.
- Return of Strength and Physical Fitness: When a person can perform muscle-strengthening exercises and improve physical fitness without triggering significant pain, it is indicative of recovery. Through rehabilitation exercises and physical activity, patients can regain the strength and physical fitness they may have lost due to the condition.
- Resumption of Daily Activities: When patients can resume their daily activities without significant restrictions or issues, it is a positive sign of recovery. Patients can return to work and engage in recreational activities as usual.
It’s important to note that the recovery process from lumbar disc herniation varies from person to person. Not everyone will experience the same rate of improvement or the same degree of recovery. Additionally, it’s crucial for individuals with this condition to follow their healthcare provider’s guidance and recommendations for treatment and rehabilitation.
- Follow-up with a Physical Therapist:
Regular follow-up with a physical therapist is crucial in the recovery process. There should be periodic assessments of progress, and the treatment plan should be adjusted as needed.
It’s important to understand that the recovery process from lumbar disc herniation varies from person to person and depends on the extent of the condition and the body’s response to treatment. Patients should always adhere to the instructions of their physician and physical therapist and avoid activities that could exacerbate spinal stress. If a patient notices any improvement in symptoms, they should consult their doctor to adjust the treatment plan appropriately.
Can Lumbar Disc Herniation Heal?
While lumbar disc herniation can be painful and disruptive to a person’s quality of life, whether it can fully heal depends on several factors. If diagnosed early and proper treatment is initiated, many individuals can experience complete healing or significant improvement in their symptoms.
Factors influencing the possibility of healing include:
- Location and Size of the Herniation: The location and size of the lumbar disc herniation play a significant role in the potential for healing. If the herniation is small and does not significantly compress nearby nerves, it may be easier to treat and heal. However, if the herniation is large and exerts substantial pressure on the nerves, more complex treatment may be required, and complete healing may not be possible.
- Age and Physical Fitness: Another factor that affects the potential for healing is the age and physical fitness level of the individual. Younger individuals with good physical fitness may be more capable of dealing with lumbar disc herniation and recovering from it.
- Early Treatment: Early diagnosis and prompt initiation of treatment can help reduce the severity of symptoms and increase the chances of healing. Early treatments may include physical therapy, appropriate medications, and surgery if necessary.
- Patient Compliance with Treatment: Patient compliance with treatment plays a significant role in the recovery process. Patients must adhere to their physician’s instructions and regularly perform therapeutic exercises to strengthen muscles and increase spinal flexibility.
- Lifestyle Changes: Patients should also consider lifestyle changes that can contribute to healing. This includes avoiding activities that put stress on the back, maintaining proper nutrition, and maintaining a healthy weight.
In general, lumbar disc herniation can heal if diagnosed and treated properly, and if patients adhere to general health care instructions. However, complete healing may take a long time and effort, and in some cases, complete healing may not be possible. It is always important to consult with a physician to assess the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
How Does a Lumbar Disc Herniation Patient Sleep?
Sleep is considered one of the essential aspects of rest and recovery for lumbar disc herniation patients. The correct sleeping position can reduce pressure on the spine, alleviate pain, and improve overall sleep quality. In this article, we will discuss some tips and positions that lumbar disc herniation patients can follow to ensure comfortable and healthy sleep.
- Choose the Right Mattress: Selecting an appropriate mattress to support the back and spine is vital. It is recommended to consult a spine specialist for guidance on the type of mattress suitable for your specific lumbar disc herniation condition.
- Sleeping Positions:
Sleeping on Your Back: Sleeping on your back may be the most suitable position for lumbar disc herniation patients. Placing a small pillow under the neck for proper support and another pillow under the knees to maintain a natural curve in the lower back is advisable. Sleeping on Your Side: If sleeping on your back is uncomfortable, sleeping on your side can be beneficial. Placing a pillow between your knees helps maintain a straight spine and reduces pressure on the herniated disc.
- Supportive Aids:
Pillows: Use a comfortable pillow that provides adequate support for the neck and head. There are pillows specifically designed for individuals with spinal issues. Additional Aids: In some cases, you may need to use additional aids like a back brace to support the affected area during sleep.
- Relaxation Techniques:
Meditation and Deep Breathing: Before sleep, meditation and deep breathing techniques can be helpful in managing pain and calming the mind.
