Learn More About Vertebral Compression on Nerves and the Appropriate Treatment
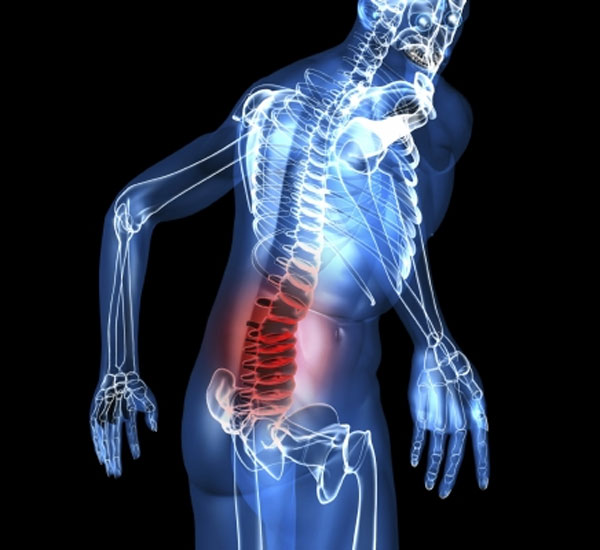
Spinal Compression on Nerves
List of Effective Practices to Deal with Spinal Compression on Nerves
- Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is one of the effective options to deal with spinal compression on nerves. This includes performing stretching exercises and strengthening the muscles around the back, improving body posture, and enhancing spinal mobility. It is advisable to consult a physical therapy specialist for guidance and appropriate exercises.
- Anesthetic Techniques: In cases of severe pain, local anesthetic techniques can be used, such as applying ice or using hot compresses, to alleviate pain and reduce swelling and potential inflammation in the affected area.
- Medication: Doctors can prescribe medication to relieve pain, reduce inflammation, and improve movement. Medicinal options include simple analgesics (such as aspirin and paracetamol) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (such as ibuprofen and naproxen).
- Radiation Therapy: In some cases, radiation therapy may be used to reduce pain and decrease the size of tumors or deformities that compress the nerves in the spinal region.
- Surgery: In severe and advanced cases of spinal compression on nerves, surgery may be the best option to improve the condition. This involves the removal of the damaged parts of the nerves or the repair of spinal deformities to relieve pressure on the nerves.
- Lifestyle Changes: Changing lifestyle is an important part of dealing with spinal compression on nerves. It is advised to avoid unhealthy postures, refrain from lifting heavy weights, maintain a healthy weight, and perform appropriate physical exercises to strengthen the muscles.
Avoid sitting for long periods and consume foods rich in calcium and vitamin D to strengthen bones and nerves. Make sure to consult your doctor before implementing any of these practices to ensure they are suitable for your health condition.
What are the symptoms of spinal compression on nerves?
Individuals may suffer from spinal compression on nerves in the neck for several different reasons, which can cause a range of disturbing and painful symptoms. In this article, we will discuss the most important symptoms of spinal compression on nerves in the neck.
Neck and Back Pain: Neck and back pain are common symptoms of nerve compression in the cervical vertebrae. The pain may be constant or episodic with acute flare-ups, and it often worsens with head or neck movement.
Numbness and Tingling: Nerve compression in the vertebrae can lead to numbness and tingling in the neck and upper extremities. Individuals may experience various patterns of numbness and tingling in the hands and fingers due to nerve pressure.
Muscle Weakness: The pressure on the nerves from the vertebrae may result in muscle weakness in the neck and upper limbs. A person may have difficulty lifting or carrying heavy objects and may generally feel weak in the muscles.
Difficulty in Balance and Coordination: Nerve compression in the neck can cause difficulties with balance and motor coordination. An individual may feel unstable while walking or engaging in activities that require good coordination between the eyes and muscles.
Concentration and Memory Difficulties: Nerve compression in the neck can affect a person’s ability to concentrate and remember. They may find it challenging to focus on daily tasks and recall information readily.
Headaches and Migraines: Nerve compression in the neck can lead to headaches and migraines. The pain may be associated with tension headaches or cluster headaches.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it is crucial to seek medical attention immediately. You should consult an orthopedist or a neurologist to assess your condition and direct you to the appropriate treatment.
Remember that prevention is better than cure, so maintain a proper posture for sitting and sleeping, avoid excessive heavy lifting, and engage in suitable exercises to strengthen the muscles of the neck and nerves.
What is the treatment for nerve compression in the vertebrae?
