What is a Herniated Disc, and What is the Difference Between It and Sciatica?

What Is a Herniated Disc?
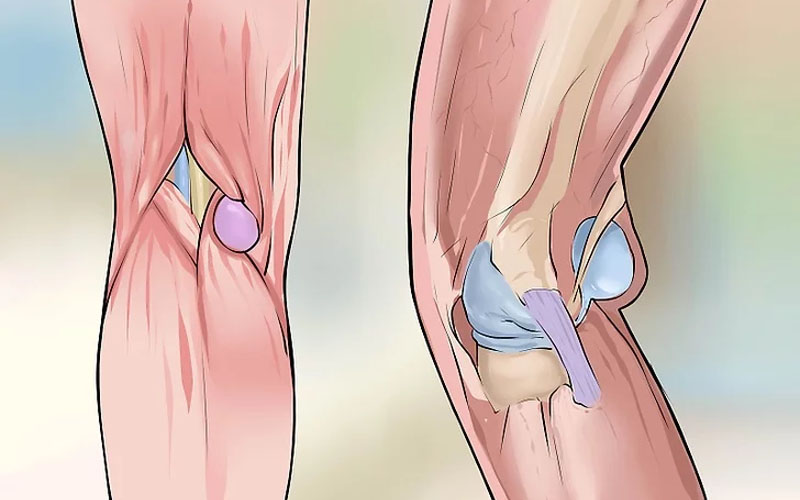
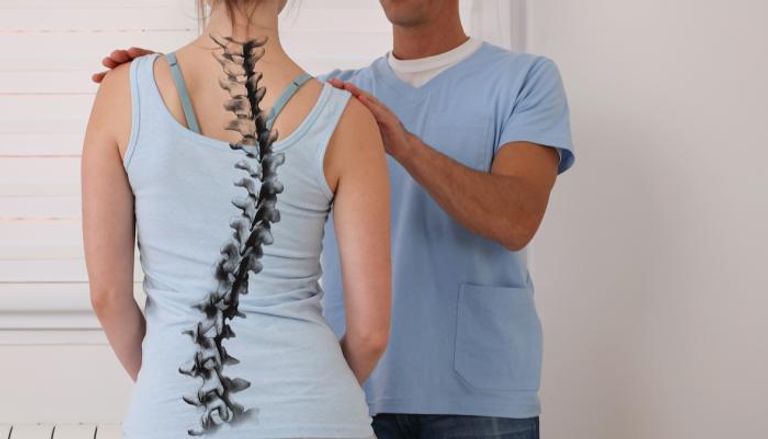
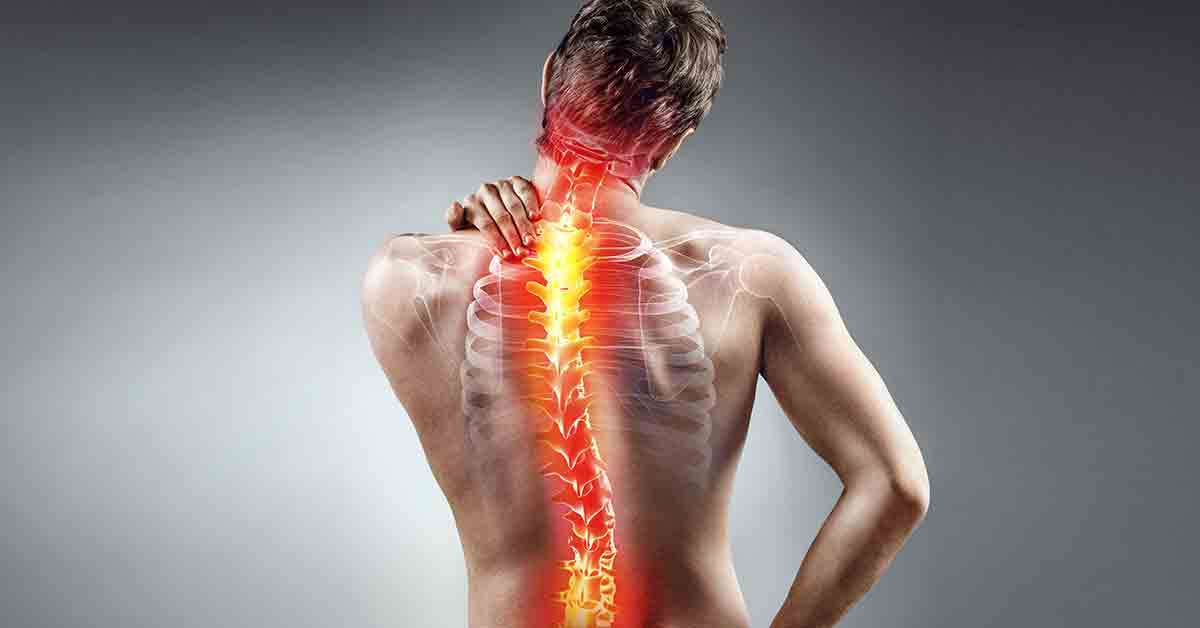
A herniated disc is a condition that occurs when the disc of cartilage between the vertebrae in the spine slips out of its usual place. The disc of cartilage is a flexible structure that exists between the vertebrae to absorb shock and provide smooth movement for the spine. However, in the case of a herniated disc, the disc slips out of its normal position, causing pain and muscle tension in the affected area.
