?What is knee osteoarthritis and what are the main treatment methods
What is knee osteoarthritis? Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people suffer from, so in this article, we will help you understand in detail the most important symptoms that indicate that you have knee osteoarthritis, in addition to its causes and the treatment methods followed to get rid of it, so follow us for all the latest on this matter.
What is knee osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people suffer from as they age and use the joint continuously. Osteoarthritis of the knees or hips is characterized by recurrent, painful pain, especially if the muscles are weak.
Taking medication helps treat knee osteoarthritis by reducing pain, swelling, and relieving symptoms of osteoarthritis. Among these medications are painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs. However, you must follow the doctor’s instructions when using them to avoid any undesirable side effects, so my experience with treating knee osteoarthritis with Dr. Amr Amal was exceptional.
Performing specific exercises sometimes helps manage spinal joint osteoarthritis. Heat or ice can be used to relieve swelling and pain. In this context, we will learn about the causes of knee osteoarthritis, its symptoms, and the methods used to treat it in this distinguished article.
Symptoms of knee osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis causes pain, swelling, and limits joint movement. Here, we will shed light on the most important symptoms that may indicate the presence of knee osteoarthritis:
- Knee pain: Pain is one of the most common symptoms of knee osteoarthritis. The severity of the pain varies from person to person and can be mild or severe. Usually, the pain increases with knee movement or activities that put additional pressure on the joint.
- Difficulty moving: You may feel difficulty in moving the knee, especially when standing or bending the knee. This is accompanied by a feeling of stiffness and heaviness in the joint.
- Swollen knee: The joint may become swollen and reddened, and the size of the swelling depends on the condition of the joint. Swelling may occur due to the accumulation of fluids in the joint or inflammation resulting from bone friction.
- Poor pulse and coldness in the feet: In some cases, a person with knee osteoarthritis may experience a poor pulse and coldness in the feet. This may be due to reduced blood supply in the area around the affected joint.
- Change in the shape of the knee and appearance of the skin: The affected knee may show changes in its shape, such as joint stiffening and rigidity. The color and appearance of the skin surrounding the knee may also change.
Causes of knee osteoarthritis
- Aging: Aging is one of the main factors that lead to knee osteoarthritis. Many people experience cartilage damage in their joints as they age, increasing the likelihood of erosion and roughness.
- Injury: Direct injuries to the knee can lead to joint osteoarthritis. For example, if you have suffered a fracture or tear in the inner cartilage of the knee, this may increase the risk of developing joint osteoarthritis later on.
- Overweight: Being overweight is an important factor in the development of knee osteoarthritis, especially among women. The extra pressure resulting from increased weight leads to faster cartilage erosion, increasing the likelihood of developing joint osteoarthritis.
- Prolonged standing: Standing for long periods daily can lead to joint irritation and an increased risk of developing knee osteoarthritis. Therefore, you should avoid standing for long periods without taking regular breaks or moving to relieve pressure on the joints.
- Not bending the affected knee much: Not bending the affected knee properly can lead to increased friction pressure on the cartilage, increasing the likelihood of damage and erosion in the joints.
- Genetic factors: Genetic factors may play a role in the development of knee osteoarthritis. If a distant relative has suffered from this problem, you may have a genetic predisposition to developing it as well.
- Joint inflammation: Chronic joint inflammation, such as rheumatoid arthritis, leads to gradual cartilage damage and erosion, increasing the likelihood of knee osteoarthritis.
- Other diseases: There are some other diseases that can increase the likelihood of developing knee osteoarthritis, such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol levels, and diabetes. Therefore, it is important to control these health conditions to maintain joint health.
My experience with treating knee osteoarthritis with Dr. Amr Amal was a wise decision, so we advise you to have this experience.