- Avoid Harmful Positions:
Avoid Sleeping on Your Stomach: Sleeping on your stomach can lead to spinal misalignment and increased pressure on the spine.
- Medical Consultation: If pain persists or worsens during sleep, lumbar disc herniation patients should consult a spine specialist or rheumatologist for advice and a precise evaluation of their condition.
Lumbar disc herniation patients can achieve comfortable sleep by following these tips and guidelines mentioned above. If you are experiencing sleep problems due to lumbar disc herniation, it is always essential to consult your physician for a comprehensive assessment and specific recommendations for your condition.
Does Rest Help Treat Herniated Disc?
Herniated disc is a common condition that affects the spine, where the soft, gel-like disc slips out of its normal position in the spinal column. Various treatments for herniated discs include rest as an essential component, but does rest alone help in treating this condition? Let’s explore this topic in more detail.
Rest and Herniated Disc:
Rest plays a significant role in the treatment of herniated discs, especially in the early stages of the condition or when there is a sudden exacerbation of pain. Here’s how rest can help:
- Pressure Reduction: Rest reduces pressure on the discs and compressed nerves in the spine, which helps alleviate pain and promote healing.
- Tissue Healing: Allowing the body and the affected discs to rest can facilitate better tissue recovery. Reducing excessive movement can contribute to accelerating tissue healing.
- Preventing Worsening of the Condition: In many cases, rest can prevent the worsening of the herniated disc condition and the occurrence of additional spinal problems.
Importance of Balance:
Despite the importance of rest, it should be balanced. Prolonged periods of rest may lead to muscle weakness and reduced spine flexibility, which can exacerbate back problems over the long term.
Other Treatments:
The effectiveness of rest in treating herniated discs depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of the pain. Other treatments that may be used in addition to rest include:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy exercises can help restore strength and flexibility in the spine.
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory medications can help control pain and inflammation.
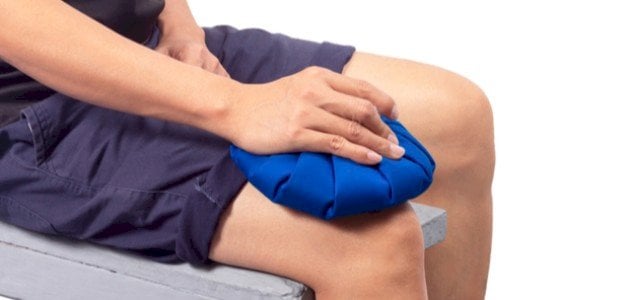
- Heat or Cold Therapy: Applying heat or cold can alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
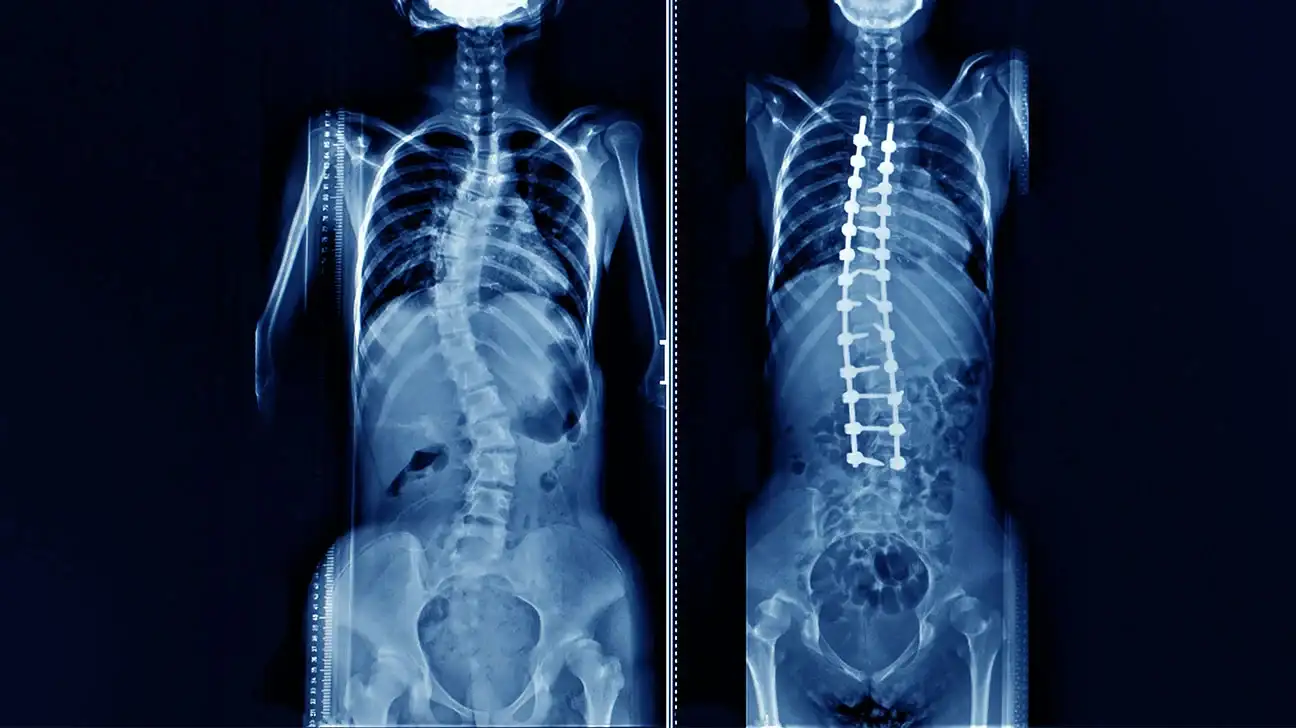
- Surgery: In severe and complex cases, surgical treatment may be required to remove damaged tissues.
Medical Consultation:
For patients, it is always necessary to consult a spine specialist or a physical therapist to accurately assess their condition and guide them towards the most appropriate treatments. Rest plays a crucial role in the treatment of herniated discs, but it is part of a comprehensive treatment plan that also includes physical therapy, medications, and regular medical follow-up.
Does Standing Affect Herniated Disc?
