Learn about the treatment of muscular tendinitis and whether walking is beneficial for it
Muscular Tendonitis Treatment
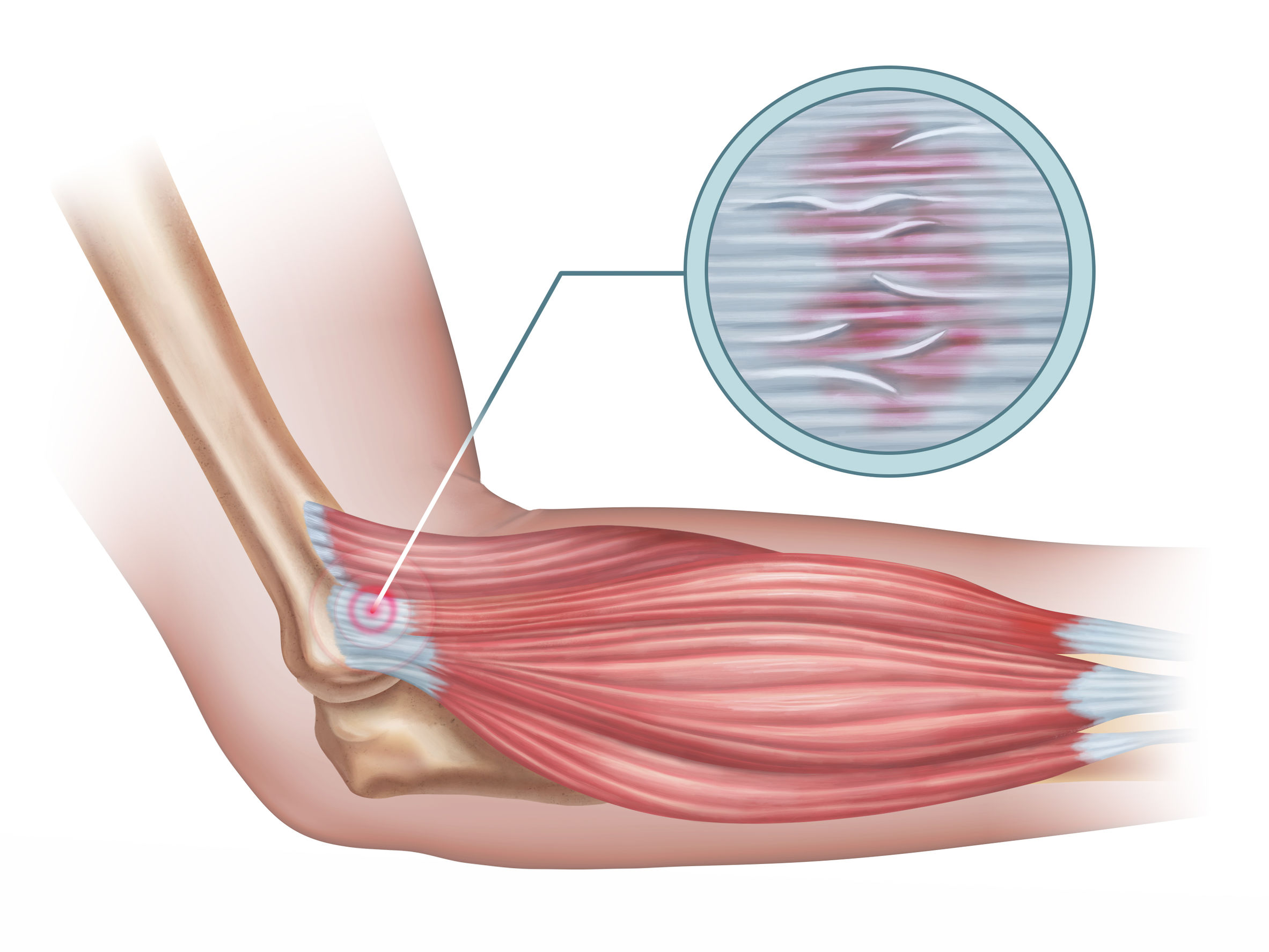
Muscular tendonitis is a common condition that individuals of various ages may suffer from. This condition can cause sharp pains and reduce a person’s ability to perform daily activities. Therefore, treating muscular tendonitis is necessary to eliminate the pain and restore normal muscle functions.