Diagnosis of knee osteoarthritis
Knee osteoarthritis, also known as bone joint disease, is one of the most common and impactful bone diseases affecting the knee joints. To diagnose this condition, several tests and examinations must be performed by specialized doctors. In this section, we will review some of the methods used to diagnose knee osteoarthritis:
- Medical history and descriptive symptoms:
The diagnostic process begins by gathering information about the patient’s medical history and checking for the symptoms they are experiencing. These symptoms may include pain, swelling, stiffness, and difficulty moving. - Clinical examination:
Using clinical examination techniques, the doctor evaluates the condition of the affected joint and the possible movements of the knee. The examination may include pressing on the kneecap joint and moving the knee in specific directions to determine the location of the pain and assess any other injuries. - X-ray imaging:
X-rays are one of the most common diagnostic tools for identifying knee osteoarthritis. X-rays can reveal changes in the shape of the joint and damage to the bones. X-ray imaging may show joint erosion, cartilage compression, and joint movement obstruction. - Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI):
In some cases, the doctor may need to use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to determine the extent of damage to the joint and assess the condition of the cartilage and surrounding tissues. MRI can accurately and in detail show changes in the structure of the knee and the level of osteoarthritis progression. - Analysis of joint fluid:
In advanced cases of knee osteoarthritis, a sample of the joint fluid may be taken for laboratory testing. This analysis can reveal the presence of inflammation in the joint and the level of cartilage and bone damage.
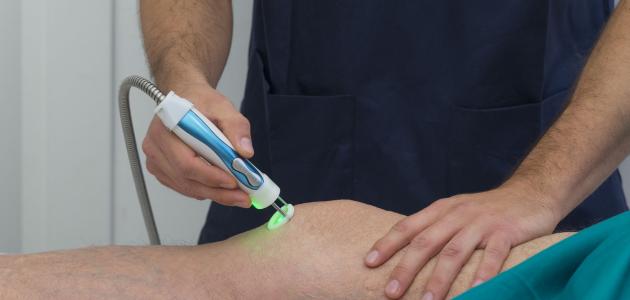
Treatment of knee osteoarthritis
Treating knee osteoarthritis is one of the major medical challenges faced by people with knee joint problems. Specializing in the treatment of joint inflammation and joint pain is of utmost importance for patients. Advanced techniques contribute to treating patients in a short period of time.
There are several ways to treat knee osteoarthritis, ranging from physical therapy and exercises that strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee and increase flexibility. Knee osteoarthritis can also be treated with oils, as essential oils and massage oils help relieve pain and improve joint movement.
Among the medications used to treat knee osteoarthritis, Durofin is an effective drug. Durofin contains glucosamine, which helps strengthen cartilage and improve joint function. Durofin also contains ginkgo biloba, which helps reduce inflammation and improve the healing process.