Herniated disc is a common condition that affects the spine and can cause significant concern for those experiencing it. This condition involves the displacement of one of the gel-like discs in the spinal column from its natural position, potentially causing pain, swelling, and nerve compression. Some people question whether standing affects this condition, making it worse or exacerbating its symptoms. In this article, we will explore whether standing has an impact on herniated discs.
Standing and Herniated Disc:
Standing for extended periods can be painful and straining on the back in general, whether you have a herniated disc or not. Prolonged standing can increase pressure on the spine and the intervertebral discs, potentially leading to worsened pain or increased symptoms.
However, it’s important to note that the impact of standing on herniated discs depends on several factors, including:
- Severity of the Condition: If the herniated disc is advanced and causing severe pain, prolonged standing may not be advisable.
- Proper Posture While Standing: Standing with correct posture and paying attention to the position of the back and spine can help mitigate the negative effects of standing.
- Rest and Breaks: Individuals with herniated discs should take regular breaks and rest periods during prolonged standing to alleviate pressure on the spine.
- Treatment and Exercises: Following the advice of a healthcare provider and performing prescribed physical therapy exercises can help reduce the impact of standing on a herniated disc.
Proper Standing:
To maintain spinal health and reduce the impact of standing on herniated discs, some guidelines should be followed:
- Weight Distribution: Try to evenly distribute your body weight on both feet and change the position of your feet occasionally.
- Use Assistive Tools: If your work requires prolonged standing, use tools like rubber mats to alleviate foot pressure.
- Isometric Exercises: Perform isometric exercises to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles to support the spine.
- Consult Your Doctor: Don’t hesitate to consult a spine specialist or physical therapist for advice tailored to your condition.
In conclusion, standing for prolonged periods can exacerbate the symptoms of herniated discs, but its impact can be reduced by taking appropriate preventive measures and seeking proper medical care. Always remember that consulting a doctor is the first step in understanding how to manage your condition correctly.
Does Cervical Herniated Disc Cause Paralysis?
Cervical herniated disc is a common condition that affects the spine and the intervertebral discs located between the vertebrae. Cervical herniated disc is characterized by the displacement or herniation of the disc from its normal position, which can cause pain and other symptoms in the neck and extremities. Depending on the location and severity of the herniation, there may be concerns about whether it can lead to paralysis. In this article, we will explore the concept of cervical herniated disc and whether it can cause paralysis.