Nerve compression in the vertebrae is a condition that can cause severe pain and negative impacts on the quality of life. However, there are several effective ways to treat this problem and alleviate the associated pain. In this article, we will review 5 effective methods for treating nerve compression in the vertebrae.
Wearing Braces: Individuals with nerve compression in the vertebrae may need to wear a splint, collar, or brace to immobilize the affected area and reduce movement. In cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, the doctor may recommend wearing a splint during the day and night to stabilize the wrist and reduce nerve pressure while sleeping.
Physical Therapy: A physical therapist can provide exercises that help strengthen and stretch the affected muscles, thereby relieving pressure on the nerves. Physical therapy can also guide patients in modifying activities that exacerbate their condition, and to reduce pain, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen or naproxen may be used.
Pharmacological Treatment:
- The use of pain relievers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can help alleviate pain associated with vertebral compression on nerves. Substances such as ibuprofen and naproxen are effective medications for reducing pain and providing relief.
Conservative Treatment: 2. In some cases, a herniated disc pressing on the nerves may not require surgery. Doctors may initially recommend conservative treatments, including observation, rest, and physical therapy. Conservative treatment depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of their symptoms.
Surgery: 3. If significant improvement is not achieved through conservative treatments and the pain becomes unbearable, the doctor may decide to perform surgery to relieve pressure on the nerve. The type of surgery varies depending on the location of the compressed nerve and may include the removal of bone spurs or a part of a herniated disc in the spine or cutting the carpal ligament to expand the space and alleviate pressure on the nerves.
By choosing the appropriate treatment and following the doctor’s recommendations, people suffering from vertebral compression on nerves can experience improvement in their condition and relief from chronic pain. Individuals experiencing any symptoms of pain or numbness in the limbs should consult a specialist for diagnosis and necessary treatment.
How do I reduce pressure on the vertebrae?
- Practice stretching and extension exercises: Stretching and extension exercises may help relieve pressure on the vertebrae. You can gently train your back muscles by stretching and bending the body and performing rest exercises such as side bends and vertical elongation. It is preferable to consult a medical rehabilitation specialist to determine the most suitable exercises for you.
- Maintain good posture: It is recommended to sit and stand with proper posture to reduce pressure on the vertebrae. Your back should be straight and level when sitting and avoid excessive bending or harsh bending.
- Use supportive cushions: Supportive cushions can be used to help relieve pressure on the vertebrae. You can use specially shaped cushions to support the back area while sitting and sleeping. It is preferable to choose cushions made of flexible and comfortable materials to provide optimal support.
- Avoid sitting for long periods: Sitting for long periods can increase pressure on the vertebrae and surrounding muscles. It is better to perform stretching exercises and walk a little during long sitting periods to relieve pressure.
- Use local heating: Warm compresses can be used on the back to relieve pain and spasms associated with vertebral compression. You can use warm pads or a warm bath to soothe the area and improve blood circulation.
Following a healthy diet: Make sure to include healthy foods in your diet, such as fruits, vegetables, and fish rich in Omega-3 fatty acids. Eating foods high in magnesium and calcium can help enhance bone health and reduce the pressure on the vertebrae.
Maintaining a healthy weight: Excess weight puts additional pressure on the vertebrae and increases the risk of injury and pain. It is important to maintain a healthy weight through light physical exercise and a balanced diet.
Getting enough sleep: Not getting enough sleep can lead to increased pressure on the vertebrae. You should try to get good sleep and sufficient rest to maintain the health of your vertebrae and reduce symptoms associated with their compression.
It is essential to consult a specialist doctor if the pain persists or if other disturbing symptoms occur to assess the condition and suggest appropriate treatment. It is also advised to avoid factors that may increase the pressure on the vertebrae, such as lifting heavy weights improperly or performing unnatural repetitive movements for the back.
What is the effect of lumbar spine compression on the nerves?
The lumbar vertebrae are an important part of the spinal column located in the lower back. When a lumbar disc is compressed or slips, it can have a negative effect on the surrounding nerves. In this article, we will discuss some of the potential effects of lumbar vertebrae compression on the nerves.
Effects of Lumbar Vertebrae Compression on the Nerves:
Back pain: Lumbar vertebrae compression on the nerves can cause severe pain in the back area. The affected person may feel sharp or chronic pain that is difficult to control and reduces the quality of daily life.
Numbness and tingling in the limbs: Compression of the lumbar vertebrae may affect the traversing nerves, which are responsible for conveying sensory and motor signals from the spinal column to the limbs. In case of compression of these nerves, you may experience numbness and tingling in the limbs or in specific areas of the body.