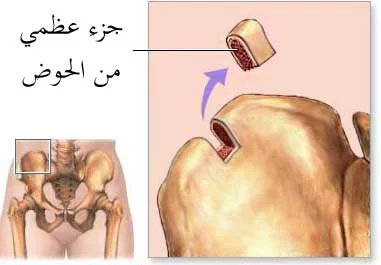
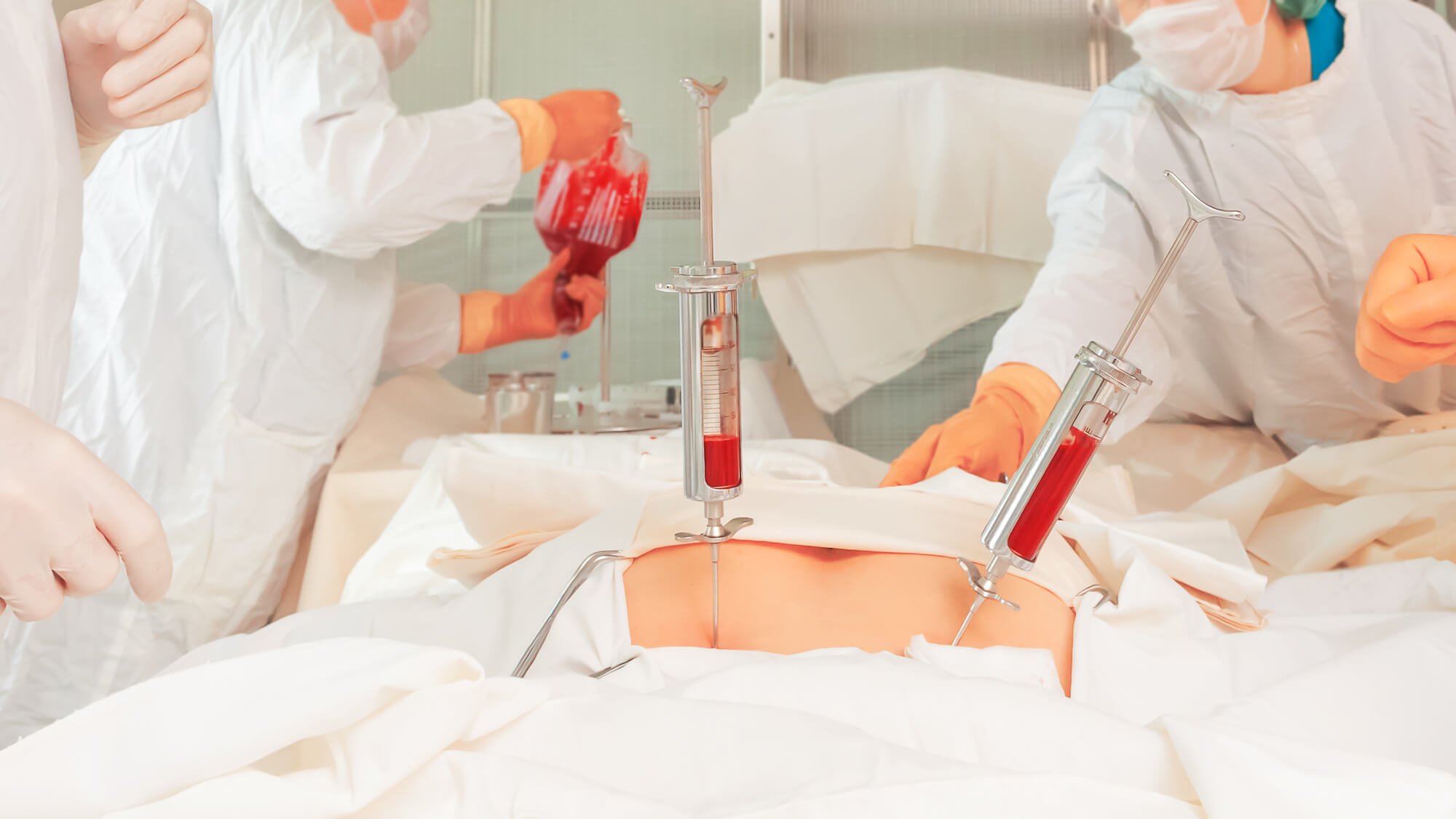
One of the most common surgical methods for treating knee osteoarthritis is injecting the knee with a viscous fluid. This fluid works to lubricate the joints and reduce bone friction during movement. This method is generally painless and does not require a long recovery period.
The belief that treating knee osteoarthritis requires major surgery or general anesthesia is completely wrong. There are effective treatment methods that rely on limited intervention and do not require complex surgeries. The appropriate treatment for each patient is determined based on their health condition and the severity of their symptoms.
“`html
How to Avoid Knee Osteoarthritis
We will provide you with valuable tips to avoid knee osteoarthritis or reduce the likelihood of its occurrence. Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people suffer from, and these tips will help you maintain the health of your knees, avoid future problems, and include the following:
- Maintain a Healthy Weight: The knee joint is significantly affected by weight gain; the more weight you gain, the less the joint can bear the pressure. Therefore, it’s important to maintain a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular physical activity.
- Strengthen the Surrounding Muscles: Strengthening the strong muscles around the knee joint reduces pressure on the joint itself. You can perform exercises that target strengthening the thigh and leg muscles, such as squats and leg lifts.
- Use Appropriate Preventive Techniques: To maintain the health of your knees, avoid high-impact sports activities on the joints, such as jumping and running on hard asphalt. Instead, swimming or high-performance cycling may be better options to maintain knee health and fitness.
- Use Supportive Aids and Cushions: If you experience knee problems or pain, supportive aids and cushions can help reduce pressure on the joint. Consult your doctor for advice on suitable assistive tools for your condition.
- Avoid Sports Injuries: Be sure to avoid sports injuries that may increase the likelihood of knee osteoarthritis. Wear appropriate protective gear for the sports activity you’re engaged in, and avoid situations that increase stress and strain on the joints.
- Pay Attention to Pain and Symptoms: If you experience persistent knee pain or notice any unusual symptoms, it’s essential to consult a doctor. Continuous knee pain may indicate larger problems that require evaluation and treatment by an orthopedic surgeon or perhaps a physical therapist.
What are the Complications of Knee Osteoarthritis?
