What is muscle stiffness? And how long does the treatment take?
What is muscle stiffness?
Muscle stiffness, also known as muscle tension or rigidity, is a common disorder that causes difficulty for the muscles to relax normally. People with muscle stiffness may feel pain and stiffness in various parts of the body. In this article, we will highlight the causes and symptoms of muscle stiffness, as well as treatment methods.
Causes: There are several reasons that can lead to muscle stiffness, the most prominent of which are:
- Psychological and physical stress: Continuous exposure to psychological or physical stress can cause muscle spasms and stiffness.
- Sports injury: An injury to the muscles during sports activity can result in long-term tension and stiffness.
- Chronic medical conditions: Some health conditions such as arthritis and tendonitis can also lead to muscle stiffness.
Symptoms: Muscle stiffness may present several symptoms, including:
- Difficulty in movement and muscle flexibility.
- Feeling pain or numbness in the affected areas.
- Slowness in muscle recovery and response after physical activity.
- General weakness in the muscles.
- Discomfort or anxiety.
Treatment methods: Muscle stiffness can be treated in several ways, including:
- Relaxation and rest: Resting and avoiding excessive activity for a while can help alleviate muscle stiffness.
- Medication: Some medications, such as pain relievers and arthritis treatments, can help reduce pain and muscle stiffness.
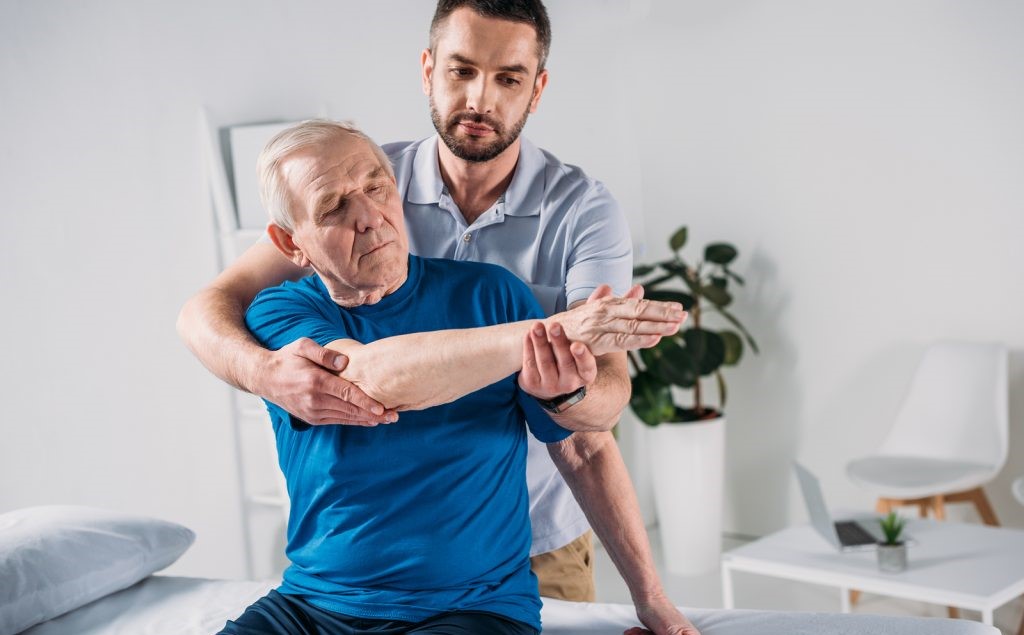
- Physical therapy: Through physical therapy exercises under the supervision of a specialist, muscles can be strengthened and range of motion can be improved.
- Massage and manual therapy: Massage and muscle manipulation can help relieve tension and stiffness.
- Heat and cold therapy: Ice packs or hot packs can be used to relieve pain and muscle stiffness.
Precautions and Prevention: To prevent muscle stiffness, some precautions can be taken, such as:
- Maintaining body fluid balance by drinking an adequate amount of water.
- Avoiding excessive strain and extreme heat.
- Practicing relaxation exercises and meditation to reduce stress.
- Avoiding excessive sports activities or strenuous workouts without adequate rest.
- Consulting a doctor in case of recurring or persistent muscle stiffness.
Muscle stiffness is common and can result from several causes and can cause bothersome symptoms. In conjunction with the treatments mentioned above, individuals with muscle stiffness should consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and be guided towards the appropriate treatment. It is essential to avoid excessive strain and follow a healthy lifestyle to prevent this disorder.
What is the treatment for muscle stiffness?