In this article, we will review 5 effective and scientifically proven methods for treating muscular tendonitis:
- Rest and Self-Care Measures
- Give your body enough rest, and give the tendon a chance to heal without straining it.
- Use a compression bandage to stabilize the affected area and reduce swelling.
- Use ice to relieve pain and reduce inflammation. Apply ice to the inflamed tendon for 10-15 minutes several times a day.
- Take pain relievers such as ibuprofen (Advil) or acetaminophen (Tylenol) after consulting a doctor.
- Physical Therapy
- Physical therapy may be effective in treating muscular tendonitis. Physical therapy focuses on exercises that strengthen the muscles and ligaments surrounding the inflamed tendon.
- These exercises can help repair and promote the regeneration of tendons.
- Therapeutic massage techniques and stimulatory exercises are popular in treating tendonitis, as they enhance blood flow and tendon regeneration.
- Medication Treatment
- The medicinal options for treating muscular tendonitis vary and include:
- Pain relievers such as aspirin, ibuprofen, and acetaminophen.
- Creams containing pain relievers that can be applied topically to the skin.
- Consult a doctor before using any medication to ensure it is safe and suitable for your condition. Some medications may cause side effects.
- The medicinal options for treating muscular tendonitis vary and include:
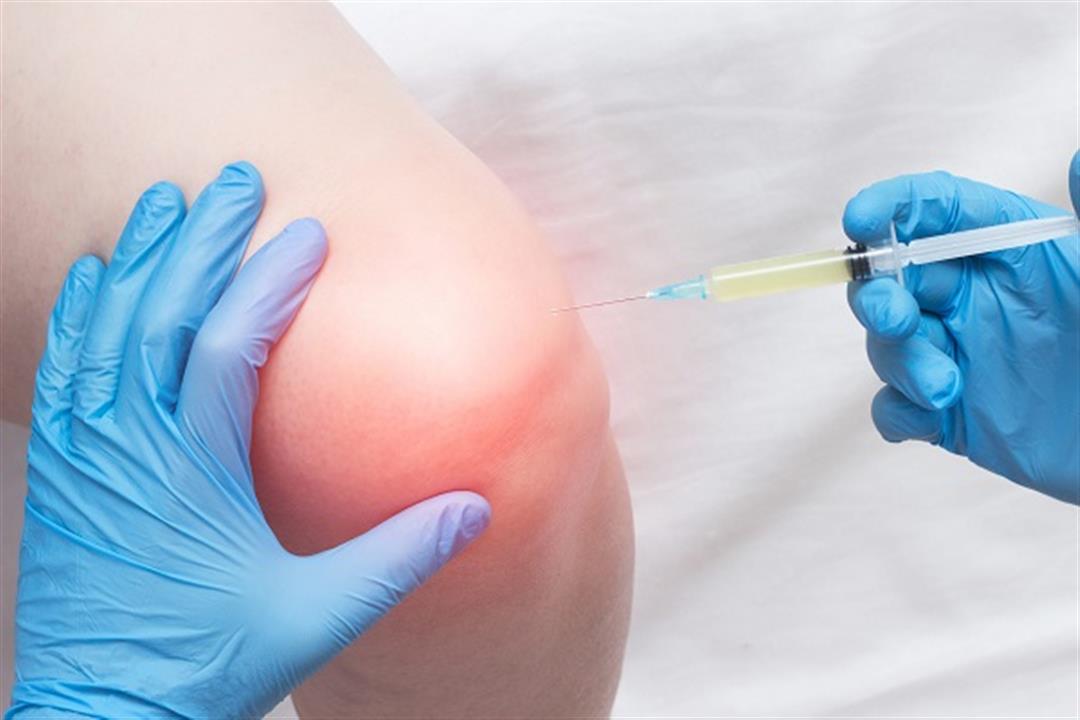
Steroid Injections If tendonitis does not respond to the above-mentioned treatments, the doctor may suggest localized steroid injections around the inflamed tendon. Some research shows promising results in the effectiveness of steroid injections in alleviating pain and inflammation. Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy This new treatment is promising in treating muscular tendonitis. The treatment involves using blood drawn from your body, processing it, and then injecting it into the area of the inflamed tendon. Although research in this area is still developing, there are positive results regarding the effectiveness of this treatment in improving chronic tendonitis conditions.