Cervical Herniated Disc:
Cervical herniated disc is a type of herniated disc that occurs when the intervertebral disc in the cervical spine slips into the cervical spinal canal, which surrounds the spinal cord. This type is characterized by an excessive accumulation of discs in the cervical spinal canal, which can exert pressure on the spinal cord and nerves.
Can It Cause Paralysis?
Cervical herniated disc can be a serious condition if not properly managed. In some cases, this herniation can increase pressure on the spinal cord, leading to interference in the transmission of nerve signals between the brain and the rest of the body. If the pressure on the spinal cord is significant, it can result in muscle weakness, numbness, and loss of control over the limbs, which are symptoms that may be associated with paralysis.
However, it should be noted that paralysis resulting from cervical herniated disc is an extremely rare condition. The likelihood of its occurrence depends on several factors, including the location and severity of the herniation and the speed of medical intervention. If cervical herniated disc is treated early through medical treatment or surgery if necessary, the chances of recovery are high, and paralysis can be avoided.
Treatment and Prevention:
To prevent and treat paralysis resulting from cervical herniated disc, it is essential to consult a specialized spine doctor. Treatment may include the following:
Medical Treatment: Medications can be used to control pain and swelling. Physical Therapy: Physical therapy sessions can help strengthen muscles and improve spine stability. Surgery: In cases of severe cervical herniated disc that do not respond to other treatments, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure on the spinal cord. To reduce the risk of paralysis resulting from cervical herniated disc, individuals should adopt a healthy lifestyle, avoid excessive loading on the back, adhere to medical and physical therapy guidelines, and be aware of symptoms and respond promptly to any issues arising from the herniation. This can help minimize the risk of paralysis and increase the chances of recovery.
What Exercises Should Be Avoided for Herniated Disc?
Herniated disc is a condition that affects the intervertebral discs between the vertebrae in the spinal column. Symptoms of this condition include pain, numbness, and weakness in the back and extremities. To improve symptoms and avoid exacerbation, patients should avoid exercises and activities that can increase pressure on the herniated discs and worsen pain. In this article, we will take a look at exercises that should be avoided for herniated disc cases.
- Heavy Lifting:
Avoid lifting heavy weights or objects from the ground in a traditional or improper manner. This can put excessive pressure on the spine and increase the risk of disc herniation or additional irritation to the intervertebral discs.
- Excessive Forward Bending:
Excessive forward bending can compress the intervertebral discs in the spine. Strong and unnecessary forward bending while lifting objects from the ground or during daily activities should be avoided.
- Jumping and High-Impact Activities:
Activities involving jumping and high-impact forces, such as running on hard surfaces or vigorous skiing, can cause significant stress on the intervertebral discs. It’s essential to avoid such activities if you have a herniated disc.
- Excessive Backward Bending:
Performing movements involving excessive backward bending, such as improper sports exercises, can harm the intervertebral discs. Excessive backward bending should be avoided, and exercises should be performed correctly.
- Excessive Spinal Rotation:
Excessive spinal rotation can lead to irritation of the intervertebral discs and increased pain. Movements involving excessive spinal rotation, such as improper sports exercises, should be avoided.
- Prolonged Sitting:
Sitting for extended periods without changing positions can exert pressure on the intervertebral discs in the spine. It is essential to take regular breaks and perform stretching and strengthening exercises for the back if you spend long hours sitting.
- Strong Backward Bending:
Performing movements involving strong backward bending, such as sharp-angle exercises, can worsen the situation. Avoid these movements and opt for exercises that strengthen the muscles without excessive backward bending.
Important Reminder: It is always necessary to consult a doctor or physical therapist before starting any exercise program or physical activities to ensure they are suitable for your specific health condition. Avoiding prohibited activities for herniated disc cases can help improve symptoms and prevent worsening, but it should be done with caution and under medical supervision.
What is Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation)?
Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc, also known as Prolapsed Lumbar Disc or Lumbar Disc Herniation, is a medical condition that affects the spine, specifically the lumbar vertebrae in the lower back region. This condition is one of the most common spinal problems and can lead to various symptoms and health issues. In this article, we will explore the concept of Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc, its causes, symptoms, and available treatment options.