Treatment of Muscle Stiffness: Effective Ways to Relieve Pain and Muscle Rigidity
Muscle stiffness is a common health issue that affects many people of all ages. This condition causes discomfort and pain in the muscles, making movement difficult. If you are suffering from muscle stiffness, you may want to know the best ways to treat it and get rid of it. In this article, we will present you with a list of three effective methods to treat muscle stiffness:
Physical Therapy: Physical therapy is one of the most important ways to get rid of muscle stiffness. This treatment provides the best and latest methods of physical therapy, focusing on the affected area and treating it through different physical therapy techniques. Modern physical therapy devices can be used to relieve muscle stiffness. The most important guidelines and tips in physical therapy for muscle stiffness include:
- Adhering to a proper sitting posture without overdoing it.
- Using anti-inflammatory drugs, such as ibuprofen, to alleviate pain and discomfort.
- Relaxation, massage, and the use of heat or cold. Heat generally works better for muscle tightness, while cold compresses work better for swelling and inflammation.
Stretching Exercises: Stretching exercises are an effective way to get rid of muscle stiffness and to prevent its occurrence again. Stretching can help maintain muscle flexibility, prevent stiffness, and reduce muscle tightness and stiffness. Some beneficial stretching exercises include:
- Stretching exercises before and after exercise.
- Daily and regular stretching exercises. Home Physical Therapy: In addition to the physical therapy provided in health centers, some simple methods can be used to treat muscle stiffness at home. These methods include:
- Rest and relaxation.
- Proper massage for tense muscles.
- Applying hot or cold compresses to the area of pain and stiffness.
When you experience muscle stiffness, you should consult a physical therapy specialist to diagnose your condition correctly and determine the appropriate treatment. The expert may also recommend a combination of these methods to alleviate the symptoms of muscle stiffness and speed up recovery.
To enjoy good muscular health and avoid muscle stiffness, it is recommended to exercise regularly and follow a healthy lifestyle, in addition to physical therapy when needed. Visit specialized health centers and inquire about available treatments for muscle stiffness, and consult doctors and specialists for suitable and personalized advice.
How long does it take to treat muscle stiffness?
When a person suffers from muscle stiffness, treatment and details about the duration of treatment can be very important. The duration of treatment may vary according to the patient’s condition and the severity of the stiffness. In this article, we will review more information about the duration of treatment and some helpful tips on how to treat muscle stiffness.
The inflammatory stage needs about 2-9 months: During this stage, the patient suffers from pain and stiffness throughout the affected muscles. Even a little muscle movement causes severe pain, especially at night or when lying on the affected side. This stage can be treated using arthroscopic surgery for the muscles to remove entangled fibers, followed by physical therapy sessions for two months.
The adhesive phase may take 4-12 months: In this stage, the pain may decrease slightly, but the movement of the muscles diminishes significantly. People with muscle stiffness may experience frustration and difficulty in using their muscles in everyday life. These patients may need to take medication and undergo physical therapy sessions to reduce adhesion and improve movement.
The relaxation phase takes about 2-3 years: During this stage, there may be a slight improvement in muscle movement, and pain may decrease slightly. However, the pain may persist for an extended period and cause a state of disruption in daily life. To alleviate the severity of adhesions and improve the overall condition, it is usually recommended to take medications and undergo physical therapy sessions.
Overall, the duration of treatment for muscle stiffness varies and depends on the patient’s condition and the severity of the stiffness. People with muscle stiffness are advised to seek appropriate medical consultation to assess their condition and be guided to the most suitable treatment. Remember that personal care and practicing medical exercises prescribed by medical specialists can also contribute to improving the condition and reducing the symptoms of muscle stiffness.
What is the cause of muscle stiffness?
Muscle stiffness is a condition in which a person experiences painful contractions in the muscles, making them difficult to move and causing pain and tension. This condition is common and may occur for various reasons. In this article, we will review the main causes that lead to muscle stiffness.
- Overstretching and tearing: Muscle stiffness occurs when there is overstretching of muscle fibers or when they tear. This may happen as a result of being subjected to stress or extreme fatigue, especially when practicing sports or strenuous work.
- Inflammations: Some bodily inflammations can cause muscle stiffness, such as myositis (muscle stiffness) or tendonitis. Myositis results from damage to muscle fibers due to intolerance or excessive stress on them.
- Muscle calcifications: Muscle calcifications are hard lumps in the muscles that may cause cramps and stiffness in the affected area. This may happen due to the accumulation of minerals or crystals inside the muscle.
- Lack of physical activity: Not maintaining the necessary physical fitness to perform activities leads to weak muscles and reduced flexibility, which increases the likelihood of stiffness upon any unusual movement.