Treatment options for muscular tendonitis vary according to the severity and nature of the condition. It is preferable to consult a doctor before taking any treatment step. The healing process may take a long time, so do not lose hope and continue to follow the treatment regularly.
How do I know if I have tendonitis?
How do you know if you have tendonitis?
Many people may suffer from tendonitis, a condition that causes pain and tenderness when moving or pressing on the tendons. Tendonitis may require rest and necessary treatment to relieve pain and recover. In this article, we will review some signs that indicate the presence of tendonitis.
- Pain: Pain is one of the most significant signs that indicate the presence of tendonitis. The affected person may feel severe pain when moving the affected joint or when pressing on the painful area. The pain may be minor in some cases, especially in the early stages of tendonitis.
- Itching and Redness: In some cases, a person may feel itching and redness in the area of tendon inflammation. This redness and itching may indicate the presence of inflammation and irritation in the area.
- Swelling: A person with tendonitis may notice swelling in the area of inflammation, which may be accompanied by pain. The swelling is due to inflammation of the tendons and congestion of the affected area.
- Difficulty in Movement: The affected person may experience difficulty moving the affected joint due to pain and swelling. Difficulty in movement can affect the person’s ability to perform daily activities normally.
- Numbness or Tingling: In some cases, the affected person may experience numbness or tingling in the area suffering from tendonitis. This numbness or tingling can be attributed to the tendons pressing on the surrounding nerves.
If you feel any of these signs, you may have tendonitis. It is important to turn to your doctor for the correct diagnosis and appropriate treatment. The doctor can provide you with a comprehensive treatment plan that includes rest, physical therapy, and the appropriate medication to relieve pain and promote recovery.
In addition, here are some measures you can take to prevent tendonitis:
- Ensure to exercise and perform activities correctly, avoiding movements that may weaken or strain the tendons.
- Avoid repeating the same movement for a long period; try to vary your activities to reduce the continuous strain on the tendons.
- Strengthen tendons and muscles by engaging in protective exercises targeting your preferred sports activity.
- Observe correct body posture and movements during physical activities and daily tasks, avoiding overexertion on the tendons.
In summary, tendonitis is a condition that causes pain and soreness in the tendon area. If you experience any of the signs mentioned above, you should consult your doctor. The doctor may help you diagnose tendonitis and prescribe a suitable treatment plan to alleviate pain and recover faster.
Is walking beneficial for tendonitis?
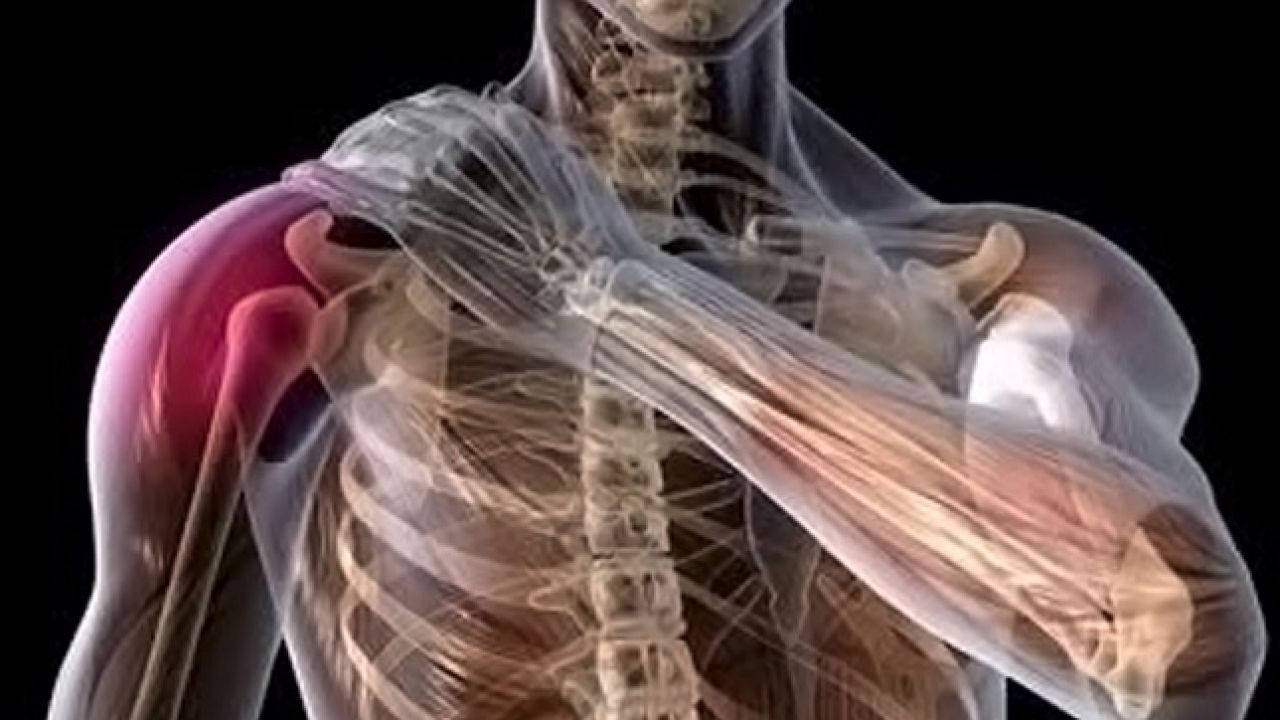
Tendons are an important part of the body’s movement system, connecting muscles to bones and enabling us to perform various movements. However, people sometimes suffer from tendonitis, a condition that causes pain, swelling, and limited joint movement.
In such cases, many wonder about the benefits of walking in alleviating tendonitis symptoms and improving healing. In this article, we will explore the benefits of walking in treating tendonitis.