Muscle weakness: Compression of the lumbar vertebrae on the nerves can lead to muscle weakness and loss of control over them. You may find it difficult to move certain organs or limbs, and you may notice a decline in strength and flexibility.
Balance disorders: Compression of the lumbar vertebrae on the nerves may lead to balance disorders and instability. It can make you unable to walk steadily or perform daily activities normally.
Problems with sexual organs: In the case of compression on the lumbar nerves, there may be an effect on the function of the sexual organs. You may experience a decrease in sexual desire or difficulty in controlling erection in men.
How to Treat and Prevent
To alleviate the impact of lumbar vertebrae compression on the nerves and to reduce the accompanying symptoms, it is important to consult a specialist doctor. Usually, the following treatments are recommended for the patient:
- Physical therapy: Includes exercises to strengthen the muscles, increase their flexibility, improve balance, and reduce pain.
- Adjunct therapy: Such as massage, heat therapy, and relaxation exercises can also have a positive effect.
- Medication: The doctor may prescribe pain relief medications or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate symptoms.
In addition to these treatments, it is advised to follow a healthy lifestyle and exercise regularly to strengthen the muscles and maintain back strength. Also, maintaining proper posture while sitting and sleeping will help prevent lumbar vertebrae compression and protect the surrounding nerves. For better and more effective guidance, it is advisable to consult with a doctor to evaluate each individual’s condition separately.
The impact of lumbar vertebrae compression on the nerves is not to be underestimated. It can significantly affect the quality of life and the ability to perform daily activities. Therefore, it is necessary that the condition be diagnosed and treated in a timely manner to avoid future complications.
Is Vertebrae Compression Dangerous?
Yes, vertebrae compression can be serious if not treated properly or if it is associated with serious spinal problems. Vertebrae compression can cause many problems and symptoms, including:
- Severe pain: Compression of the vertebrae can cause acute pain in the back, neck, or lower body area, which may be constant or intermittent.
- Muscle weakness: Compression of the vertebrae can lead to muscle weakness in the affected areas, making movement and daily performance more difficult.
- Numbness and tingling: Compression of the vertebrae can cause numbness or tingling in the upper or lower limbs, reflecting its effect on the nerves.
- Problems with balance and control: Compression of the vertebrae can lead to problems with balance and control of movement.
- Spinal nerve damage: In serious cases, vertebrae compression can lead to damage to the spinal nerves, causing severe problems such as paralysis or loss of sensory functions.
Therefore, if you suspect vertebrae compression or are suffering from the above-mentioned symptoms, you should consult a spine specialist (Dr. Amr Amal) for assessment and appropriate treatment. Treatment can include medication, physical therapy, and surgical interventions in serious cases.
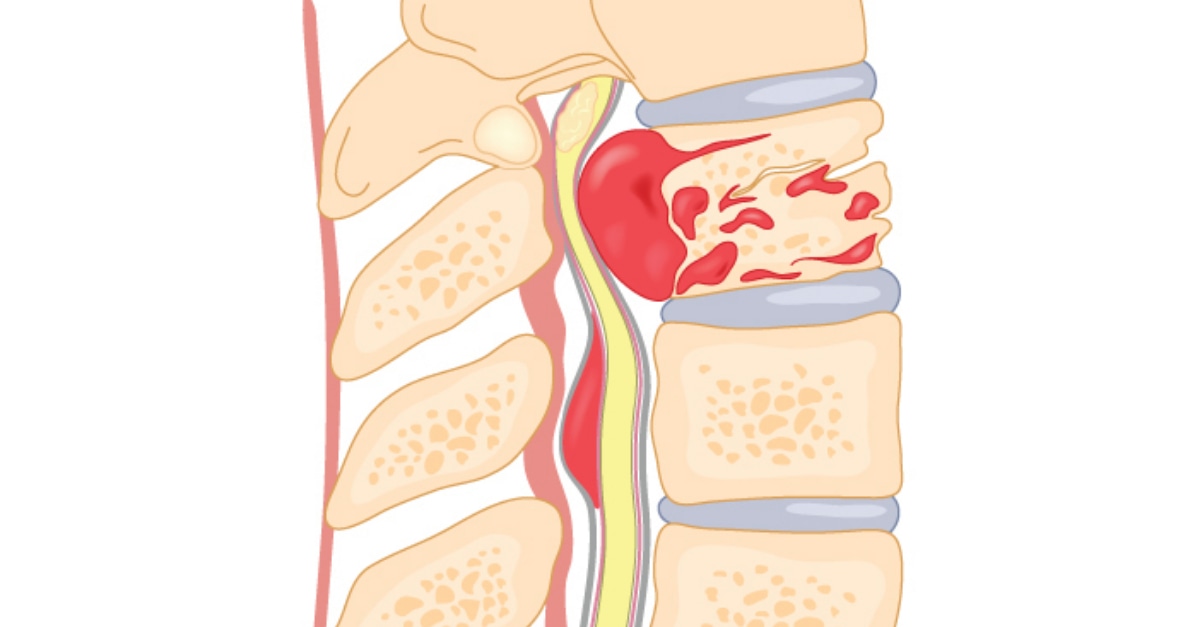
What is the Difference Between a Herniated Disc and Vertebrae Compression?