- Injury and muscle strain: Injuries and muscle strains can also lead to contractions and stiffness in the muscles. This may happen as a result of acute injury, such as a car accident or fall, or due to excessive load and abnormal twisting of the muscles.
- Environmental factors: Some environmental factors can increase the likelihood of muscle stiffness, such as working in a cold or damp environment. These conditions may cause muscle cramps and increase their friction and difficulty of movement.
Please note that these causes are some of the common potential reasons for muscle stiffness, and there may be other reasons as well. If you are suffering from persistent muscle stiffness, it is important to consult a doctor for accurate diagnosis and determination of appropriate treatment.
What are the symptoms of muscle stiffness?
Muscle stiffness is one of the health conditions that people suffer from, accompanied by a number of uncomfortable symptoms. In this report, we will highlight the most prominent symptoms of muscle stiffness and how to deal with them.
- Difficulty in movement: This is a primary symptom of muscle stiffness, where the patient feels muscle cramps and finds it difficult to move them normally, especially after a period of rest.
- Muscle pain: The patient may suffer from pain in the affected muscles, feeling a prick or tightness in the stiff muscle, with these pains being continuous or intermittent.
- Muscle cramps: The affected muscles are cramped and contracted, causing discomfort and continuous tension.
- Difficulty in carrying out daily activities: Muscle stiffness can affect the ability to carry out normal daily activities, such as walking or lifting heavy objects.
- Muscle weakness: In some cases, the patient may feel weakness in their muscles, affecting their overall performance and hindering them in carrying out simple activities.
- Feeling of severe fatigue: Severe fatigue is one of the symptoms associated with muscle stiffness, where the patient feels exhausted and tired easily, even after minimal effort.
- Feeling anxious and depressed: The patient’s mood and mental state can be affected by the continuous feeling of pain and the inability to carry out activities normally, causing anxiety and depression.
To alleviate symptoms of muscle stiffness, patients are advised to practice some stretching exercises, regular muscle relaxation, and to avoid overexertion. Natural treatments such as massage and physical therapy are effective methods to reduce muscle spasms and pain.
However, if symptoms of muscle stiffness persist and worsen over time, it is advised to visit a doctor for diagnosis and consultation on the appropriate treatment required.
What is the difference between muscle pain and nerve pain?
Many people confuse muscle pain with nerve pain due to the similarity of some symptoms between them. However, in reality, there are important differences between them in terms of cause, symptoms, and treatment. In this condensed list, we will review more information about the difference between muscular pain and nerve pain.
Cause: Muscle pain: Occurs due to chronic muscle contraction and muscular tension. Nerve pain: Occurs due to irritation of nerves and narrowing of nerve channels or compression on them. Symptoms: Muscle pain: Can include muscle stiffness, a feeling of cramping, swelling, bloating, and muscular strain. Nerve pain: May have different symptoms such as prickling, nervous tension, numbness, and neuralgic headache.
Treatment:
- Muscle pain: The usual treatment includes pain reduction methods such as applying an ice pack, using pain relief medications, and ointments designed to soothe the muscles.
- Nerve pain: Requires a different treatment that includes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, physical therapy, massage, and sometimes local anesthesia.
Examinations and Diagnosis:
- Muscle pain: May not require a special examination and can be identified based on medical history and accompanying symptoms.
- Nerve pain: May require additional tests such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or X-rays to determine the source of the nerve pain.
Duration:
- Muscle pain: Can be acute and temporary or chronic, lasting for a long time.
- Nerve pain: Usually persistent and chronic for long periods exceeding 6 months.
Location:
- Muscle pain: Can occur in any part of the body where there are muscles.
- Nerve pain: Can occur in any part of the body where nerves extend.
How do we distinguish between bone and muscle pain?
While some may feel pain in their body, it may be difficult for some to correctly identify the source of this pain. One of the more challenging aspects in this regard is distinguishing between muscle pain and bone pain. Therefore, in this article, we will review some guidelines and information to help you distinguish between these two conditions.
Part One: Differences in Symptoms When considering the distinction between bone pain and muscle pain, one should take into account the symptoms that accompany the pain. Here are some of the main differences in symptoms:
Bone Pain vs. Muscle Pain Bone Pain Muscle Pain It appears more severe, deeper, and more debilitating. It is less severe and may be mild and difficult to endure. It may last longer and require greater medical attention. It may be short-term and improve after a brief period. You may feel bone pain even with light touch. You may feel muscle pain when pressing on them or using them.