- Improving Blood Circulation: When you walk, the blood flow to the tendonitis area increases, enhancing the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to the damaged cells. Thus, walking helps improve blood circulation and accelerate the healing process.
- Strengthening Surrounding Muscles: Thanks to the walking motion, the muscles around the affected tendons are activated. This helps strengthen these muscles, relieving pressure on the tendons and reducing excessive tension on them. It is known that strong tendons recover faster and are less prone to injury.
- Increasing Tissue Flexibility: Walking also helps improve the flexibility of tissues surrounding the tendons. Regular stretching and flexing increase the level of elasticity in these tissues. Consequently, the chances of future damage and injury can be reduced.
- Reducing Inflammation: Walking is also known as a gentle activity that can activate the immune system and alleviate swelling and inflammation. When the feet press against the ground, a mild pressure is applied to the affected joint, which helps in reducing inflammation and accelerating the healing process.
- Improving Mood: Studies have shown that walking is one of the sports that improve mood and reduce stress and anxiety. When individuals suffer from tendonitis, they may have higher levels of psychological stress. Therefore, walking may be an effective way to reduce psychological pressure and improve mood.
Please note that walking alone may not be sufficient for a comprehensive treatment of tendonitis. Rest, appropriate medical treatment, and targeted physical exercises by a physiotherapy specialist are always recommended. If you have any unusual symptoms or do not see an improvement in your condition after a period of walking, please consult a doctor to assess your situation and direct you to the appropriate treatment.
In summary, walking can be beneficial in alleviating the symptoms of tendonitis, speeding up the healing process, and strengthening the muscles. Therefore, it may be useful to include walking in your daily lifestyle as part of a comprehensive treatment program.
What are the causes of tendonitis and what is its treatment?
Tendonitis is a common condition that affects many people. Tendonitis occurs when a tendon is irritated and inflamed due to overuse or repeated movement of a particular action. Tendonitis can occur in any part of the body where there is a tendon. Several causes can lead to tendonitis, including sudden injuries, repeated movements, unhealthy habits, and other diseases.
There is no specific cure for tendonitis, and the treatment depends on the severity of the condition, its symptoms, and its location. Common treatment options for tendonitis include:
Resting the affected tendon: Once tendonitis is diagnosed, it may be important to reduce movement in the affected area and give the tendon time to heal. Applying ice: Ice can be used to relieve pain and swelling in the area of tendonitis. Ice should be placed in a plastic bag, wrapped in a cloth, and applied to the affected area for 15-20 minutes several times a day. Using pain relievers: Direct analgesics such as aspirin or ibuprofen can be used to relieve pain and swelling. You should consult a doctor before using any type of pain reliever. Therapeutic exercises: The doctor may recommend therapeutic exercises to strengthen the muscles and tendons surrounding the affected tendon. These exercises may help improve the condition of the tendons and relieve symptoms.