The causes of a herniated disc are diverse and can result from various factors, including:
- Aging: Aging is one of the significant factors contributing to the occurrence of a herniated disc. Over time, the cartilage disc deteriorates, becoming less flexible and more susceptible to damage and slipping.
- Injuries: Acute spinal injuries can lead to disc herniation. For example, an injury from a car accident or a fall from a height can result in disc herniation.
- Excessive Pressure and Stress: Excessive pressure and stress on the spine can damage the cartilage disc and increase the likelihood of herniation.
- Inflammation: Infections in the areas surrounding the cartilage disc can weaken it and lead to herniation.
- Structural Abnormalities: Some structural abnormalities in the spine can increase the likelihood of disc herniation. For example, abnormalities in the vertebral column or irregularities in disc shape.
To prevent the occurrence of a herniated disc and reduce associated risks, you can follow some preventive measures, including:
- Maintaining Proper Posture: It’s essential to sit and stand with proper body posture to reduce stress on the spine. Supporting your back and head when sitting and avoiding excessive bending or overextension is important.
- Regular Exercise: Regular exercise may help strengthen the muscles in your back and maintain the stability and flexibility of the spine.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity can increase the burden on the spine and the likelihood of disc herniation. Therefore, it’s important to maintain a healthy and balanced weight.
- Stress and Pressure Reduction: Avoid excessive psychological stress and pressure, as they can increase pain levels and the risk of disc herniation.
- Using Proper Body Mechanics: Some body mechanics techniques, such as lifting objects correctly using leg strength rather than the back, can help avoid disc injury.
In summary, preventing herniated discs involves taking favorable preventive measures for spine health. By maintaining proper body posture, engaging in appropriate exercise, and following a healthy lifestyle, you can reduce the likelihood of disc herniation and promote spine health.
How Do You Know If You Have a Herniated Disc?
Herniated discs are common conditions that many people experience. However, an accurate diagnosis of this condition requires a visit to a specialist doctor and the necessary tests. Nevertheless, there are some symptoms that may indicate the presence of a herniated disc and help you detect it early. In this article, we will highlight some common symptoms of a herniated disc.
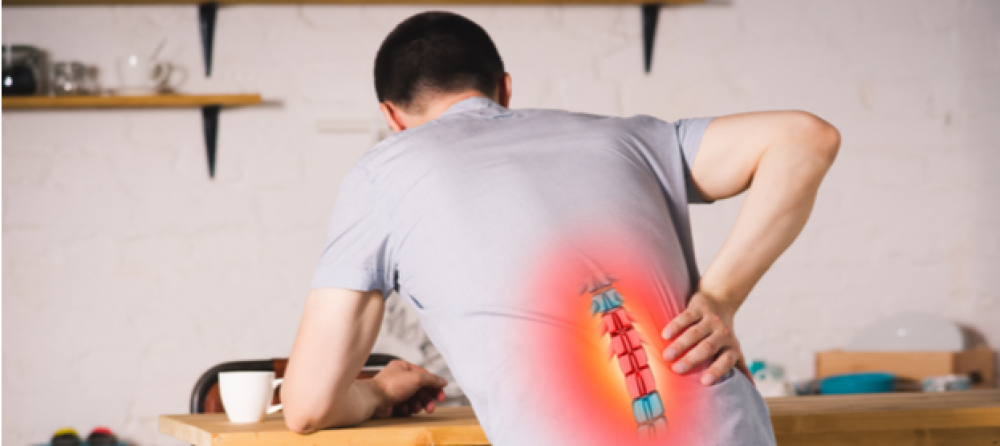
Back Pain: One of the primary symptoms of a herniated disc is experiencing pain in the back, especially in the lower part. The pain can be constant or intermittent and may increase after engaging in physical activities or lifting weights.
