Learn more about knee tendinitis
Tendonitis may affect any place in the human body if a certain part is neglected or overused, but knee tendinitis is more common among many individuals, especially those who practice some sports. Follow the following article with us to be more familiar with this topic and learn how to deal with it.
Knee tendinitis
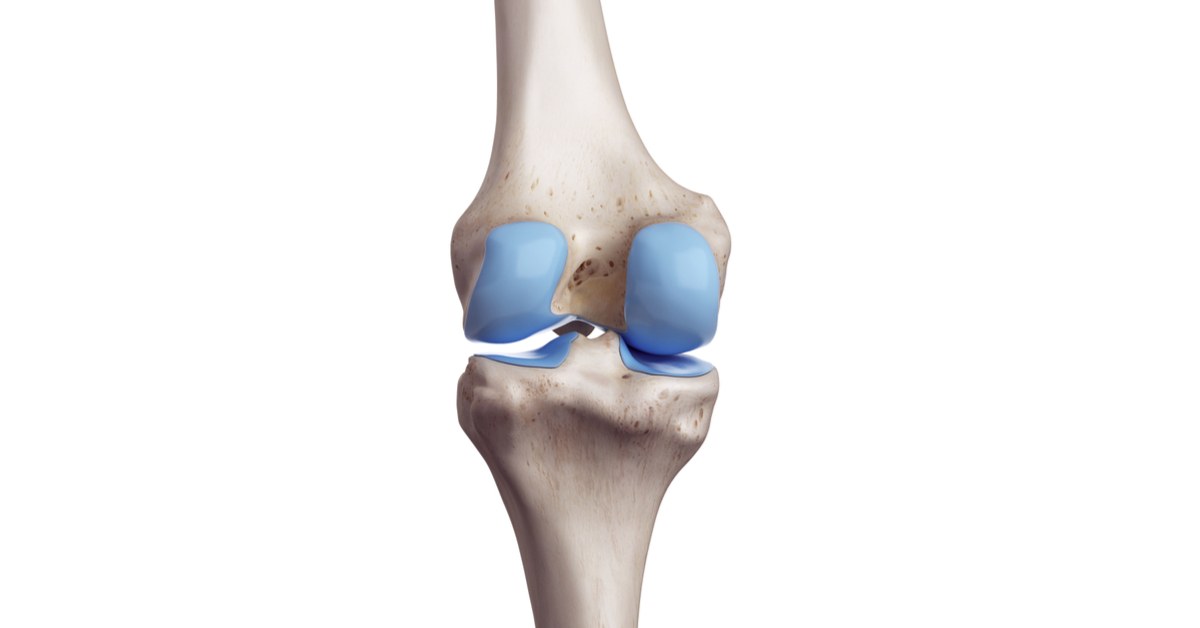
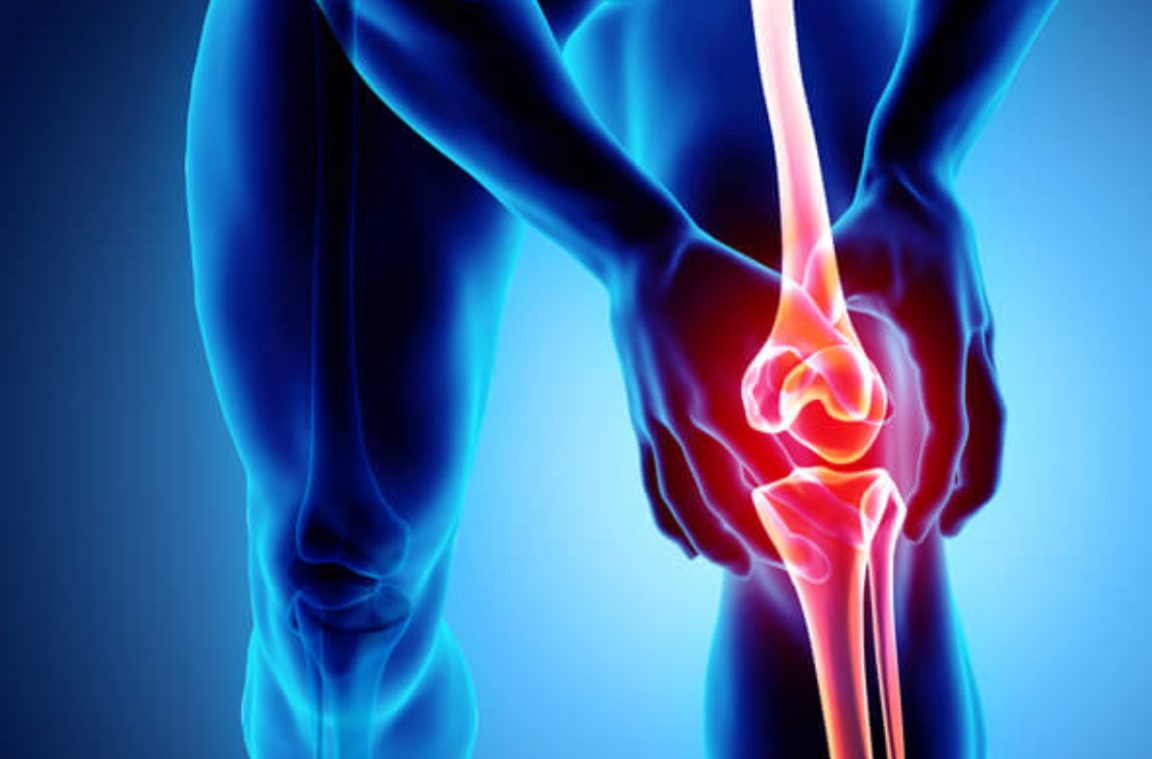
Knee tendinitis causes a lot of pain for individuals, especially when making a move, and this inflammation is more prevalent among those who practice certain sports that require jumping a lot, as exposing the tendons in the knee to excessive pressure is the main cause of these infections, and it should be noted that the human knee contains four main tendons, which are the quadriceps femoris tendon, the popliteal tendon (Achilles tendon), the patellar tendon, and the iliac band.
The patellar tendon is the one that connects both the patellar bones and the tibia in the leg to secure its stability, stability, and move effectively, in addition to providing great support for the square-headed thigh muscle, and a large number of functions of this tendon, in particular, makes it more susceptible to infection than others in the knee joint, and for this reason, talking about inflammation in the hamstrings refers specifically to the patellar tendon.
Is knee tendonitis dangerous?
Knee tendinitis is dangerous if it is not treated in its early stages, as this negligence causes many serious consequences, as the tendon injury intensifies with time, and this causes the intensity of pain in the knee area to intensify to the extent of the inability to move it well, and as the condition worsens further, a severe illness may occur in the knee area, and the patient may lose the ability to move the knee completely.
What are the symptoms of knee tendonitis?
- Feeling severe pain, especially when moving the affected foot.
- The pain spreads to other areas of the leg and is not limited to the knee only.
- Swelling and mild inflammation.
- Redness of the skin surrounding the injury area.
- Feeling of heat emanating from the affected knee.
How long does knee tendonitis last?
The normal time in which knee tendinitis is treated is within the passage of two to four weeks in cases of mild injuries, but if the inflammation in the tendons is severe, the recovery period has developed from two months to six months, and the injury may be chronic in athletes in particular because they continue to perform exercises despite their injury.
What is the treatment for knee tendinitis?
It is possible that the treatment of knee tendinitis is very simple and does not require severe medical intervention unless the symptoms are severe and do not improve within a few days, and many methods can be used to treat knee tendinitis, such as:
- Home treatment: Individuals may develop knee tendinitis as a result of excessive use. Therefore, the first treatment step is to get plenty of rest and avoid pressure on the knee in any way, while making sure to make some ice packs and tie the knee well to limit its movement.
- Avoid sitting for long periods: Excessive rest may be counterproductive as a result of putting more pressure on the tendons, which increases the severity of the inflammation that occurs in them and thus increases the feeling of pain.