Physical Therapy: Your doctor may recommend physical therapy sessions to alleviate pain and improve the mobility of the affected tendon. This includes tendon massage, muscle strengthening exercises, and stretching exercises. Steroid Injections: In some severe cases, the doctor may suggest corticosteroid injections into the tendon inflammation area to reduce pain and inflammation. However, advanced use of this treatment is advised only in cases that do not respond to other treatments. Surgery: Surgery may be necessary in cases of tendon rupture or when the condition does not respond to conventional treatments. Surgery can include repairing or removing the affected tendon.
In addition to the above treatments, certain preventive measures can also be taken to reduce the risk of tendonitis. This includes avoiding overuse of the tendon, avoiding unhealthy movements, practicing proper exercise, and using correct techniques during daily activities. It is also advisable to properly warm up muscles before starting any heavy physical activity.
If you suffer from symptoms of tendonitis, you should consult a doctor for an accurate assessment and prescription of the appropriate treatment. Care should be taken and the doctor’s instructions followed precisely to speed up the healing process and alleviate symptoms. Tendonitis may take time to fully improve, so you must be patient and committed to the treatment prescribed for your condition.
How long does tendonitis treatment take?
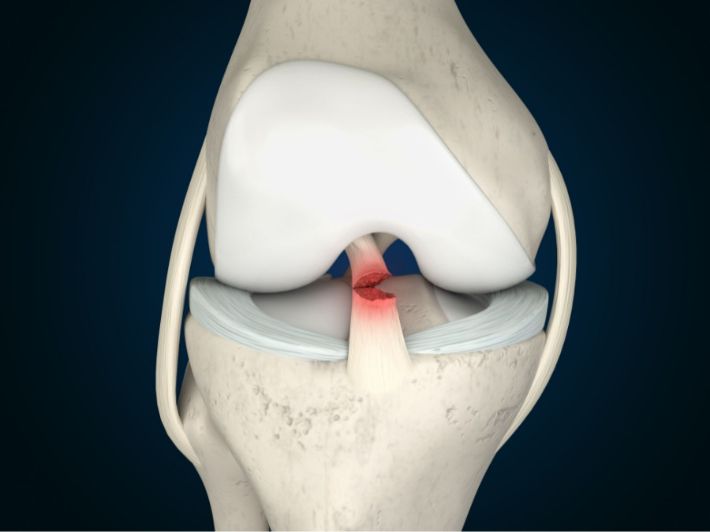
Tendonitis is a common condition that affects the normal movement of the affected parts of the body and can cause annoying pain. Tendonitis results from damage to the thick fibrous cords that connect muscles to bones, known as tendons.
Tendonitis may be the result of many causes, with sports injuries and repetitive movements that cause stress and pressure on the tendons being among the most prominent. Certain diseases and medications may also play a role in the occurrence of tendonitis.
In this article, we will provide you with information about the duration of tendonitis treatment, treatment methods, and how to prevent this painful condition.
Duration of Tendonitis Treatment
The duration of treatment for tendonitis varies from case to case and largely depends on the severity of the injury and the location of the affected tendon. Recovery from tendonitis in mild cases may take from two to four weeks. In cases of long-term inflammation, recovery may take from two to six months. Sometimes, tendonitis may become a chronic condition.
Symptoms of Persistent Tendonitis
If tendonitis persists for an extended period, some indicative symptoms may appear, such as:
- Mild pain in the affected joint when moving it.
- Discomfort and a feeling of sensitivity in the affected area.
- Slight swelling in the affected joint.
Causes of Tendonitis
Tendonitis can arise due to repetitive movements and the resulting strain. Several risk factors may contribute to this condition, such as:
- Advancing age, as tendons become less flexible and more prone to injury.
- Repetitive movements in jobs, like sports movements, difficult body postures, or continuous exertion.
- Certain diseases, such as arthritis, gout, thyroid disorders, and kidney diseases.
- Some medications, like fluoroquinolones and cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins).
