The damages of the thermal frequency process and how to conduct it
The term frequency process is one of the modern techniques that help treat a group of diseases related to joints, nerves, and types of tumors as well. In this article, we explain full information on how to perform radiofrequency and the instructions that follow it.
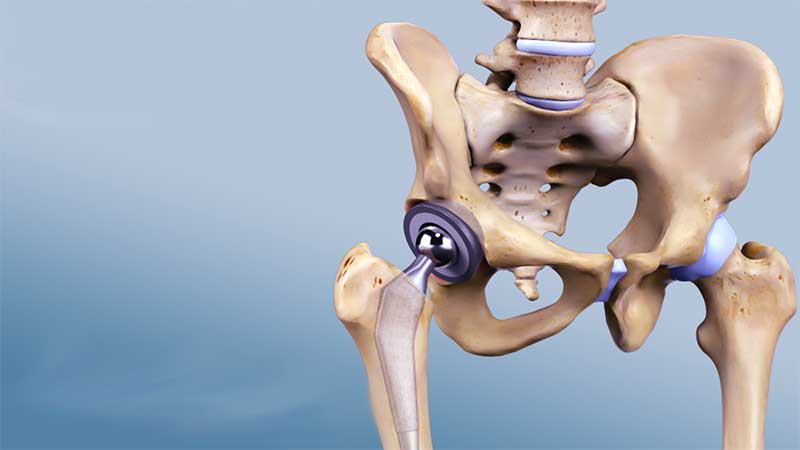
Spinal radiofrequency surgery
Nerve injury can occur as a result of inflammation, which results in severe pain in the affected part. Traditional treatment methods for the inflamed nerve often last for a long time, and the resulting pain can be intolerable, especially when a herniated disc affects the nerves of the spinal cord.
It is possible to perform more than one type of treatment for neuritis, and one of the modern methods of treatment is the thermal frequency, which works to improve the condition of the patient faster and helps to reduce the pain signals that come out from the roots of the nerve cells, and thus the severe pain that the person feels appears.
How is thermal frequency performed for a herniated disc?
When the spine is affected by a herniated disc in one or more vertebrae, it can cause severe pain caused by pressure on the spinal cord that runs close to the vertebrae, and thus inflammation occurs and results in continuous pain felt by the patient and intensifies over time.
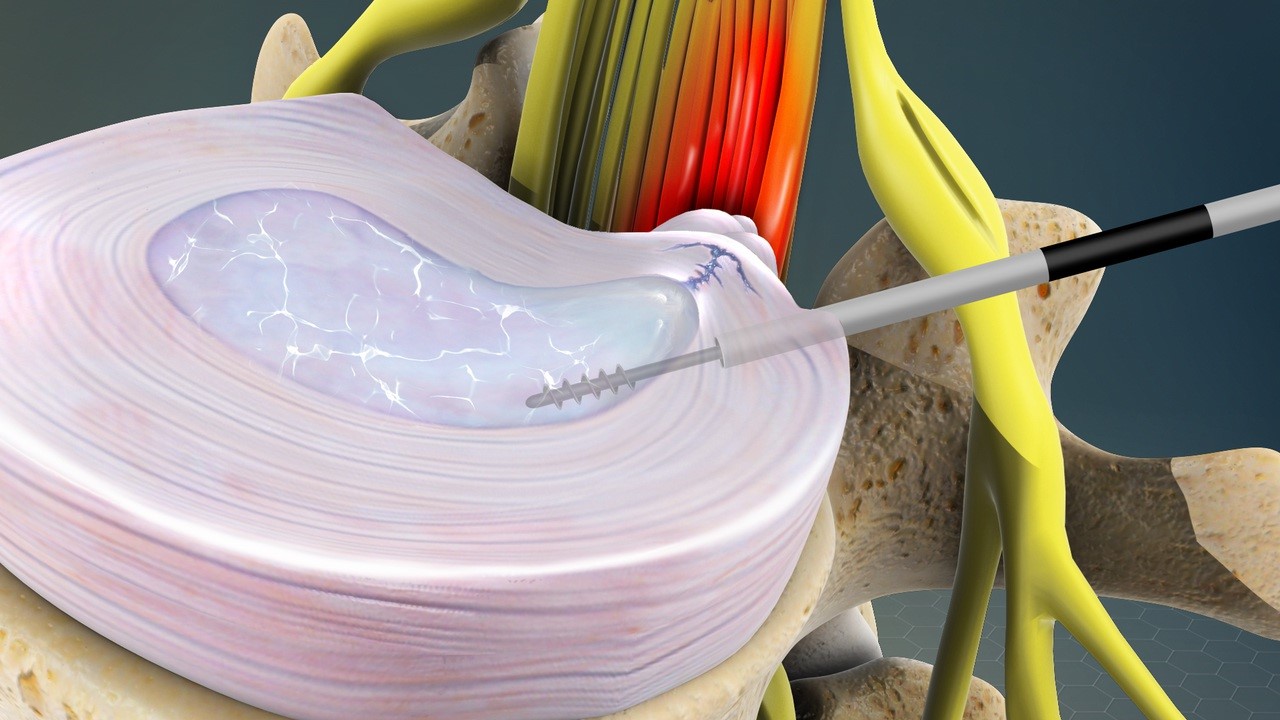
It is possible to work on improving the condition of nerve inflammation and reducing the severity of pain through thermal frequency, which is a non-surgical medical procedure that does not cause tissue damage. Thermal frequency burns the nerve to stop sending nerve signals that cause pain at the site of injury.