Leg Pain: Pain can radiate from the back to the leg in the case of a herniated disc, and this pain is often referred to as “sciatic pain” or “sciatic nerve pain.” The pain can be sharp or chronic and may worsen when sitting for extended periods or when lifting heavy objects.
Weakness in Leg Muscles: If you have a herniated disc in the spine, you may notice weakness in the affected leg muscles. The herniation can put pressure on the leg nerves, affecting muscle function.
Tingling and Numbness in the Leg: Tingling and numbness in the leg are common symptoms of a herniated disc. This tingling occurs due to the pressure of the herniation on leg nerves, affecting the proper transmission of nerve signals.
Difficulty in Movement and Bending: You may find it challenging to perform certain movements and bending due to pain, which can be an indicator of a herniated disc. Sudden bending or twisting of the spine can be painful and may be accompanied by abnormal spine movement.
What About the Severity of Herniated Discs? Although a herniated disc can impact a person’s quality of life, it is not usually considered a serious illness. With appropriate treatment and a healthy lifestyle, the vast majority of individuals gradually improve.
The issue with a herniated disc lies in the fact that it can cause severe symptoms and affect your ability to perform daily activities. Some individuals may require physical therapy or additional medical assistance to alleviate pain and restore normal spinal function.
However, what is the difference between a slipped joint and a disc joint? The terms “slipped joint” and “disc joint” refer to the same condition. Both indicate that the disc of cartilage in the spine has slipped out of its usual position.
What Are the Treatment Options for Herniated Discs?
The treatment of a herniated disc depends on the severity of the symptoms and their impact on your daily life. In some cases, symptoms can be alleviated through monitoring, rest, and medication to reduce pain and swelling.
However, some people can return to their normal activities, including appropriate exercises and physical therapy. It is advisable to visit a specialist doctor for an accurate diagnosis and to develop an appropriate treatment plan.
Avoiding Aggravation of Herniated Disc Condition: There are some measures that can be taken to avoid worsening the condition of a herniated disc and to maintain the health of the spine. These include:
- Regularly engaging in physical exercise to strengthen the back and abdominal muscles.
- Avoiding improper lifting of heavy objects.
- Maintaining a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the spine.
- Avoiding sitting for long periods without movement.
If you experience symptoms similar to those indicating a herniated disc, it is essential not to ignore them and to consult a specialist doctor. They can diagnose your condition and develop an appropriate treatment plan to help alleviate the symptoms and return to your normal activities.
Can Herniated Discs Be Completely Cured?
Can herniated discs be completely cured? Herniated discs are conditions that can cause pain and impair the lives of those affected. Therefore, a question that arises in the minds of many sufferers is whether a complete cure is possible for this painful condition.
To answer this question, it is necessary first to understand what a herniated disc is. A herniated disc occurs when the cartilage in the spine moves out of its usual position, putting pressure on surrounding nerves and tissues, resulting in pain and swelling. This condition typically affects individuals who use computers for extended periods or sit for prolonged periods in unhealthy postures.
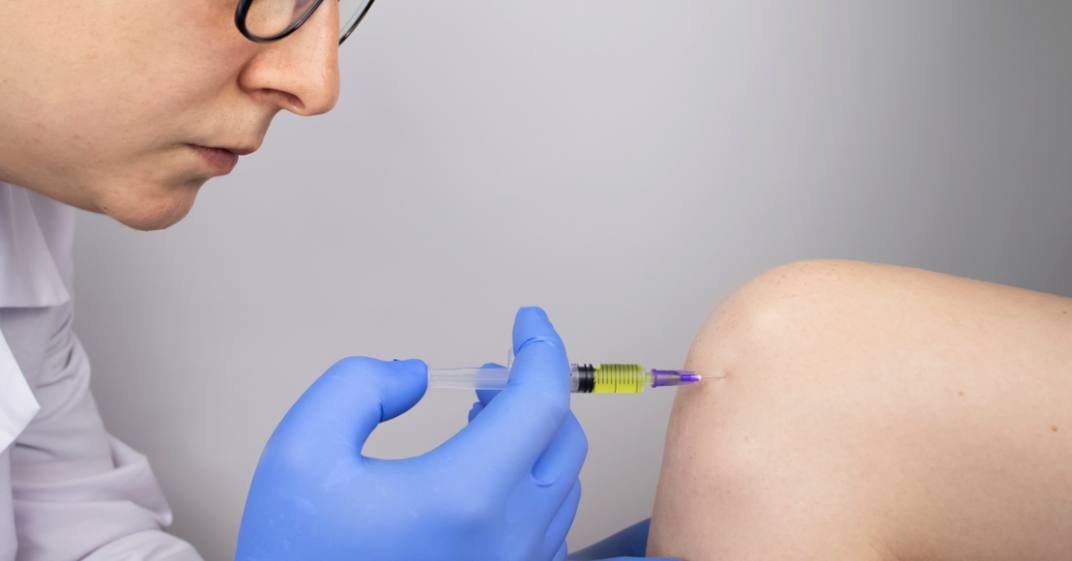
Is it possible for patients to fully recover from herniated disc pain? In some cases, complete recovery from lumbar and cervical herniated discs can be achieved through non-surgical interventions. These interventions include physical therapy, medication, and injections, as well as exercises to strengthen the muscles surrounding the spine.