When knee osteoarthritis is ignored or not properly treated, it may develop into complications that significantly affect the individual’s daily life. In this article, we’ll discuss some common complications that can occur as a result of knee osteoarthritis, such as:
- Walking Problems: Many people with knee osteoarthritis have difficulty walking due to pain and stiffness in the joint. This may reduce physical activity and make it challenging to perform simple daily tasks.
- Mobility Impairment: Independent movement may become difficult due to knee osteoarthritis. Pain and swelling may reduce the ability to perform usual activities like climbing stairs, driving, and doing household chores.
- Decreased Quality of Life: Knee osteoarthritis affects the individual’s overall quality of life. They may experience depression or anxiety due to the inability to engage in preferred activities. It may also affect sleep and comfort.
- Arthritis Development: Cartilage wear and tear in the joint can lead to irritation of surrounding joints and arthritis development. This inflammation can cause knee swelling, continuous pain, and difficulty in joint movement.
- Knee Dislocation: In severe cases, knee dislocation may occur, leading to joint deformity and loss of full joint use. This condition may require corrective surgery to rebuild the joint.
My experience with Dr. Amr Amal in treating knee osteoarthritis has been excellent, and I recommend you to undergo this experience.
How Does Obesity Affect Knee Osteoarthritis?
Obesity significantly affects knee osteoarthritis. When weight increases significantly, the joint is subjected to excess loads that lead to joint cartilage damage. Weight gain is considered one of the most influential factors in knee osteoarthritis, leading to cartilage erosion and reduced joint movement.
Additionally, obesity exposes the individual to other risks such as osteoporosis and structural muscle disorders in the knee and hip. Therefore, it is recommended to follow a healthy and balanced lifestyle and engage in regular exercise to maintain a healthy weight and reduce the negative impact of obesity on knee osteoarthritis.
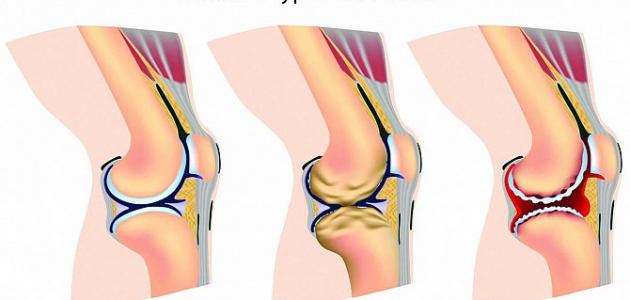
Degrees of Knee Osteoarthritis
Degrees of knee osteoarthritis are a condition that affects the knee joint and causes a number of problems and symptoms. Depending on the degree of the condition, the severity of the condition can be determined, and appropriate treatment can be provided to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. In this article, we’ll discuss the different degrees of knee osteoarthritis, symptoms, and suitable treatment for each degree as follows:
First Degree of Knee Osteoarthritis:
In this degree, patients usually do not experience any pain, and there are no apparent symptoms of osteoarthritis in the joint. There may be slight stiffness in the joint during movement, but it does not have a significant impact on the person’s daily life.
Second Degree of Knee Osteoarthritis:
In this degree, patients may feel mild pain in the joint during movement, and inflammation may become prominent after strenuous physical activity. Additionally, patients may experience reduced flexibility and limited movement in the joint. For this condition, it’s preferable to consult an orthopedic doctor to provide an appropriate treatment plan, which may include physical therapy sessions and the use of anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain and swelling.