The steps for performing spinal term frequency are:
- The location of the lesion is determined by magnetic resonance imaging.
- Local anesthesia is used to prevent the patient from feeling the needle.
- Thermage needs a specific needle to be inserted into the affected part.
- The needle emits electromagnetic waves which result in wave heat pulses.
- The heat waves calm and stop the signals that cause pain in the nerve.
- This operation takes a short period of no more than 45 minutes, and the patient can leave the hospital on the same day as the operation.
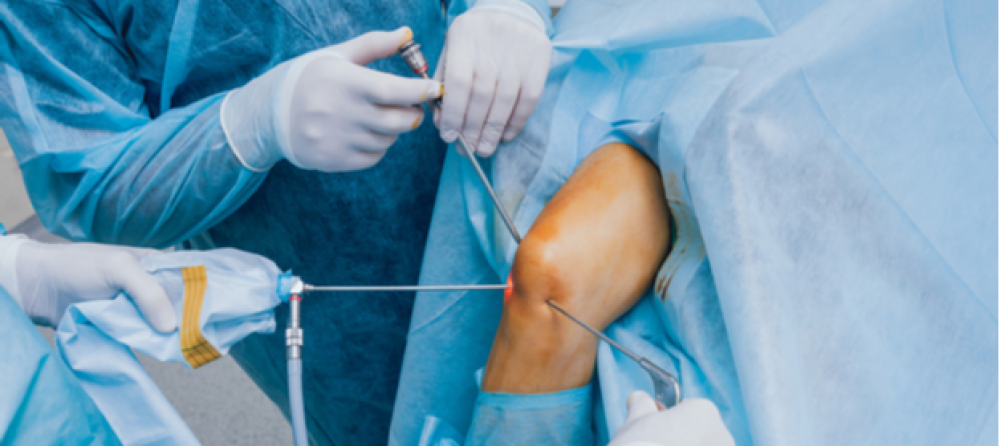
Knee thermal surgery
The thermal frequency procedure can be used to treat more than one disease, including infections in the fifth nerve, treatment of pain in the joints, as well as varicose veins, treatment of liver tumors, and other diseases that can be used with limited intervention thermal frequency technology.
A special needle is used to deliver frequency waves to the affected part of the knee, and this is done under the influence of local anesthesia. Thermal frequencies raise the temperature of the nerve slightly until the pain in it stops, and the pain signals are not transmitted from the nerve roots to the brain.
After the thermal frequency procedure, the patient may experience slight pain in the area of the injury, but it quickly disappears with the use of painkillers that do not need a prescription, and the patient is often able to return to his normal activity within only a few days after this medical procedure.
Post RF Help?
Thermal frequency is not considered a process in its literal sense, but it works to improve the condition of the patient and reduce the pain he feels as a result of inflammation or other diseases that the person was exposed to, and there are some steps that must be adhered to after performing the thermal frequency, including:
- Take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs prescribed by your physician.
- Be careful not to drive a car immediately after the operation.
- Take enough rest at home without putting in much effort.
- Make sure to walk 20 to 30 minutes a day.
Heat frequency damage
Thermal frequency is considered one of the relatively safe types of treatments, which helps the patient to feel more improvement after doing it, but in some rare cases, the patient may be exposed to complications, including:
- Infection or inflammation at the site of injury.
- Exposure to mild bleeding.
- Minor burns.