Definition and Causes:
Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc occurs when the intervertebral disc between the lumbar vertebrae in the lower spine slips out of its natural position. The intervertebral disc consists of a gel-like substance called the nucleus pulposus and an outer ring-like covering. When the outer covering tears due to stress or damage, a portion of the nucleus pulposus may leak out of the covering, exerting pressure on nearby nerves and surrounding tissues.
Causes of Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc:
Several factors can increase the likelihood of developing Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc, including:
- Aging: With age, intervertebral discs lose their ability to retain water, becoming less flexible and more susceptible to tearing.
- Excessive Spinal Stress: Improperly lifting heavy weights or experiencing strong injuries can contribute to disc damage.
- Excess Weight: Being overweight places extra pressure on the spine and increases the risk of disc herniation.
- Aging: The likelihood of disc herniation increases with age due to disc wear and tear.
- Genetics: Genetic factors may play a role in an individual’s susceptibility to disc herniation.
Symptoms:
Symptoms of Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc vary from person to person and depend on the extent of nerve and tissue damage caused by the herniated disc. Some common symptoms include:
- Severe pain in the lower back and hips.
- Numbness or weakness in the legs.
- Increased pain when sitting or standing for extended periods.
- Changes in bowel or bladder function if the lower lumbar nerves are affected.
It’s essential to consult a healthcare professional or physical therapist before starting any exercise program or physical activities to ensure they are suitable for your specific health condition. Avoiding prohibited activities for lumbar disc herniation cases can help improve symptoms and prevent worsening, but it should be done with caution and under medical supervision.
Treatment Options:
Treatment options for Prolapsed Lumbar Intervertebral Disc (Lumbar Disc Herniation) include:
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy sessions can help strengthen the muscles surrounding the back and improve proper posture to reduce pain.
- Medications: Pain relievers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can be used to alleviate pain and inflammation.
- Epidural Injections: Targeted injections, under medical supervision, can reduce inflammation and pain.
- Surgery: Surgery is considered the last resort and is offered in rare cases when symptoms cannot be controlled by other treatments.
In conclusion, anyone experiencing pain in the lower back and hips and suspecting a Prolapsed Lumbar Disc should consult a doctor. Providing appropriate care and treatment early on can reduce the condition’s progression and improve the quality of life.
Does Swimming Benefit Lumbar Disc Herniation?
Swimming and lumbar disc herniation are two topics of significant interest in the world of health and fitness. Swimming is considered a low-impact physical activity that can be beneficial for overall health, especially for individuals dealing with spinal issues like lumbar disc herniation. In this article, we will explore the effectiveness of swimming as a means to alleviate pain and improve the condition for individuals with lumbar disc herniation.
Basic Understanding of Lumbar Disc Herniation:
To understand how swimming can be beneficial in cases of lumbar disc herniation, it is essential to first comprehend the nature of this condition. Lumbar disc herniation occurs when the outer covering of the intervertebral disc between the vertebrae tears, leading to the displacement of a portion of the nucleus pulposus (gel-like substance within the disc) from its natural position. This herniation can compress nearby nerves, causing pain and other symptoms.
Benefits of Swimming for Lumbar Disc Herniation Patients:
Swimming can be effective for patients with lumbar disc herniation for the following reasons:
Low Impact: Swimming is a low-impact activity on the joints and spine, reducing the risk of worsening pain and cartilage damage.
Spinal Extension: During swimming, the body can naturally extend the spine, helping to alleviate pressure on the intervertebral discs.
Muscle Strengthening: Swimming strengthens the muscles around the spine, providing stability and support.
Increased Flexibility: Swimming improves muscle and tendon flexibility, enhancing spinal mobility.
Stress Reduction: Swimming is a calming activity that can help reduce stress and improve mood, positively impacting the patient’s overall well-being.
Important Tips for Swimming for Lumbar Disc Herniation Patients:
- Consult your doctor before starting a new swimming program to ensure it is suitable for your condition.
- Start slowly and gradually increase your swimming time.
- Choose swimming styles that emphasize gentle movements and coordination, such as freestyle or backstroke.
- Avoid swimming forcefully or performing jumps in the water.
- Maintain proper body posture while swimming.
- Ensure proper body warming before and after swimming.
In conclusion, swimming can be a beneficial activity for individuals with lumbar disc herniation, but caution and medical consultation should be exercised before starting any new exercise program. The exercise should be appropriate for the patient’s condition and performed under the supervision of fitness or physical therapy professionals.