However, the time required for recovery from a herniated disc varies depending on the degree and severity of the problem. Typically, the recovery period for a herniated disc is around 4-6 weeks. After this time, the person affected can gradually return to their normal level of activity. It requires adherence to the treatment prescribed by a specialist doctor, which may include pain relievers, cortisone injections, and others.
Although some individuals regain their previous health from a herniated disc after a specific period, it does not necessarily mean they experience permanent healing. In some cases, the pain may return, especially if the affected individual does not follow the recommendations for treatment and prevention.
If individuals continue to engage in unhealthy habits and behaviors, herniated disc pain may worsen and develop into more severe conditions. Therefore, it is advisable to follow a healthy lifestyle and adhere to the recommendations of specialist doctors to prevent herniated disc occurrence or exacerbation.
Treatment methods for herniated discs focus on relieving pain and reducing the pressure of the disc on surrounding nerves. People can turn to physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises to strengthen muscles and improve flexibility. Pain-relieving medications and tension-relieving interventions may also be used in some cases.
In general, doctors prefer to use non-surgical interventions before resorting to surgery, except in severe and emergency cases. This is because non-surgical interventions provide safety and security for patients, in addition to focusing on pain relief.
In summary, some individuals with herniated discs can be completely relieved of pain and swelling using various non-surgical interventions, such as physical therapy and medication. However, recovery takes time and is associated with adhering to treatment instructions and protection from future tears. Additionally, adopting a healthy lifestyle and engaging in appropriate exercises to strengthen the back muscles and maintain ideal weight are crucial. These measures can help prevent herniated disc occurrence or exacerbation in the future.
How is Recovery from Herniated Disc Achieved?
Herniated discs are a common medical condition that many people around the world suffer from. Here, we will discuss some methods and treatments that can help in recovering from this condition.
Conservative Treatment
Conservative treatment involving various approaches is the available option for most individuals with a herniated disc. This type of treatment aims to alleviate pain and improve the condition of patients without the need for surgical intervention. Conservative treatment techniques include the following:
- Exercise: Prescribed exercises by a physical therapist can help strengthen the back and abdominal muscles, contributing to the restoration of spine posture and stability.
- Medication: Pain-relieving medications such as paracetamol or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs like ibuprofen can be used to alleviate herniated disc pain.
- Application of Cold and Heat: Localized heating and cooling can be used to reduce pain and inflammation in the herniated disc area.
Functional Rehabilitation
Functional rehabilitation therapy aims to effectively restore and enhance the functions and movements of patients with a herniated disc. Functional therapy treatment methods include:
- Body Positioning Techniques: Techniques for improving body positioning during daily movements and activities that target reducing pressure on the herniated disc.
- Stability and Muscle Coordination Training: Training techniques for stability and muscle coordination can enhance muscular stability and balance as much as possible to prevent further injuries or exacerbation of the herniated disc.
Surgery:
Individuals with herniated discs who do not respond to non-surgical treatments or conservative practices may require surgical intervention. Increased surgical risks are associated with the complexity of the injury and the severity of symptoms. In some cases, a portion of the deteriorated disc may be removed or replaced with an artificial disc.
Complementary Treatment
In addition to the treatments mentioned above, there can be some complementary therapies that may help alleviate the symptoms of a herniated disc and promote the healing process. These therapies include:
- Massage Therapy: Massage can help relieve pain and improve blood circulation in the affected area.
- Rehabilitation Therapy: Rehabilitation therapy is an effective method for reducing herniated disc symptoms and includes techniques such as exercise therapy and aquatic therapy.
- Proper Nutrition: Individuals with herniated discs should follow a healthy and balanced diet that includes essential nutrients that promote disc health, such as calcium and vitamin D.
In the end, the appropriate treatment for a herniated disc should be specific to each individual’s condition. Therefore, individuals with this condition should consult with their specialized physician for an accurate diagnosis and the suitable treatment according to their individual circumstances.