Spinal problems are among the most common health issues that people suffer from all around the world. Among these common issues are herniated discs and vertebrae compression. Although both cause back pain and may have similar symptoms, they differ in several aspects. In this list, we will review the main differences between a herniated disc and vertebrae compression:
Disc Herniation:
- Definition: Disc herniation refers to the displacement or tearing of the discs separating the vertebrae of the spinal column. This displacement or tear can cause pressure on the surrounding nerves and resulting symptoms such as pain and numbness.
- Causes: Disc herniation is related to several causes, including hard labor, sports injuries, heavy lifting operations, severe ups and downs, as well as genetic factors. Symptoms: The affected person may feel sharp pain in the back, neck, or legs, which may be accompanied by numbness and tingling. The pain may increase due to movement or sitting for long periods.
- Diagnostic Methods: Disc herniation is diagnosed through the patient’s medical history and physical examination, in addition to radiological examinations such as X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Vertebral Compression:
- Definition: Vertebral compression occurs when a vertebral disc is torn or compressed, leading to pressure on the surrounding nerves. This pressure may cause symptoms such as pain, numbness, and tingling.
- Causes: Vertebral compression may result from the deterioration of the discs between the vertebrae or due to chronic diseases such as arthritis or spinal stiffness.
- Symptoms: Those suffering from vertebral compression may experience sharp pain in the back or neck, which may intensify with spinal movement. This pain may be accompanied by numbness and tingling in the affected areas.
- Diagnostic Methods: Vertebral compression is diagnosed through medical history and physical examination, along with radiological examinations such as X-rays and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
In summary, both disc herniation and vertebral compression can cause back pain and accompanying symptoms, but they differ in their causes and mechanisms of occurrence. It is essential to consult a doctor to confirm the correct diagnosis and implement the appropriate treatment.
Does vertebral compression cause paralysis?
Yes, in some cases, vertebral compression on the spinal cord can lead to paralysis. When the pressure on the spinal cord is severe and chronic, it can cause damage to the nerves and nerve fibers present in the spinal cord. This damage can affect the transmission of nerve signals between the brain and the rest of the body, leading to loss of movement and sensitivity in the affected areas.
What should a patient do if they feel symptoms of vertebral compression on the spinal cord?
If you have symptoms indicating vertebral compression on the spinal cord, it is important to consult your doctor. The doctor may diagnose the condition using medical history and a clinical examination, and may recommend additional tests such as X-rays, or magnetic resonance imaging to assess the severity of the compression and its location. Based on these results, the doctor can determine the appropriate treatment plan.
Overall, vertebral compression on the spinal cord is considered a serious medical condition that may lead to paralysis in some cases. If you suffer from similar symptoms, it is necessary to consult a doctor to diagnose the condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan. Treatment may include medication, physical therapy, or in some cases, surgery. Remember, early detection and rapid treatment can be key in relieving symptoms and reducing potential complications.
What is the cause of spinal compression?
Spinal compression is a common problem suffered by many people. This issue arises from the presence of excessive pressure on the vertebrae of the spinal column in the back region. This pressure can be due to many different reasons and factors. In this article, we will review some of the main causes of spinal compression.
- Incorrect sitting and poor posture: Sitting for long periods in an incorrect and poor posture can be one of the leading causes of spinal compression. When the spinal column is in an unnatural position, the pressure accumulates on the spinal discs and nerves in the back.
- Excessive activity and heavy lifting: Working with heavy loads and performing strenuous activities can put extra pressure on the spinal column. Carrying heavy weights and making sudden and unnatural movements can lead to the compression and damage of the back vertebrae.
- Age and spinal readiness: Over time, the spinal column becomes less flexible and less capable of withstanding pressure. Aging can naturally lead to spinal compression due to the decreased flexibility of the spinal column.