Part Two: Differences in Causes After understanding the differences in symptoms, let’s now shed light on the differences in causes:
Bone Pain Muscle Pain Caused by problems with the skeletal structure such as falls or fractures. Caused by muscle tension, strain, or other muscle injuries. Results from diseases such as arthritis or osteoporosis. Results from overuse of muscles or sports injury. Bone pain may indicate chronic diseases such as cancerous tumors. Muscle pain can be due to exposure to cold or dampness.
Part Three: When to Visit a Doctor There may be times when distinguishing between bone pain and muscle pain is difficult. Therefore, if you are suffering from persistent pain or the pain does not improve naturally, it is advisable to visit a doctor. The doctor can perform the necessary examinations and provide proper guidance.
What Causes Back Muscle Stiffness?
Back muscle stiffness is a common problem that many people worldwide suffer from. Stiffness can result from several causes, including environmental factors, poor habits, and diseases associated with the spine. Here are some of the most common causes of back muscle stiffness:
- Spinal disorders: Back pain and muscle stiffness can be the result of spinal disorders such as arthritis, disc herniation, and spinal misalignment.
- Poor habits: Sitting for long periods incorrectly and not exercising regularly can cause muscle stiffness in the back area.
- Psychological and emotional stress: Ongoing psychological and emotional stress can lead to back muscle spasms and stiffness.
- Sports injuries: If you sustain a back injury while playing sports, this can lead to stiffness in the affected muscles.
- Genetic factors: Stiffness in muscles can be due to genetic factors, where muscle spasms occur frequently and recurrently.
- Inflammatory diseases: Some inflammatory diseases such as arthritis and myositis can cause stiffness in back muscles.
- Poor sleeping posture: Bad sleeping positions or using unsuitable pillows can lead to back muscle stiffness.
- Exposure to cold temperatures: Constant exposure to cold can cause muscle spasms and stiffness.
Caring for Your Back Health:
To maintain the health of your back muscles and avoid stiffness, you can follow some of the following tips:
- Exercise regularly and properly, focusing on strengthening back muscles.
- Maintain correct posture while sitting and sleeping, and use comfortable and appropriate pillows.
- Avoid psychological and emotional stress, and work on reducing daily stress levels.
- Avoid long exposure to cold heat or severe cold, and ensure to warm up back muscles well in winter.
- Take care of the health of your spine by following a balanced and healthy diet and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Consult your doctor if back pain is persistent and increases in intensity, for diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Avoiding back muscle stiffness is important to maintain spinal health and enjoy a life free of pain. Remember that following a healthy lifestyle and practicing regular exercise can help strengthen muscles and avoid back stiffness.
What is the Herbal Treatment for Muscle Stiffness?
Muscle stiffness is a common ailment that affects many individuals, causing difficulty in the movement of joints and muscles. Although there are many medical treatments available for this condition, some people look for alternative treatments using herbs.
In this article, we will review the best herbs used effectively to treat muscle stiffness.
- Eucalyptus:
- Contains natural compounds that help in pain relief and calming.
- Can be used by massaging the affected area with ground herbs.
- Devil’s Claw:
- Contains strong anti-inflammatory agents that help in alleviating pain and swelling.
- Can be used in the form of an ointment or massage oil.
- Tamarind:
- Acts as a circulatory stimulant and helps in easing muscle cramps.
- Can be consumed as a dietary supplement or used in cosmetic preparations.
- Rooted Sumac:
- Characterized by antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Can be used in the form of preparations like creams or massage oils.
- Indian or Arabic Frankincense:
- Contains compounds that assist in soothing pain and reducing swelling.
- Can be used as a natural oil or in supplemental pills.
- Turmeric:
- Contains curcumin, which helps in pain relief and improving joint mobility.
- Can be used as a dietary supplement or added in cooking.
- Cinnamon:
- Known for its pain-relieving properties and muscle spasm soothing effects.
- Can be used in tea or added to food dishes.
- Ginger:
- Acts as a circulatory stimulant and aids in reducing swelling and calming pain.
- Can be used fresh or in powdered form.
Before using any type of herbs to treat muscle stiffness, it is essential to consult a doctor or a specialist. Additionally, the appropriate herbs should be chosen according to each individual’s condition based on prior medical diagnosis.
Also, do not forget that maintaining a healthy lifestyle plays a significant role in preventing and treating muscle stiffness. One should avoid sitting for long periods and engage in regular physical exercise.
Caution: Side effects may occur due to the consumption of certain herbs with other medications, therefore it is crucial to consult a doctor before beginning their use.