- The use of pressure waves: This treatment works by directing pressure waves toward the inflamed tendons, this enhances blood flow to them, and this method is a very good solution in treating tendonitis because it is painless and we avoid surgical intervention, and its results are very effective and fast and this method does not have any side effects.
- Medications: A treatment plan for tendinitis may include taking anti-inflammatory medications to relieve pain.
- Massage: Making some massage movements in the affected area helps to greatly reduce the pain and help relax the muscles.
- Physiotherapy: Physiotherapy is not dispensed with in any treatment plan, whether surgical intervention is required or not, because it greatly contributes to the healing process.
- Steroid injections: The doctor may inject directly into the knee area if other treatment methods do not help relieve symptoms, and this helps stop the pain for a few weeks.
- Surgery: This is the last resort, as it is resorted to if all other methods of treatment fail miserably.
Knee tendonitis treatment
When you have an infection in the tendons of the knee, the treatment, in this case, is by taking rest for a few days and being careful to avoid any effort that causes pressure on the knee, in addition to making some cold compresses on the area of pain to calm the inflammation and reduce the severity of the pain that results from it, and if the symptoms are severe, the patient may take some painkillers that do not require a doctor’s consultation.
Herbal treatment of osteoarthritis
Many herbal remedies are used to treat knee osteoarthritis, such as:
- White willow: The white bark contains salicin, which is similar in effect to aspirin and some other anti-inflammatory drugs, and has a major role in relieving pain and reducing inflammation.
- Turmeric: It contains curcumin, which has many anti-inflammatory properties, which is why it is very effective in treating tendonitis.
- Boswellia: Known by another name, frankincense, this herb contains boswellic acid, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
- Burdock: This herb contains many anti-inflammatory properties that help fight oxidative stress, and its results are especially effective for those suffering from osteoporosis in the knee area.
- Devil’s claw: This herb contains anti-inflammatory components, in addition to being effective in treating many pains such as muscle pain, arthritis, and back pain.
Knee tendinitis treatment
If the inflammation in the tendons of the knee is the result of excessive exercise, the method of treatment, in that case, is by placing ice packs on the area of pain and making sure to rest it completely and avoid pressure on it in any way for a few days, and it is also possible to focus on doing some exercises that help strengthen the muscles, as the thigh muscles can bear the pressure more.
Exercises for the treatment of osteoarthritis of the knee
In order to reduce the inflammation that occurs in the hamstrings of the knee, many doctors recommend practicing some types of exercises, and it should not be noted that it is preferable to do them under the supervision of a specialist to prevent any mistakes that may lead to many risks, and examples of exercises recommended by doctors:
- Leg raise: This exercise focuses on strengthening the thigh muscles, which is the large muscle that is located in the front of the thigh, and which works to stabilize the knee joint in the place designated for it when moving, and this exercise is done by standing and making the feet hip-width apart with placing the hands on both hips to maintain balance, then point with the right foot in front of you while keeping the legs straight and pressing on the quad.
- Flexion in the hamstrings: This exercise works on the back of the legs, and it has a major role in maintaining the stability of the back of the knee joint and improving the movement of the front part of the leg, that is, it focuses on the hamstrings, which is the muscle opposite the quadriceps that raises the standing leg.
- Wall squat: To do this exercise, stand shoulder-width apart and take a few steps towards the wall, then lean back against the wall with your upper back, and then bend your knees and lower yourself on the wall so that the top, middle and lower back are against the wall.
- Heel raise: the exercise works to strengthen the lower legs and ankles to provide the necessary support for the knee joint, and this exercise is done by standing with feet hip-width apart and hands on the hips, then moving your weight forward with the help of the toes and climb up on the fingers.
- Back leg lifts of the thigh: This exercise focuses on stabilizing the inner leg and strengthening the middle space and the inner part of the knee. In order to do it, you must stand with your feet hip-width apart, hands on hips, and right foot facing in front of you, then cross your right foot over your body towards the left and rotate the outer leg by squeezing the quad and pulling the kneecap up and lifting the leg up one foot.