- Injuries and muscle strain: Accidents, sports injuries, and excessive muscle strain can increase the pressure on the back vertebrae. A spinal injury or continuous muscle strain can cause irritation and compression of the back vertebrae.
- Arthritis and neurological diseases: Some diseases, such as arthritis and certain neurological conditions, can lead to irritation and compression of the back vertebrae. These conditions are usually associated with numbness and tingling in the back and require some precautions and correct body postures to manage.
Knowing the cause of spinal compression is important in taking appropriate measures for prevention and treatment. It is advised to consult a specialist doctor in cases of chronic or persistent back problems. Spinal compression is often treated through a combination of therapies such as physical therapy, muscle strengthening, and appropriate exercises, along with adopting a healthy lifestyle with proper sitting postures and constructive activities for the spinal column.
The issue of spinal compression requires monitoring and attention by the individual suffering from it. It is important to follow the advice and guidelines of the specialist doctor to maintain a healthy spine and back. One should avoid violent activities and sudden movements and pay attention to correct body postures.
Is walking beneficial for spinal compression?
Is walking beneficial for spinal compression? This is a dilemma faced by many individuals. It is good to shed light on the impact of walking on spinal compression and whether it is an effective solution to alleviate this problem. In this article, we will explore some points related to the validity of walking for patients with spinal compression.
Weight Distribution: Proper walking helps distribute weight across the different vertebrae in the spine. As a person walks, the weight spreads evenly across the back, neck, and pelvis, which reduces the focus on a single vertebra.
Muscle Strengthening: Regular walking helps strengthen the muscles of the back, abdomen, and buttocks, which positively affects the stability and support of the spine. Therefore, regular walking can reduce the pressure on the vertebrae and alleviate pain.
Improving Circulation: Walking is one of the best exercises for improving blood circulation in the spine and surrounding tissues. This helps in providing oxygen and nutrients necessary for the tissues and promotes the healing process.
Improving Flexibility: Walking can contribute to increased flexibility and elasticity in the tissues surrounding the vertebrae. Thus, the pressure on the vertebrae can be reduced and greater, more comfortable movement can be achieved.
Strengthening the Skeletal Framework: In addition to its benefits on the spine, walking is a useful exercise for strengthening the skeletal structure in general. It positively affects bone density and reduces the risk of bone diseases such as osteoporosis.
Does vertebral compression cause dizziness?
Yes, vertebral compression may cause dizziness in some cases. When the vertebrae in the neck or back are compressed, displaced, or irritated, it can affect the nerves or blood vessels in the adjacent area. This effect may lead to interference in nerve signals or blood flow to the brain, which can cause dizziness.
Dizziness is a condition where you feel as if the ground is spinning around you or that you are losing your balance. If you are suffering from compression of the vertebrae in the neck or back and also experience symptoms of vertigo or dizziness, there may be a relationship between them. It is important to have your condition evaluated by a spine specialist to determine the cause of the dizziness and take appropriate treatment.
Note that there are other causes of dizziness as well, such as disorders of the inner ear or problems with blood pressure or middle ear issues, so additional examinations may be needed to determine the exact cause of dizziness.
Do neck vertebrae compress nerves?
Compression of the neck vertebrae on the nerves is a common problem that can cause many symptoms and health challenges. In this article, we will look at some of the potential causes of neck vertebrae compression on nerves and the symptoms associated with this condition.
Spinal Degeneration: Usually, compression of the neck vertebrae on the nerves is a result of spinal degeneration, such as the wear of cartilage between the vertebrae. This degeneration in the spine leads to pressure on the nerves in the neck.
Disc Herniation: A disc herniation can occur in the neck, which is a slipping of the cartilage disc between the vertebrae. This slip can compress the nerves and cause symptoms such as neck pain, numbness, and weakness in the arms and hands.
Neck Inflammation: Neck inflammation can cause swelling in the nerves and surrounding tissues, which in turn can lead to nerve compression. Common causes of neck inflammation may include muscle tension, strains, and infections.
Injuries and Accidents: Injuries and accidents, such as a fall on the neck or a car accident, can cause neck vertebrae to compress the nerves. These injuries may cause tearing in the surrounding tissues and swelling, leading to nerve compression.
Emergency Situation: In some rare cases, compression of the neck vertebrae on the nerves may occur as an emergency situation. For example, in the case of severe swelling due to common problems such as a herniated disc, immediate surgical intervention may be required.
Remember that diagnosing and treating neck vertebrae compression on nerves requires consultation with a specialist physician. Delaying diagnosis and appropriate treatment may lead to worsening of symptoms and exacerbation of the problem.