Diagnosis and Treatment of Tendonitis
Tendonitis is usually diagnosed through a physical examination by a doctor. The doctor can gently move the affected tendon to determine the presence of pain. In some cases, additional tests such as X-rays or ultrasound imaging may be required to confirm the diagnosis of tendonitis and rule out other conditions.
The treatment methods for tendonitis vary according to the severity of the injury and the duration of its persistence. Treatments include the following:
- Rest: Allowing the affected area to rest, avoiding overexertion.
- Ice application: Placing a cold compress or ice pack on the affected area to reduce inflammation and pain.
- Pain relief medications: Pain and fever-reducing medications, such as analgesics, can be used to alleviate symptoms.
- Physical therapy sessions: Physical therapy can help strengthen the muscles and ligaments around the affected tendon, improve movement, and relieve pain.
- Steroid injections: An injection with a solution containing anti-inflammatory substances is performed to relieve pain and swelling.
- Tendon surgery: In some severe cases and when a tendon tear occurs, surgical treatment may be necessary.
Accelerating Recovery from Tendonitis
In addition to traditional treatments, there are some methods that can help speed up the recovery process from tendonitis. These methods include:
- Practicing stretching and flexibility exercises: These exercises aim to improve the flexibility of the tendons and contribute to their healing and pain relief.
- Engaging in strengthening exercises: These exercises are used to rebuild the tendons and strengthen the surrounding muscles, which helps in improving movement and stability.
- Ultrasonic heat therapy: Ultrasonic heat therapy is considered effective in improving blood circulation and pain relief and can be used to accelerate the tendon healing process.
In conclusion, it should be noted that tendonitis may take some time to heal completely. Patients may need additional rest and self-care for several weeks or months until they regain their normal movement ability. If symptoms persist for a long time or worsen, the patient should consult a doctor to evaluate the condition and discuss the necessary treatment.
It is also worth mentioning that prevention of tendonitis can be beneficial to avoid this painful condition. It is recommended to reduce repetitive movements, avoid excessive strain, maintain good physical fitness, and avoid excessive exposure to cold and humidity. In short, it is important to provide rest and good care for the tendons to avoid painful inflammations.
What is the vitamin that strengthens tendons?
Tendons play an important role in the health of bones and muscles, as they connect muscles to bones to enable the body to function. Ligaments, on the other hand, connect bones to each other; both are components of connective tissue. The body needs various vitamins and nutrients to maintain tendon health and strengthen them.
In this article, we will review a list of vitamins that the body needs to strengthen tendons and ligaments:
Vitamin A: Vitamin A contains a high level of collagen, which contributes to the strengthening of connective tissues, including tendons and ligaments, in addition to maintaining the health of bones and cartilage. Vitamin A can be obtained from natural sources such as carrots, mangoes, and sweet potatoes, as well as dietary supplements, but a doctor should be consulted before taking them.
Vitamin C: Vitamin C is an antioxidant and helps fight inflammation and protect tendons and ligaments from the risk of injury. It also promotes the production of collagen in the body. Vitamin C can be obtained from citrus fruits like oranges, apples, lemons, kiwi, and pineapple, as well as leafy vegetables such as spinach, lettuce, cabbage, and kale.
Vitamin D: The body should get an adequate amount of Vitamin D daily, as its deficiency affects the health of bones and tendons and increases the risk of joint and tendon inflammation. Vitamin D can be obtained from sunlight or from compensatory doses of vitamin tablets or injections after consulting a doctor.
Copper and Zinc: A deficiency in copper and zinc in the body can increase the risk of tendon weakness, leading to poor bone health. A doctor may prescribe dietary supplements containing copper or zinc to improve the health of bones and tendons in case of medical injuries.
Glucosamine: Glucosamine is a natural component found in connective tissue, and its intake has been proven to protect against any problems or medical injuries in the tendons and bones, as well as accelerate wound healing. Glucosamine can be obtained through dietary supplements, but a doctor should be consulted before taking it.
These nutrients are naturally available in healthy foods, but it may sometimes be beneficial to take dietary supplements when the body’s needs for these vitamins and nutrients are not met through diet. However, a doctor should be consulted before taking any dietary supplements to ensure the proper dosage and to match individual and health needs.
By paying attention to the intake of these important vitamins and nutrients, individuals can enhance the health of their tendons and improve their strength and flexibility, leading to a reduced risk of muscle strains and other troublesome injuries.