How to Differentiate Between Back Muscle Pain and Herniated Disc?
How can you distinguish between back muscle pain and a herniated disc?
Many people suffer from back pain, and this pain can result from various different causes, including a herniated disc. However, it is important to differentiate between back muscle pain and a herniated disc to determine the appropriate treatment. In this article, we will highlight how to distinguish between these two types of pain.
Back Muscle Pain
Back muscle pain is a very common type of back pain and is often the result of tension or stretching of the back muscles. Those affected may feel varying degrees of pain in the upper or lower back region, as a result of muscle stretching or tension. Patients may describe this pain as similar to what one might experience when lifting something heavy or exerting themselves.
Here are some signs that may indicate the presence of back muscle pain:
- The pain is localized in the back area and is not felt in other parts of the body.
- Pain improves when applying home treatment methods such as rest, localized ice or heat application, and performing muscle-strengthening exercises.
- The absence of additional symptoms such as numbness in the legs or loss of bladder control.
Herniated Disc
A herniated disc is a more severe condition that affects the spinal column, where the spinal disc of a vertebra slips towards the nerve canal, resulting in pressure on the nerves and surrounding tissues. Herniated discs can cause sharp back pain that radiates to a part of the leg.
Here are some signs that may reveal the presence of a herniated disc:
- Sharp back pain that radiates to the lower part of the leg and is felt in only one leg.
- Numbness or tingling in the legs or feet.
- Weakness in the affected leg muscles, affecting movement and the ability to control the foot.
If you are experiencing back pain, it is important to consult a doctor for a diagnosis. Additional tests such as X-rays or MRI scans may be required to determine the actual cause of the pain.
Given the symptoms mentioned above, individuals who can distinguish between simple back muscle pain and a herniated disc can take appropriate action to treat the condition. Cases of herniated discs may require more complex treatment steps, such as physical therapy or surgery in some instances.
Regardless of your condition, it is best not to underestimate back pain and to follow the treatment plan recommended by medical experts.
What is the difference between a herniated disc and sciatica?
Herniated disc and sciatica are two different medical conditions, although they may share some symptoms and occur in the back and leg area. In this article, we will explore the differences between herniated discs and sciatica and how they can be diagnosed and treated.
Herniated Disc (Herniated Disk)
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped disc, occurs when the disc of the spinal column tears and its material enters a nerve pathway. This usually happens due to the natural wear and tear of the discs between the vertebrae or as a result of an injury or trauma to the disc due to a strong impact on the spinal column.
Diagnosing a herniated disc is typically done through a clinical examination and based on the patient’s medical history. Patients may be asked to undergo additional diagnostic tests such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to clarify the precise picture of the affected disc and its impact on nearby nerves.
Symptoms of Herniated Disc include:
- Pain in the back area that may radiate to the leg and foot.
- Weakness of muscles and loss of sensation in the leg or foot.
- Numbness in the leg or foot.
- Increased pain when moving or sitting for extended periods.
Sciatica
Sciatica is a condition that results from irritation or compression of the sciatic nerve, one of the largest nerves in the body, which originates from the spinal column and extends through the buttock, leg, and foot. Pressure on the sciatic nerve can occur due to several reasons, including:
- Spinal canal narrowing.
- Disc formation.
- Disc herniation.
- Enlargement of back muscles.
Diagnosing sciatica largely relies on the patient’s medical history and symptoms identified by the doctor. The patient may be asked to undergo additional diagnostic tests such as X-rays or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine the source of irritation or constriction.
Symptoms of sciatica include:
- Severe pain that intensifies in the buttock and radiates down the leg.
- Weakness of muscles and loss of sensation in the leg and foot.
- Numbness in the leg or foot.
- Difficulty walking or moving.
Treatment and Management
When diagnosed with a herniated disc or sciatica, conservative treatment typically begins with medications and physical therapy. Rest and regular application of ice to the affected area are usually recommended. Treatment may take several weeks for the pain to subside, and for the patient to regain strength and abilities.
In cases where the patient does not respond to conservative treatment or serious problems such as loss of bladder control or significant muscle weakness occur, surgical intervention to relieve pressure on the affected nerve may be suggested. The decision to undergo surgery should be based on a comprehensive evaluation by the treating physician, taking into account the patient’s condition and its impact on their life.
In conclusion, herniated disc and sciatica may share some symptoms, but they are two different medical conditions that require proper diagnosis and treatment. Patients should consult with a specialist doctor to obtain an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment for their condition.