Third Degree of Knee Osteoarthritis:
In this case, the pain in the joint increases and becomes continuous and bothersome to the patient, even during rest. Patients in this degree may experience stiffness and difficulty in movement, and they may notice swelling and redness in the joint. Doctors may recommend conducting some tests such as X-rays and MRI imaging to evaluate
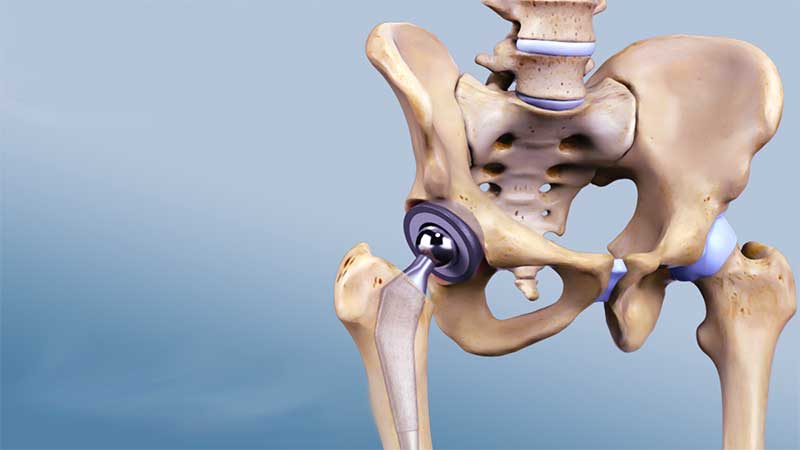
Grade Four Knee Osteoarthritis:
This grade is considered the most severe and challenging. Patients in this condition suffer from severe narrowing of the space in the joint, significant bone spurs, and noticeable loss of cartilage. There may be a noticeable deviation from the normal shape of the joint. Patients may experience severe pain, inability to move normally, and severe swelling in the joint. Doctors may recommend joint replacement surgery in this case to improve movement and alleviate symptoms.
How to avoid getting knee osteoarthritis
We will provide you with valuable tips to avoid getting knee osteoarthritis or reduce the likelihood of it occurring. Knee osteoarthritis is a common condition that many people suffer from, and these tips will help you maintain the health of your knees and avoid future problems:
- Maintain a healthy weight: Maintaining a healthy weight is very important for people with knee osteoarthritis. Increasing weight can put more pressure on the joint and worsen symptoms. Therefore, it is recommended to follow a healthy and balanced diet and exercise regularly.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise is one of the best ways to treat and relieve knee osteoarthritis. It helps strengthen the muscles surrounding the knee, improve flexibility, and strengthen the joint barrier. It is recommended to perform lubricating exercises for the joint, such as swimming, stationary cycling, and walking.
- Avoid standing for long periods: People with knee osteoarthritis should avoid standing for long periods without rest. It is preferable to use comfortable chairs or stools if the condition requires it. It is also recommended to distribute weight evenly on both feet to reduce pressure on the knee.
- Avoid high-impact activities: People with knee osteoarthritis should avoid activities that require a high load on the knee, such as running and jumping. Instead, low-impact activities like swimming or walking can be chosen.
- Use supportive aids: Supportive aids such as crutches or walking aids can be used when needed. These aids provide the necessary support for the patient and reduce pressure on the affected knee.
- Pain management: It is recommended to apply ice to the affected knee to relieve pain and swelling. Pain medication can also be used when needed and after consulting a doctor.
- Massage and physical therapy: Massage and physical therapy techniques can also be used as part of the treatment. These techniques may help improve blood circulation, reduce inflammation, and improve knee movement.
- Avoid excessive fatigue: People with knee osteoarthritis should avoid activities that require excessive strain on the knee. It is advisable to rest and relax between activities and avoid continuous excessive exertion.
For more information about the recommended exercises for treating knee osteoarthritis and the prohibited exercises, we recommend that you read this article.

Best doctor for treating knee osteoarthritis in Egypt
Searching for the best doctor for treatment requires a thorough evaluation and a good study of the characteristics and experiences of different doctors. When it comes to treating knee osteoarthritis in Egypt, Dr. Amr Amal emerges as a prominent and promising choice for patients seeking healing and relief.
Thanks to his specialization in treating joint inflammation and joint pain, Dr. Amr Amal uses a variety of therapeutic methods to alleviate symptoms and improve the condition. Among these methods, he uses medication, local injections, and arthroscopy to achieve the desired results. Patient testimonials indicate a significant improvement in their health condition after visiting Dr. Amr Amal.
In addition to all this, Dr. Amr Amal is deeply concerned about the health and well-being of his patients. He works tirelessly to provide professional care and the necessary support for patients throughout their treatment. Dr. Amr Amal provides valuable advice and personal guidance for a speedy recovery and better results.
Dr. Amr Amal proves himself to be the best doctor for treating knee osteoarthritis in Egypt. With his high scientific appreciation and technical skills, Dr. Amr Amal ensures an outstanding patient treatment experience. Therefore, if you suffer from knee problems, Dr. Amr Amal is the best choice for excellent healthcare that ensures healing and well-being.